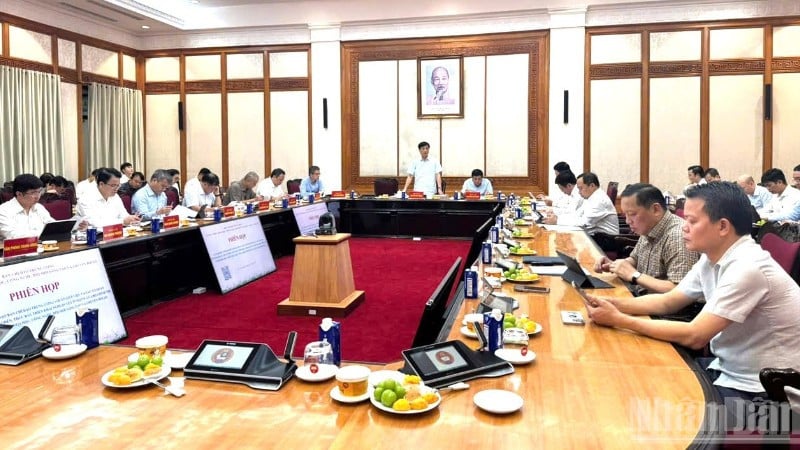

Notice No. 47-TB/TGV announces the Conclusion of the meeting of the leaders of the Central Steering Committee on Science , Technology, Innovation and Digital Transformation with the Standing Committee of the Working Group and relevant agencies to remove existing problems, limitations and bottlenecks in science, technology, innovation and digital transformation. The content of Notice No. 47 is as follows:
Implementing the conclusion of the General Secretary, Head of the Central Steering Committee on science, technology, innovation and digital transformation development (referred to as the Steering Committee) at the conference to review the implementation of Resolution No. 57-NQ/TW, dated December 22, 2024 of the Politburo in the third quarter of 2025 and key tasks and solutions at the end of 2025 (Notice of Conclusion No. 07-TB/CQTTBCD dated October 15, 2025), on October 16, 2025, Comrade Nguyen Duy Ngoc, Politburo member, Secretary of the Party Central Committee, Chairman of the Central Inspection Committee, Deputy Head of the Steering Committee and Comrade Nguyen Chi Dung, Party Central Committee member, Deputy Prime Minister, Member of the Steering Committee chaired a meeting with the Standing Committee of the Working Group and relevant agencies and units to remove existing problems, limitations and bottlenecks in science, technology and innovation. Creation and digital transformation in 6 groups of issues including: (1) Registration and protection of intellectual property rights (industrial property); (2) Localization rate in science, technology, innovation and digital transformation products; (3) Registration of tasks, arrangement of funds and disbursement of state budget for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation; (4) Ordering mechanism and public-private partnership; promoting the development of science and technology market associated with the urgent promulgation of national standards and technical regulations; (5) Deployment of strategic technology development programs; (6) Completing and operating the National Innovation Portal and Science and Technology Exchange; and a number of other related issues.
Attending the meeting were representatives of leaders of ministries and agencies: Science and Technology, Finance, Industry and Trade, Justice, Public Security, Central Party Office, Central Policy and Strategy Committee; representatives of a number of experts, scientists and a number of related units.
Based on the report of the Standing Committee of the Working Group and the unanimous opinions expressed at the meeting, the Steering Committee's leaders concluded as follows:
1. On registration and protection of intellectual property rights [1]
a) Existence and limitations
- The application review process is still complicated and not transparent; The average time to grant a patent is still long (44 months, 2.4 times longer than the 21-month period), not meeting practical requirements.
- Information technology infrastructure serving intellectual property work is still outdated and has not been upgraded synchronously (public service software, management software, search, servers, transmission lines).
- Data on patents, designs, and trademarks is still scattered and difficult to access, and artificial intelligence (AI) has not been applied to improve processing efficiency.
