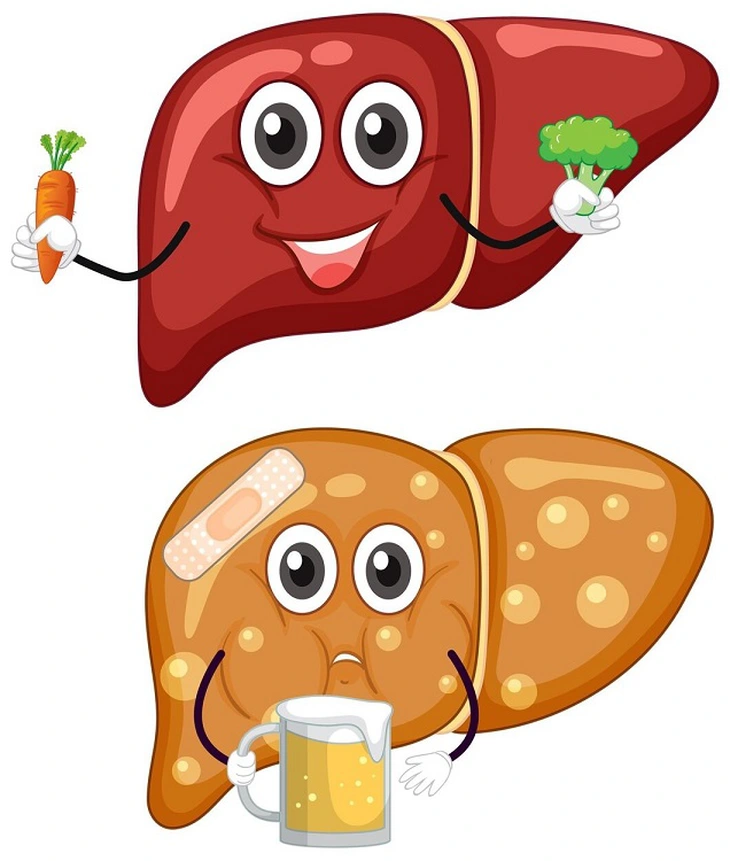
Unhealthy lifestyle increases the risk of fatty liver - Photo: BVCC
According to experts, fatty liver is a potentially serious disease that can lead to liver cancer from stage F1, F2 without necessarily going through the cirrhosis stage.
In addition, fatty liver disease increases the risk of colon cancer 20 times and has an impact on extrahepatic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, sleep apnea syndrome... However, if detected early and prevented, good results can be achieved.
What is fatty liver?
According to MSc. Luu Thi Minh Diep - Center for Liver and Gallbladder Digestion, Bach Mai Hospital, fatty liver is a condition in which excessive fat accumulates in the liver (over 5% of liver weight), affecting liver function.
Of which, the 5 main causes leading to fatty liver include:
- Unhealthy eating habits: Consuming too much food containing sugar, fat, processed food, fast food, drinking alcohol from small to large amounts.
- Obesity and overweight: Excess body fat can cause fat to accumulate in the liver.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of exercise will reduce the body's ability to burn fat.
- Diabetes, high blood pressure: These diseases can be factors that increase the risk of fatty liver (metabolic disorder).
- Genetics: Some people have a genetic tendency to get this disease.
Is fatty liver dangerous?
Dr. Diep said that initially, fatty liver has almost no obvious symptoms, making it difficult for patients to detect.
When the condition becomes more serious, some symptoms may appear such as fatigue, discomfort; itchy skin, hives, allergies; hives or itchy skin are also signs of fatty liver.
In addition, some people experience pain or a feeling of heaviness in the right abdomen; loss of appetite, nausea, unexplained weight loss, especially when eating greasy foods...
In severe cases, the disease can lead to cirrhosis or hepatitis, causing serious liver dysfunction, symptoms include jaundice, nosebleeds, bleeding gums...
Fatty liver can be divided into different levels depending on the development and level of liver damage. Currently, medicine is temporarily divided into 3 groups: mild, moderate and severe.
- At a mild level, only fat accumulates in the liver but does not cause inflammation or damage to liver cells. This level may not cause obvious symptoms and can be reversed by changing lifestyle and diet.
- Moderate fatty liver, more fat accumulates and can start to cause liver inflammation. However, this condition can still be controlled by changing diet and exercise.
- Severe fatty liver - this is the most serious level, when fat accumulates and causes hepatitis, leading to cirrhosis and can develop into liver cancer. This condition requires active treatment and regular management.
How to prevent fatty liver disease
Dr. Diep instructed that in addition to medications prescribed by specialists, lifestyle and diet play an important role in treating fatty liver disease.
- Healthy diet: Increase intake of green vegetables, fresh fruits, foods containing fiber, limit sugar, fat and processed foods.
- Increase physical activity: Exercise regularly, at least 30 minutes a day. Walking, jogging, swimming or yoga can help control weight and reduce body fat.
- Weight loss: Achieving and maintaining an ideal weight helps reduce the risk of fatty liver. Each level of weight loss will improve liver problems. If you lose >3%, you will improve the degree of fat infiltration. If you lose >5-7%, you will improve hepatitis. If you lose >10%, you will improve fibrosis.
This level also applies to cases of thin people with fatty liver, however it is fat loss and muscle gain.
- Control underlying diseases: If you have diseases such as diabetes or high blood pressure, you need to control these diseases well to prevent complications of fatty liver.
- Regular health check-ups: If you have risk factors, have regular health check-ups to detect disease early.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/gan-nhiem-mo-lam-tang-nguy-co-ung-thu-dau-hieu-nao-nhan-biet-som-20250411122801966.htm




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the 16th meeting of the National Steering Committee on combating illegal fishing.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/07/1759848378556_dsc-9253-jpg.webp)




















![[Photo] Super harvest moon shines brightly on Mid-Autumn Festival night around the world](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/07/1759816565798_1759814567021-jpg.webp)





































































Comment (0)