Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common type of liver cancer, accounting for a high proportion of the total number of liver cancer cases worldwide . Of which, fatty liver disease related to metabolic disorders is one of the main risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conditions such as high cholesterol, diabetes, and high blood pressure can also increase a person's risk of developing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
In that context, scientists have studied to identify foods, nutritional components and contaminants that can increase the risk of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma, according to Eating Well (USA).
The research results were published in the scientific journal Nutrition Reviews (UK), clarifying the important link between eating habits and the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
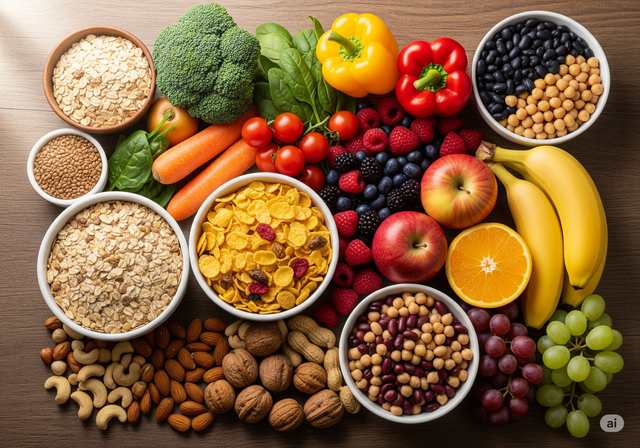

Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with a 32% reduced risk of liver cancer
Photo: AI
Foods that help reduce the risk of liver cancer
Certain foods and nutrients have been found to reduce or increase the risk of liver cancer, specifically:
Meat : The researchers reported that, based on the data they reviewed, people who ate white meat had a 24% lower risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma, and people who ate fish had a 9% lower risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma. On the other hand, eating processed meat was associated with a 20% higher risk of liver cancer.
Fats : Researchers say eating lots of omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish and flaxseed) can reduce the risk of liver cancer by 51%. On the other hand, consuming lots of saturated fat can increase the risk of liver cancer by 34%.
Grains, vegetables, fruits, beans, and nuts : Whole grains and fiber, especially from grains and fruits, are thought to have a protective effect. Regular fiber consumption was associated with a 34% reduction in liver cancer risk; for every 50 grams of fiber consumed per day, the risk was reduced by 23%. Legumes, such as peas and lentils, may also reduce risk by 14% when consumed at 8-40 grams per day.
Micronutrients : Some antioxidants such as vitamin E, folate, beta carotene... can help reduce the risk of liver cancer. In addition, people with low vitamin D levels have a risk of liver cancer more than 2 times higher.
Although not directly associated with a reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, there is strong evidence supporting the role of the Mediterranean diet in preventing weight gain, which may indirectly reduce the risk of liver cancer. Adherence to this diet was associated with a 32% reduction in liver cancer risk, after adjusting for factors such as body mass index (BMI), diabetes, and smoking.
Although the study highlights important links between dietary habits and liver cancer risk, it has some limitations. More research is needed in the future to strengthen and clarify the conclusions.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/nghien-cuu-moi-bo-sung-nhung-thuc-pham-sau-giup-giam-nguy-co-ung-thu-gan-18525081810222973.htm
























![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attends the opening ceremony of the National Data Center](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/18/b5724a9c982b429790fdbd2438a0db44)










































































Comment (0)