- The system does not yet allow applicants to look up the status of their application online or conveniently manage and pay fees to maintain the validity of their protection certificates.
b) Solution
- Regarding institutional and policy improvement: Improve legal regulations on establishing rights in the direction of simplifying, streamlining, and making the registration and appraisal process more efficient, ensuring transparency, publicity, clearly defining responsibilities, enhancing decentralization, and post-auditing. Research solutions for handling complex applications and similar groups of applications to shorten the time and reduce backlog of applications.
- Digital transformation in intellectual property work: Promote comprehensive digital transformation in application management and appraisal activities: standardize and synchronize databases; upgrade the application processing system towards paperless, apply digital signatures and process completely electronic records; integrate artificial intelligence (AI), open data, connection APIs, multilingual interfaces and automatic warning systems, helping to improve productivity, accuracy and transparency in management, serving people and businesses.
- Develop a state policy to partially support international registration costs as required by Resolution 68-NQ/TW dated May 4, 2025 of the Politburo.
c) Responsibility
The Ministry of Science and Technology shall preside over and coordinate with relevant ministries, agencies and localities to promptly deploy the above solutions; report to the Standing Steering Committee on the implementation results in December 2025.
2. On the localization rate in science, technology, innovation and digital transformation products
a) Existence and limitations
- The ability to master core technology and source materials is still weak.
- The link between FDI enterprises and domestic enterprises is still loose and not linked to the technology transfer process. The rate of localization of products is still low.
- Lack of highly skilled human resources for precision manufacturing technology industries.
- Financial policy is not innovative enough to encourage localization.
Causes of existence
- Investment in research and development (R&D) is still scattered and not focused on basic technology.
- Lack of attractive enough incentive mechanisms for FDI enterprises to transfer technology to increase product localization rate, lack of domestic technical standards for Vietnamese enterprises to participate in the supply chain.
- The training system is not closely linked to the practical needs of the manufacturing, materials and microchip design industries.
- The capital disbursement mechanism for R&D and high technology is still complicated, inflexible and lacks a risk acceptance mechanism.
b) Solution
- Clearly identify industrial and technological products that need to be localized (for example: semiconductor chips, electronic materials, electric vehicle batteries, etc.) and have a mechanism to assign specific tasks, along with budgets, to key corporations and research institutes.
- Invest in building specialized training centers on chips, artificial intelligence (AI),... and precision manufacturing techniques according to international standards, linked to the recruitment needs of multinational companies and large domestic corporations and enterprises.
- Research and prioritize localization policies in strategic technology products.
- Review and develop: (i) A set of localization criteria by industry (for each key industry such as electronics, digital equipment, new materials, renewable energy, cyber security, digital infrastructure, etc.; the criteria must be based on domestic added value, the ratio of key components and technologies produced domestically, and the level of mastery of core technology). The set of criteria is applied uniformly in public investment, public procurement and national bidding, with an implementation roadmap of 3-5 years.
c) Responsibility
The Ministry of Finance, the Ministry of Industry and Trade, and the Ministry of Science and Technology, according to their functions and tasks, shall preside over and coordinate with relevant ministries, branches, and localities to promptly deploy the above solutions; report to the Standing Steering Committee on the implementation results in December 2025.
3. On registration, arrangement, allocation of funds, disbursement of state budget capital for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation , monitoring mechanism , coordination mechanism between the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Science and Technology
a) Existence and limitations
- The overall disbursement rate of 62% in the middle of the fourth quarter is slow. There is a large difference in disbursement between levels, especially the allocation of resources to the commune level is unreasonable and extremely limited (only 3.3 billion VND, an average of 1 million VND/commune), directly affecting the effectiveness of policy implementation at the grassroots level.
- Strategic technology has not been properly invested: The budget allocated for strategic technologies has only reached 934.4 billion VND, accounting for less than 10% of the total 10,163 billion VND proposed to be allocated from the additional 25,000 billion VND, showing the disproportion between development requirements and budget allocation actions.
