Some universities in Japan have agreed to increase tuition fees to improve the learning environment and training quality, but this has caused many mixed opinions.
The increase in tuition fees in Japan is aimed at improving the quality of education and enhancing the country's international competitiveness, but this has caused many conflicting opinions. The President of Keio Private University, Mr. Kohei Itoh, proposed to increase tuition fees at national universities from 3,400 USD to 9,600 USD to deal with the current low public spending on education. According to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), spending on higher education in Japan is only half the average of 38 member countries.
Japan’s young population is declining sharply, forecast to fall by more than 20% by 2040, making high-quality human resources increasingly scarce. In this context, Japan needs to develop advanced information technology and language skills to meet the demands of the age of artificial intelligence (AI). Mr. Kohei Itoh emphasized that universities need to change to maintain global competitiveness, but this requires large financial resources, part of which can be shared by students.
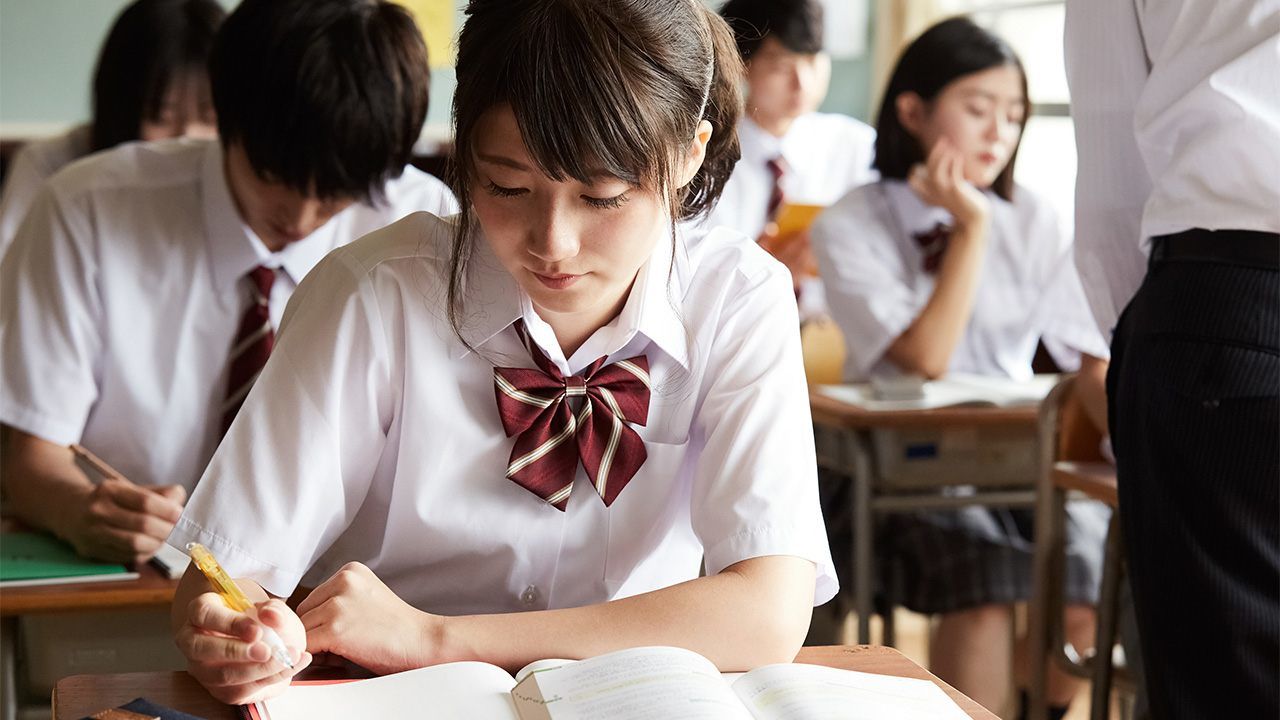

Some universities in Japan have accepted to increase tuition fees to improve the learning environment and training quality. IG.
However, current tuition fees have placed a significant burden on many families. A 2019 OECD report found that average annual tuition fees at national and public universities in Japan were the fifth highest among member countries, while public spending accounted for just 0.5% of GDP, the lowest among the G7. This highlights the tight financial situation that many Japanese families face when sending their children to university.
The University of Tokyo, Japan’s top university, is considering raising tuition fees by $640 a year. Meanwhile, the school is also expanding financial aid, including raising the threshold for full tuition waivers from $25,000 to $38,000. But the plan has met with opposition from students, especially those from rural areas. A third-year student at the University of Tokyo said the tuition hike would make rural students reconsider their choice of study due to financial difficulties. She has to work three jobs to cover her living expenses and tuition.
To ease the financial pressure on students, some other universities such as Ehime University have refused to raise tuition fees and sought funding from local businesses. However, these schools are still facing great difficulties in maintaining operations due to sharp reductions in government subsidies and rising operating costs.
Some universities in Japan have accepted tuition increases to improve the learning environment and training quality. Tokyo Institute of Technology, in 2019, increased tuition to 635,400 yen, and spent an additional 900 million yen of this revenue to invest in smaller classes, improve libraries, and hire more foreign lecturers. The school also increased financial support for students from disadvantaged backgrounds, ensuring that they are not left behind in the process of change.
Students from disadvantaged families receive tuition waivers and financial support through funds contributed by private companies. A master's student at the Tokyo Institute of Technology commented that the tuition increase was necessary to invest in research andeducation , but thanks to support policies, he was able to maintain his studies.
Japan is not alone in facing similar challenges. Musashino Art University recently announced that it would increase tuition fees for international students by $2,500 from 2025. This has raised concerns that Japan will lose its appeal to international students, who choose the country for its affordable tuition and high-quality education.
In the UK, many universities have also proposed increasing tuition fees to address financial difficulties after the Covid-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine conflict. However, increasing tuition fees is not simply a budget issue but also related to the global competitiveness of the education system. Countries need to find a balance between investing in education and reducing the financial burden on students.
Source: https://danviet.vn/dai-hoc-nhat-ban-tang-hoc-phi-vap-lan-song-phan-doi-manh-me-20241201190133542.htm




















































![[Maritime News] More than 80% of global container shipping capacity is in the hands of MSC and major shipping alliances](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/16/6b4d586c984b4cbf8c5680352b9eaeb0)











































Comment (0)