Tensions escalate
The US Central Command has confirmed that a ballistic missile attack by Houthi rebels on January 15 hit the container ship Eagle Gibraltar off the Gulf of Aden. The ship is owned and operated by Eagle Bulk Company based in Stamford, Connecticut (USA).
The incident has prompted a series of major international shipping lines to flee the Red Sea, raising concerns that the crisis in the region could derail hopes of a global economic recovery.
Moreover, the spreading crisis once again threatens the global supply chain, which was previously disrupted by the Covid-19 pandemic. The risk of inflation could rise again.
According to the World Bank (WB), the crisis in the Middle East, along with conflicts in other regions, has created real dangers. It increases economic and geopolitical instability. Important transport routes are disrupted, weakening supply networks. All of this will weaken world economic growth further.

Tensions in the Red Sea could persist as US President Joe Biden and British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak have both recently said they are ready to take further action if the Houthis continue to attack ships in the Red Sea. The Houthi leader has vowed to respond to any US attack on the group.
Houthi forces recently announced that they would add more US ships to their list of targets in the Red Sea. Several liquefied natural gas (LNG) tankers have been intercepted.
Britain is not ready to send aircraft carriers to the Red Sea due to a naval personnel crisis, while China remains neutral despite importing about half of its crude oil from the Middle East and exporting more to the European Union (EU) than the US.
China's stance on the Red Sea region will likely be similar to that on the Russia-Ukraine issue, although escalating transport costs will greatly affect China's ability to recover economic growth.
The world into a new spiral?
Thus, at the beginning of the new year, the world economy has faced new challenges. Many forecasts say that the global economy in 2024 will face mounting difficulties.
Before tensions in the Red Sea escalated, the United Nations forecast global economic growth would slow to 2.4% this year, compared with an estimated 2.7% growth in 2023.
Growth rates below 3% are all lower than before the pandemic broke out in 2020.
Worryingly, many economists warn, the world will face another disruption to global supply chains.
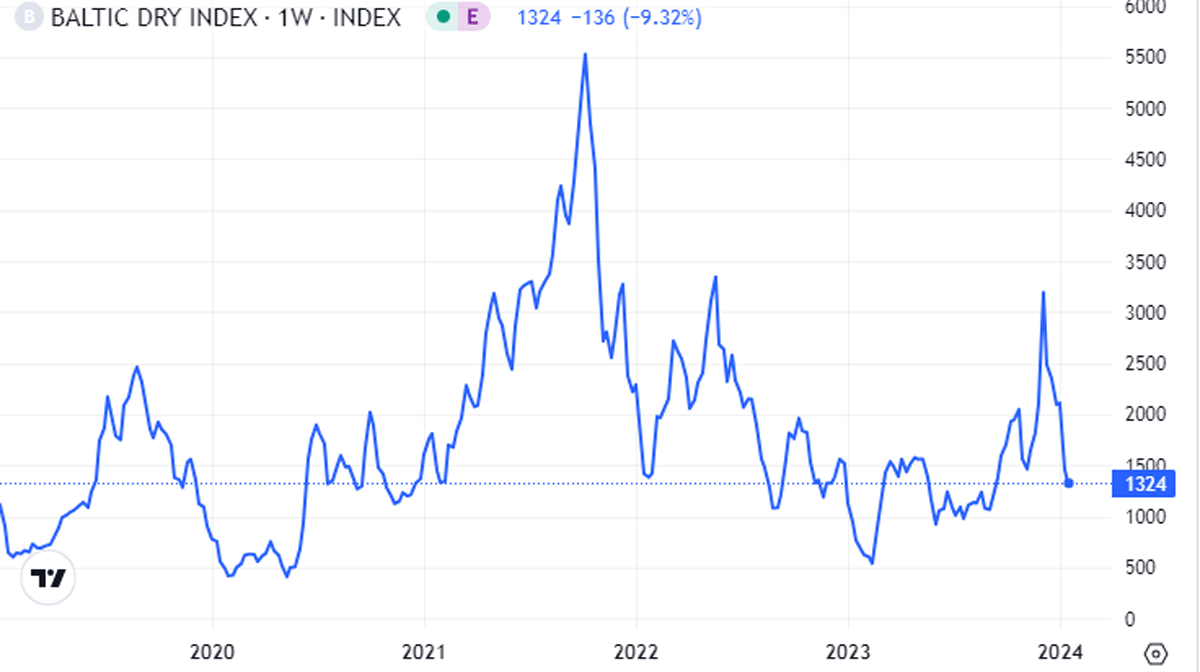
Ocean freight rates have skyrocketed recently. Tensions in the Red Sea have forced many ships to divert around the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa, adding several thousand dollars to the cost of a 40-foot container from Asia to Europe. Transit times have also increased.
In addition to new risks, according to Business Insider, in 2024 the world economy will also face the risk of persistent inflation, which is the unpredictable impact of the US Federal Reserve's (Fed) tight monetary policy that will last from March 2022 to near the end of 2023.