- Coordination between the sector management ministry (Ministry of Science and Technology) and the budget management ministry (Ministry of Finance) is not smooth and tight. The Ministry of Science and Technology has not yet provided specific guidance on the scope of each sub-sector/group so that the Ministry of Finance can adjust management tools and detailed tracking software as required, helping to speed up the registration, allocation and disbursement process.
- Some agencies and localities are still confused. in determining investment items; implementation is not resolute and not close to actual requirements.
- Funding allocation is being carried out mainly on a bottom-up basis, so tasks are fragmented and lack focus and emphasis on strategic technologies.
b) Solution
Implement regulations on the allocation of science, technology and innovation budgets to ministries, branches and localities annually; assign ministries, branches and localities to directly manage topics and tasks; assign the Ministry of Science and Technology to perform the function of monitoring and managing the allocation structure and output efficiency.
Regulations on the state budget will be allocated in the form of top-down orders, with an appropriate proportion of the total budget for science, technology, innovation, and digital transformation. Accordingly, the Ministry of Science and Technology will directly place orders, while ministries, branches, and localities are also responsible for placing research orders. This funding source will focus on prioritizing strategic technology research and development tasks.
- Ministry of Science and Technology
+ Preside over and be responsible for professional content; issue guidelines on criteria, scope, and economic-technical norms for expenditure items in the fields of science, technology, innovation, and digital transformation.
+ Perform the role of professional orientation; organize training, guide budget preparation, manage the use and settlement of state budget funds to perform tasks and support activities in the fields of science, technology, innovation and digital transformation for ministries, branches and localities.
+ Preside and coordinate with ministries and branches to research and develop management tools to ensure the allocation, use and settlement of state budget expenditures according to regulations.
+ Regarding budget allocation for 2026, preside over and coordinate with the Ministry of Finance to research and report to competent authorities for consideration to allocate an appropriate budget proportion to prioritize strategic and key national tasks (key laboratories, strategic technologies, etc.), the remaining allocation is based on practical needs and proposals of ministries, branches and localities.
- The Ministry of Finance shall preside over and coordinate with the Ministry of Science and Technology to research and develop a new capital allocation mechanism to ensure timely and sustainable implementation of tasks for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation according to the assigned tasks in Conclusion Notice No. 45-TB/TGV dated September 30, 2025 and Conclusion Notice No. 07-TB/CQTTBCD dated October 15, 2025.
- During the process of appraising documents and approving budget estimates for science, technology and digital transformation, the Ministry of Science and Technology and the Ministry of Finance proactively and promptly exchanged and guided ministries, agencies and localities to remove obstacles and avoid confusion during implementation.
- Ministries, branches and localities:
+ Responsible for organizing and effectively implementing assigned tasks and projects, ensuring adherence to industry management agency guidelines, avoiding duplication and waste.
+ Assign focal points to synthesize and guide plans and estimates (including investment and regular expenditures) to ensure consistency and synchronization (at Ministries and central agencies: Department/Division/Department of Planning and Finance, at localities: Department of Finance/Department of Science and Technology).
+ Effectively organize and implement assigned tasks and projects in accordance with the direction in Conclusion Notice No. 07-TB/CQTTBCD dated October 15, 2025; ensure adherence to the instructions of the industry management agency, avoid duplication and waste.
c) Responsibility
The Ministry of Science and Technology and the Ministry of Finance, according to their functions and tasks, shall preside over and coordinate with relevant ministries, branches and localities to promptly deploy the above solutions; report to the Standing Steering Committee on the implementation results in December 2025.
4. Ordering mechanism and public-private partnership; promoting the development of the science and technology market associated with the urgent promulgation of a system of national technical standards and regulations
a ) Existence and limitations
- The law on intellectual property and credit institutions does not have clear regulations on: (i) Ownership, exploitation and transfer of Intellectual Property (IP) arising from R&D projects with state capital combined with private capital; (ii) lack of guarantee mechanism and inability to use Intellectual Property (IP) as collateral according to current regulations.
- The financial mechanism for science and technology tasks is still rigid, management is based on input instead of output, and payment procedures are complicated.
