Athlete's foot (athlete's foot) is a common skin disease, especially in the rainy season, caused by the fungi Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton interdigitale and Epidermophyton floccosum.
Dr. Tran Nguyen Anh Thu, a specialist in Dermatology - Cosmetic Dermatology, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, said as above, explaining that these strains normally exist on the skin surface but are not harmful. When the environment is humid, fungi multiply and cause skin diseases. Therefore, in the rainy season, diseases easily develop and spread quickly.
High risk factors for the disease include wearing damp shoes and socks; sharing personal items or skin that comes into direct contact with pathogens; infection on open wounds; soaking feet in dirty water for a long time...
Athlete's foot usually starts between the 3rd-4th and 4th-5th toes, and is characterized by thickened, moist, white or red skin, scaly, cracked areas between and under the toes.
As the disease progresses, the skin between the toes becomes swollen, painful, ulcerated, and festering. Improper hygiene can easily lead to infection leading to cellulitis (acute soft tissue infection in the deep layers of the skin).
Athlete's foot is difficult to cure completely. Therefore, patients should go to medical facilities to perform tests, find the fungus causing the disease and treat it early. The main treatment method uses topical medications, more severe cases will require oral medications. To reduce itching and treat accompanying infections, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
Before applying the medicine, wash your feet with soap and warm water, then dry the skin of your feet. Use a sufficient amount, do not apply too much because it can burn and waste the medicine. Apply the medicine evenly and thinly on the infected area and the surrounding skin. Patients should not stop taking the medicine on their own even if the symptoms of the fungus have decreased.
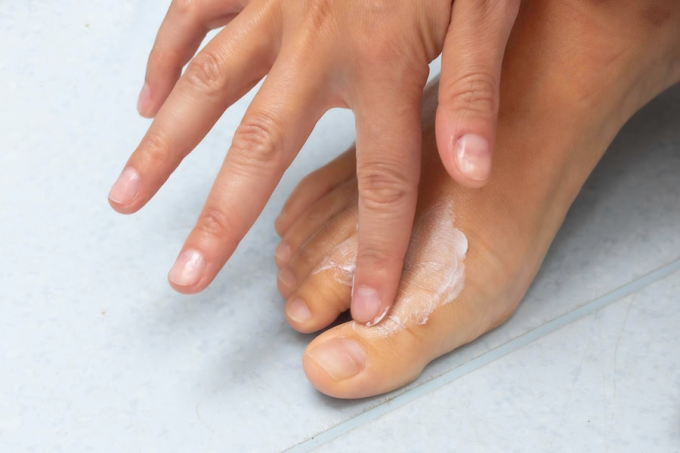
Wash your feet and apply medicine to treat athlete's foot. Photo: Freepik
Topical and oral antifungal drugs can cause certain side effects. Therefore, do not use the drug for the elderly, people with kidney, liver or poor filtration; patients who are taking antacids for stomach treatment. Pregnant and lactating women should avoid using systemic antifungal drugs. Consult your doctor when using antifungal drugs in parallel with other drugs.
Doctor Anh Thu noted that when experiencing side effects such as loss of appetite, bloating, fatigue, yellow eyes and skin, dark yellow urine, patients should stop taking the drug immediately and see a Dermatologist - Cosmetic Dermatologist for appropriate treatment.
To prevent and reduce the risk of recurrence, keep your feet clean and dry, especially after contact with dirty water, wearing socks or shoes all day. Choose socks with good absorbent material, wash with hot water to kill harmful bacteria and fungi. Limit wearing shoes and socks all day. Avoid sharing towels, shoes, socks with others, especially those with fungal infections. When itching between the toes, do not scratch hard because it can cause scratches, inflammation and make the disease worse.
Phan Yen
Source link






![[Photo] Urgently help people soon have a place to live and stabilize their lives](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F09%2F1765248230297_c-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)







































































![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam works with the Standing Committees of the 14th Party Congress Subcommittees](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/09/1765265023554_image.jpeg)


































Comment (0)