The meeting took place during the APEC 2023 Trade Ministers' Meeting held in Detroit (Michigan - USA) on May 24 and 25 in the US.
This is the first ministerial-level exchange between the two countries in months, after a series of tensions over trade and national security, which are believed to slow down plans to re-engage between the world's two largest economies .
Reuters quoted the US Department of Commerce as saying that the two sides had a frank and substantive discussion regarding US-China trade relations, including the overall environment in both countries regarding trade, investment, and potential areas of cooperation.
Ms. Raimondo raised concerns about a series of recent actions by China against U.S. companies operating in the country. Meanwhile, Xinhua said Mr. Wang also expressed concerns about U.S. policies toward China's economy and trade, especially on semiconductors, as well as issues related to export controls and the review of overseas investments by U.S. companies.
China's Ministry of Commerce said it was a frank, professional and constructive exchange.
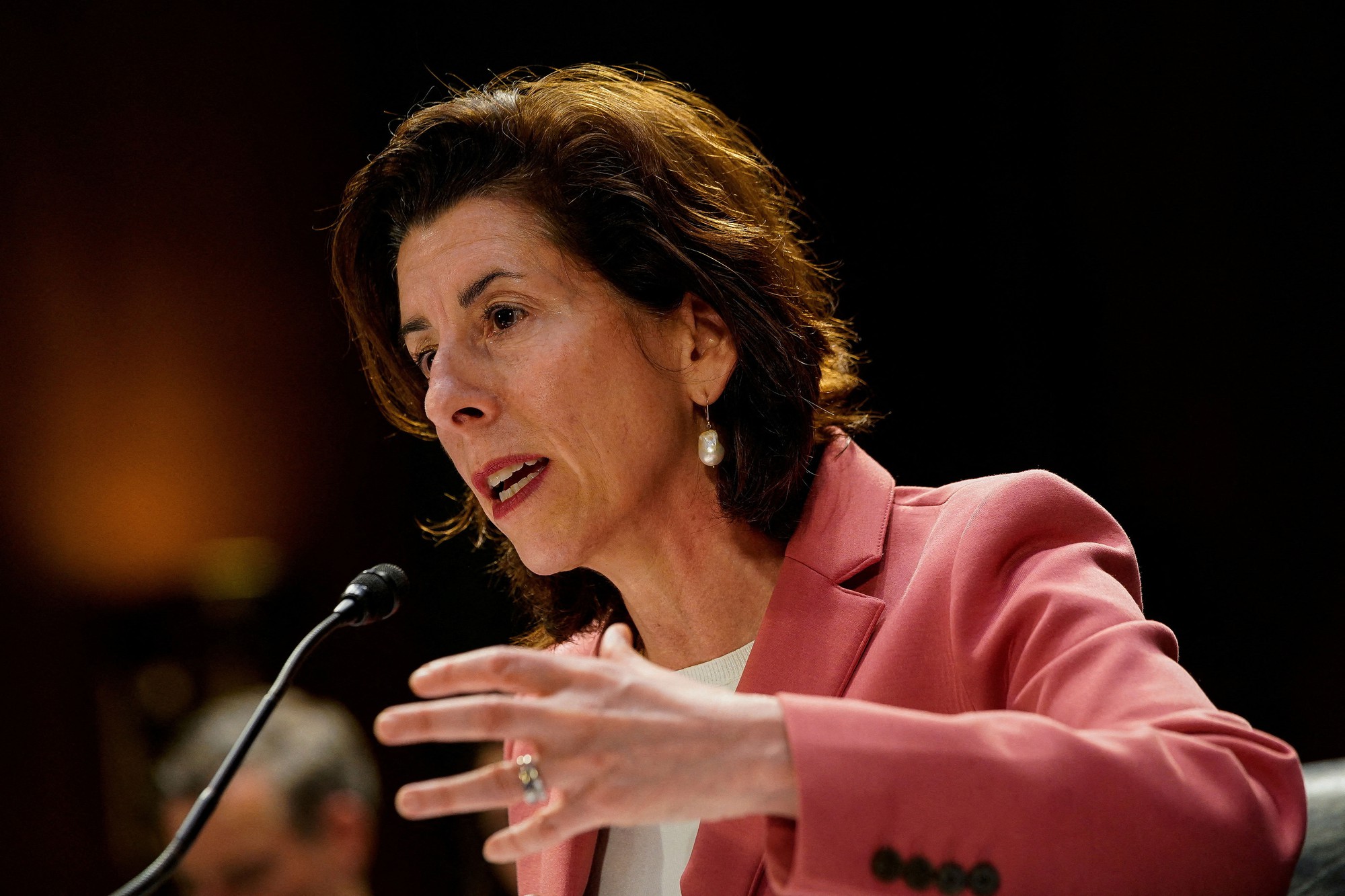

US Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo. Photo: REUTERS
Both sides agreed to establish and maintain open channels of communication and agreed to maintain and enhance exchanges on relevant issues.
Wang is also expected to meet with US Trade Representative Katherine Tai on the sidelines of APEC; while Raimondo, US Secretary of State Antony Blinken and US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen have all expressed their desire to visit China.
According to the latest Bloomberg survey, many economists predict that the People's Bank of China may cut the reserve requirement ratio for banks sooner than expected as the country's economic recovery is "losing momentum".
The cut is expected to be 0.25 percentage points, reducing the reserve requirement ratio — which refers to the amount of cash banks must hold in reserve — to 10.5% from 10.75%. Experts say the decision will be made by the end of the third quarter of 2023, rather than the fourth quarter as originally forecast. The cut rate could remain in place until at least the end of 2024.
The loss of momentum in the recovery has come in recent weeks after an initial surge in consumer activity as China eased COVID-19 pandemic-era policies.
Data this month showed industrial output, retail sales and fixed investment all grew more slowly than expected, while inflation was near zero and consumers were reluctant to borrow.
This prompted economists surveyed to lower their forecast for China's GDP growth this year to 5.5%, slightly lower than the previous estimate of 5.6%. The Chinese government had previously set a rather conservative GDP growth target of 5%.
Source




















































![[Maritime News] More than 80% of global container shipping capacity is in the hands of MSC and major shipping alliances](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/16/6b4d586c984b4cbf8c5680352b9eaeb0)












































Comment (0)