- State Science and Technology Development Funds operate under the public investment model instead of the venture capital fund model, reducing flexibility and risk tolerance.
- The approval, review and settlement process for scientific and technological tasks is still cumbersome, lengthy and unattractive to private enterprises.
- The fear of risk in state agencies leads to a tendency to choose safe, non-innovative solutions.
- Mechanisms and policies to promote technology transfer, develop science and technology markets, innovation and digital transformation have been prescribed. It takes time for policies to continue to be perfected and implemented in practice.
- The relationship between technology supply and demand is not effective. Most businesses lack technology information and are limited in both technology acquisition and transfer capacity and finance.
- Intermediary organizations of the science and technology market have not effectively promoted the function of connecting supply and demand, consulting on technology transfer, and are not professional in providing services; lack a team of professional consultants and brokers; there is no typical intermediary organization capable of leading the network of intermediary organizations; technology exchanges have not demonstrated their leading role in the system of intermediary organizations.
- Science and technology trading floors do not have information and data connections; businesses still have difficulty accessing information about technology to be able to choose suitable technology.
- The innovation capacity and financial resources of enterprises are still weak, the ratio of spending on research and development (R&D) is still low, and there is a lack of technical human resources.
b) Solution
* Financial mechanism for developing the market for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation
- Implement the Strategic Technology Program; identify strategic technologies as core technologies, as a basis for the Ministry of Science and Technology, ministries, branches and localities to order core technologies.
- Regulate public-private partnerships under a new mechanism, apply co-funding of research with businesses at an appropriate rate. Orientate research budget spending for businesses in the total budget for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation, thereby creating conditions for the formation of a co-funding mechanism.
- Review legal regulations on intellectual property and credit institutions to handle problems related to ownership and mortgage of intellectual property (IP) when implementing public-private partnership activities in the fields of digital infrastructure, R&D centers and technology incubation.
- Pilot implementation of Pre-Commercial Ordering (PCP) mechanism: Select 3 priority sectors (e.g. healthcare, education, smart cities) to apply PCP, allowing state agencies to order R&D services to seek pioneering technology solutions, creating incentives for innovative businesses.
- Convert the management mechanism of current Funds into a Venture Capital Fund model, allowing professional fund managers to have greater autonomy in evaluating, investing and accepting risks (researching operating options according to the business model).
- Review and research to prioritize disbursement of capital sources for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation for projects with public-private partnership commitments, with the proportion of counterpart capital from the private sector reaching at least 70% of total investment capital.
- The most important solution to develop science, technology, innovation and digital transformation in the country is to create and expand the market through increasing budget spending, prioritizing the use of Vietnamese products, and supporting businesses to participate. The State will allocate a larger proportion of the budget for purchasing new technology, assign key businesses to carry out large projects, and at the same time issue vouchers to small and medium-sized enterprises to encourage the use of digital transformation products and services.
- Review and fully promulgate documents guiding the implementation of issued laws.
- Enhance the effectiveness of the three-way connection, promote technology supply and demand: Build a mechanism for ordering R&D from businesses; Encourage the model of co-funding research and application between institutes, schools and businesses. Develop a national technology supply and demand connection network.
- Continue to invest, upgrade, and have policies to support and encourage the development of intermediary organizations and science and technology exchanges that operate effectively and transparently.
- Manage and link data of technology platforms at the central and local levels
- The State continues to invest in and lead key and strategic technology fields; promote the activities of Science and Technology Funds; and support businesses to promote innovation.
- Specific solutions for technology exchanges: (i) Investing in building a national technology exchange; investing in upgrading and enhancing the capacity of local exchanges; (ii) Regulating and building a mechanism for connecting and communicating technology information and data on technology exchanges from the central to local levels; (iii) Building and promulgating standards for technology exchanges; building and promulgating a list of public career services and building technical and economic norms for public career services using the state budget in accordance with the functions of the technology exchanges.
* On technical standards for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation
- With the aim of increasing competitiveness and protecting the domestic market, it is necessary to focus on standards in the following areas: (1) Smart cities; (2) Strategic technologies; (3) Artificial intelligence; (4) Blockchain technology; (5) Data platforms, Open data; (6) Information security, network security.