In fact, the US is still recording inflation that is much higher than the 2% target that has been maintained for the past decade. The latest report shows that US inflation recorded in December 2023 was 3.4% compared to the same period in 2023, higher than the 3.1% recorded in November.
This is also a factor that has pushed the USD up again, with the DXY index soaring above the 103-point threshold, despite having previously reached the 100-point threshold at the end of 2023. Investors are concerned that the Fed may not reverse its rate cut to continue to curb inflation. At that time, the weight of a USD and the stagnation of the world's number 1 economy could negatively affect the global economy.
Other risks to the world economy include the prolonged recession of China's real estate market, the rising bad debt situation in the world's second largest economy and the extremely high private debt situation in South Korea...
Another common situation in many countries is the decline in consumption and the rapid increase in public debt. In the US, Business Insider said, people have basically used up all their savings from the Covid-19 pandemic. Therefore, consumer spending is still on a downward trend.
Returning to the emerging issue, ocean freight rates are rising rapidly but can be seen to still be much lower than the peak recorded in 2021. Supply chain disruptions are assessed to exist but are unlikely to be severe. Businesses have learned lessons from the pandemic and have experience to handle inventory and cost issues more reasonably.
In addition, the world is not in a shortage of empty containers like during the pandemic or the Suez Canal blockage caused by the Ever Given ship stuck in early 2021. After achieving record profits from 2021 to early 2023, many companies rushed to buy ships, leading to a situation of excess capacity in the container market.
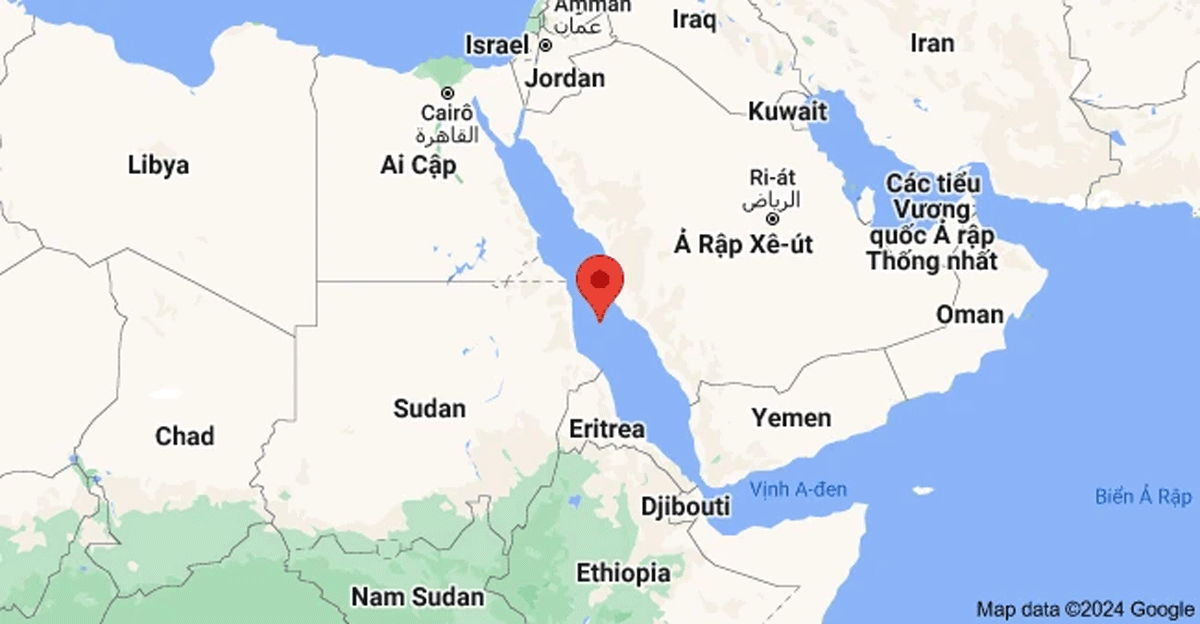
For Vietnam, the picture is brighter. The cost of shipping certainly affects the domestic economy. However, Vietnam’s largest trading partners are China, the US, South Korea and Japan. Therefore, the impact in the Red Sea region may not be too great. Although shipping from Asia to Europe is difficult when crossing the Red Sea, the overall level of shipping with the BDI index has even cooled down recently.
Most organizations forecast that Vietnam's GDP growth in 2024 will be superior to the world's, the second highest in Southeast Asia. The World Bank forecasts that Vietnam's GDP will increase by 5.5%, compared to the world's 2.4%. Vietnam's main growth drivers in 2024 are exports, FDI...
Vietnam's economy will breathe easier in the second half of 2024 when countries simultaneously lower interest rates.

Source










![[Video] More than 100 universities announce tuition fees for the 2025–2026 academic year](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/18/7eacdc721552429494cf919b3a65b42e)

















































































![[Infographic] In 2025, 47 products will achieve national OCOP](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/16/5d672398b0744db3ab920e05db8e5b7d)





Comment (0)