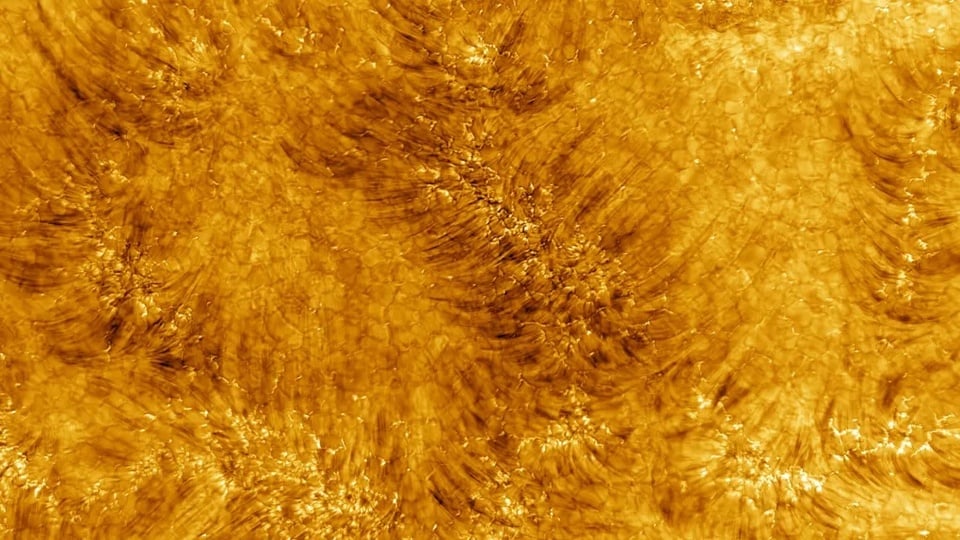
 |
Close-up photos of the Sun provide a lot of useful information for science . Photo: NSO . |
After being launched into space in 2018, the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) brought the Parker Solar Probe closer and closer to the Sun. Dubbed the fastest object ever built by humans, the probe broke many records on its journey.
Now, it looks like NASA is using Parker Solar Probe to take the closest images of the Sun ever.
In the years since its launch, Parker Solar Probe has been getting closer and closer to the star at the center of the solar system. In December 2024, the probe came within 6.1 million kilometers of the center of the solar system. During its closest flyby, the probe captured many images of the sun’s atmosphere.
Essentially, Parker Solar Probe is traveling within the Sun's corona. The fact that the probe has traveled within the vicinity of the Sun and continued to fly without any problems is a testament to human invention and innovation, and promises further advances in space exploration .
Parker's success opens up opportunities to learn more about the Sun's atmosphere, discovering ways to predict solar activity such as coronal mass ejections and solar storms.
From there, scientists can come up with ways to minimize the impact of dangerous solar storms, and even come up with better protections against all the cosmic energy, which is extremely important for spacecraft traveling outside the protective range of the Earth's magnetic field.
The close-up images released by NASA were taken by the Parker Solar Probe's Wide Field Camera, a useful tool for taking still images around the Sun. The camera looks at space in visible light, seeing things just like the human eye does.
But what makes this camera particularly effective is that it isn’t pointed directly at the Sun. Instead, it captures solar material as it leaves the surface, giving scientists a close-up, direct look at the source of the solar wind.
Source: https://znews.vn/buc-anh-gan-mat-troi-nhat-tu-truoc-den-nay-post1568736.html




































































































Comment (0)