The ministries and agencies: Science and Technology, Construction, Public Security, according to their functions and tasks, shall preside over and coordinate with the ministries and agencies: (1) Research and promulgate the List of standards and technical regulations for the above 6 fields. To be completed in November 2025; (2) Build modern laboratories and measurement laboratories with sufficient capacity and authorized by international standards publishing organizations to evaluate and grant certification, as well as accept measurement certificates of qualified international laboratories.
Based on the list of issued standards and technical regulations, the organization shall publicize and widely communicate to agencies, organizations and individuals and provide guidance on implementation. At the same time, evaluate and appraise products and solutions according to the proposed needs of agencies, organizations and individuals.
- Build modern laboratories and testing facilities that are capable and accredited to international standards. Implement mutual recognition agreements (MRAs) and implement a mechanism to accept conformity assessment results from foreign conformity assessment organizations that meet the conditions according to international regulations and practices.
- Based on the list of issued standards and technical regulations, the organization shall publicize and widely communicate to agencies, organizations and individuals and provide guidance on implementation and implementation of conformity assessment activities for products and appraisal of solutions according to the proposed needs of agencies, organizations and individuals.
c) Responsibility
The Ministry of Science and Technology and the Ministry of Finance, according to their functions and tasks, shall preside over and coordinate with relevant ministries, branches and localities to promptly deploy the above solutions; report to the Standing Steering Committee on the implementation results in December 2025.
5. On strategic technology development
a) Existence and limitations
- Although the Strategic Technology Catalogue has been identified, to date its implementation has not received specific guidance from the competent authorities.
- Lack of high quality human resources;
- The connection between institutes, schools and businesses is still weak, leading to difficulty in commercializing research products.
- Lack of investment capital for the early stages and commercialization support funds.
b) Solution
- Issue a Program for implementation and evaluation standards; invest in national key laboratories from 2026. The budget for strategic technology needs to be prioritized and arranged appropriately in the total science and technology expenditure, with a budget mechanism for purchasing strategic technology products (first batch) or issuing vouchers for businesses to use.
- Select large enterprises to be the target for ordering strategic technology deployment. Enterprises will act as general contractors, directly receiving orders, and proactively coordinating and placing orders back to research institutes and universities to deploy research, develop and master strategic technology.
- Timely promulgate national standards to directly serve research and development activities of strategic and core technologies, ensuring consistency and uniformity and creating a legal-technical foundation for the implementation process.
It is necessary to clearly define the goals of strategic technology development, which are: Technological autonomy, serving localization, increasing competitiveness and creating a foundation for future development.
It is necessary to establish a model of 3 pillars: the State is the creator, the Enterprise is the center, and the School is the place of creativity.
Each strategic technology needs a specific implementation program, in which component programs (for each specific strategic technology product) can be identified, key enterprises and participating research institutes and universities can be selected;
Determine the allowable localization rate for each strategic technology product. May allow for the purchase of components and equipment available from multiple suppliers.
It is necessary to expand and attract a network of experts and scientists to participate in developing strategic technologies.
Example of implementation:
For technologies that businesses are not ready for (for example, technologies that businesses have limited potential for) or that do not have a market but the State has a current need for (for example, technologies related to security and defense): The State can invest in a "promotion" direction through funding for schools and businesses up to 80%, schools and especially businesses can match 20%.
For technologies that have been and are forming a market: Enterprises invest in the direction of creating "traction" of at least 50%, the State shares risks with enterprises in R&D activities, through funding for schools to research topics proposed by enterprises.
Develop data on the network of Vietnamese experts and intellectuals in each field and mobilize them to participate in projects, programs and tasks to develop strategic technology industries.
Method of constructing the topic:
Method 1 (Top-Down) - The State builds the project and orders the implementation organizations. Projects come from the following sources:
+ For Technology Group 1: The State issues detailed requirements for a strategic technology that needs to be mastered and localized. The Council for issuing the requirements includes representatives of domestic and foreign enterprises and scientists, based on the technology development situation in the world (can be based on available foreign prototypes) to issue the requirements: specific requirements, clear roadmap, the created products must comply with international standards/regulations (or if there are no standards/regulations, it must be accompanied by the task of developing standards/regulations for the products). Then, the State calls for selection with a commitment of sufficient resources to complete the task. For example: satellite technology, dual-use unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology, quantum technology...
+ For Technology Group 2: For each strategic technology, identify one or a group of core enterprises, which are enterprises that are strongly developing related products. These enterprises will support the development of necessary science and technology development topics to master and localize each part with clear criteria, roadmap and goals. The State and enterprises jointly invest in the form of public-private partnership. State funding is mainly invested in the school sector to research with enterprises, as well as support enterprises in technological innovation. For example: technology related to electric vehicles, high-speed railways, etc.
- Method 2 (Bottom-Up) - Call for proposals (traditional method): The State calls on businesses and schools to propose strategic technology development research projects/topics (with special priority given to proposals involving cooperation between businesses and schools with clear output orientations). The State (Ministry of Science and Technology) organizes the selection and funding.
- Method 3 (Open Innovation): Create a network and openly share and coordinate the participation of members: Recently, the Ministry of Finance has directed the National Innovation Center to initiate and sponsor the establishment of the Vietnam Innovation Network, developed in 22 countries and territories with more than 2,000 members who are experts, scientists, intellectuals, and Vietnamese businessmen abroad, with extensive experience working at large technology corporations, research institutes, and universities around the world. In particular, there are specialized Networks to develop strategic technology fields that have been formed such as the Network on semiconductors, artificial intelligence, quantum, cyber security, and aviation, space, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV). Expanding the model and developing the Vietnam Innovation Network is necessary. Ministries, agencies and localities are requested to coordinate with the National Innovation Center and the Ministry of Finance to implement joint research cooperation projects, share knowledge and resources, and focus on solving major problems of strategic technology sectors.
c) Responsibility
The Ministry of Science and Technology and the Ministry of Finance, according to their functions and tasks, shall preside over and coordinate with relevant ministries, branches and localities to promptly deploy the above solutions; report to the Standing Steering Committee on the implementation results in December 2025.
6. About the Innovation Portal and Science and Technology Exchange
a) Existence and limitations
The Innovation Portal and the Science and Technology Innovation Platform have not yet been fully completed as required by the Steering Committee in Notices No. 12, 15 and 27 of the Steering Committee's Working Group. Specifically: (1) The legal framework and operating mechanism have not been completed; (2) There is a lack of a clear financial model and public-private partnership; (3) Data connection and communication are not synchronized; (4) Coordination, monitoring and reporting of results are still scattered.
The role and requirements of the Portal that have not yet been met are to create favorable conditions for all organizations and individuals with innovative and creative thinking to be able to register scientific and technological initiatives; ensure that the process of receiving, reviewing, selecting, announcing and commercializing initiatives is carried out publicly, transparently and in accordance with regulations; at the same time, fully protect the intellectual property rights and copyrights of organizations and individuals throughout the process of reviewing, announcing and implementing commercialization of products and solutions. The Portal serves 3 main groups of subjects: (1) Scientists, individuals and organizations with initiatives and technological solutions that need support, announcement, connection and commercialization; (2) State agencies and enterprises that need to apply technological solutions and innovations to improve operational efficiency; (3) Investment funds and innovation support organizations that need to find potential initiatives to sponsor and invest in.
b) Solution
* Perfecting institutions and legal corridors
- Urgently issue Guidelines clearly stipulating: (1) Procedures for supporting registration and protection of intellectual property for initiatives; (2) Mechanism for data sharing and information security; (3) Clearly defining the roles, responsibilities and rights of participating entities.
- Specify detailed regulations and instructions for implementing the Law amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Law on Technology Transfer after it is passed by the National Assembly, including regulations on the mechanism of socialization and public-private partnership in operating the Science and Technology Exchange.
* Promote digital transformation and data integration
Complete API standards, metadata, and shared security protocols between systems linked to the Portal.
- Deploy Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications and big data analysis to automate the process of suggesting, connecting, and evaluating the commercialization potential of initiatives.
- Set up real-time monitoring dashboard on the Monitoring System.
* Strengthen coordination, monitoring and reporting
- Review the internal coordination mechanism of the Ministry of Science and Technology, clearly assign focal points to each group of tasks.
- Set up periodic reporting forms (monthly/quarterly) on the results of Portal and Exchange operations (send to the Steering Committee and update to the Monitoring System).
- Organize independent evaluation (every 3-6 months) of performance, connectivity, and user feedback.
* Strengthen communication and engagement of stakeholders
- Promote propaganda and promotion of the Innovation Portal and Science and Technology Exchange on digital platforms and social networks.
- Sign cooperation agreements with universities, research institutes, and business associations to expand the supply of innovations and demand for technology.
- Organize periodic forums/fairs on innovation and technology transfer, thereby promoting cooperation and product commercialization.
* Immediately search for and support some valuable initiatives on the system, especially those from people and businesses: create inspiration and spread policies.
c) Responsibility
The Ministry of Science and Technology shall preside over and coordinate with relevant ministries, branches, localities, organizations and individuals to promptly deploy the above solutions; report to the Standing Steering Committee on the implementation results in December 2025.
7. Regarding some related key tasks
a) Ministry of Science and Technology
- Preside over and coordinate with the Ministry of Finance and relevant agencies to urgently develop a plan to propose the allocation of the remaining funding for 2025 for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation, ensuring focus on urgent, key and strategic tasks. Report to competent authorities for consideration and decision in October 2025 .
- Focus on completing draft laws (Law on Digital Transformation, Law on High Technology, Law on Technology Transfer, Law on Artificial Intelligence, Law on amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Law on Intellectual Property) to be submitted to the 10th session of the 15th National Assembly. At the same time, proactively develop draft guiding documents according to the principle that each law only issues one detailed decree.
Regarding the Digital Transformation Law project, the research and development process ensures highly feasible regulations, creating a synchronous legal corridor to promote national digital transformation, especially the effective implementation of Plan No. 02-KH/BCĐTW, dated June 19, 2025 of the Steering Committee.
- Proactively study international experience, propose plans and mechanisms to encourage FDI enterprises to transfer technology and increase the localization rate, report to the Prime Minister for consideration and decision. To be completed before October 30, 2025.
- Preside and coordinate with the Ministry of Home Affairs to report to the Government for consideration and resolution of personnel and financial management mechanisms, ensuring compliance with the specific nature of the Intellectual Property Office's operations. To be completed in November 2025 .
b) Ministry of Finance
- Closely coordinate with the Ministry of Science and Technology in guiding, allocating funds and monitoring and synthesizing the disbursement situation for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation.
- Urgently direct the National Innovation Center (NIC) to review and complete the Investment Project for the Accommodation Area for Experts at Hoa Lac High-Tech Park, and start the project in the fourth quarter of 2025 (Notice No. 30-TB/TGV, dated June 30, 2025 and Notice No. 42-TB/TGV, dated August 22, 2025).
c) Ministry of Justice
- Preside, review, and synthesize the implementation of legal documents related to science, technology, innovation, and digital transformation (laws, decrees, circulars), clarify the progress and responsibilities of each ministry and branch. Report monthly or ad hoc to the Standing Committee of the Steering Committee. Regular tasks.
- Preside over and coordinate with the Ministry of Public Security, the Ministry of Home Affairs, the Government Office, the Central Party Office and relevant ministries, branches and localities to seriously and effectively implement the task of reviewing, evaluating and proposing plans to reduce and simplify administrative procedures at the provincial and communal levels as required in Clause 8, Section III of Conclusion Notice No. 07-TB/CQTTBCD dated October 15, 2025. The implementation process must ensure scientific, methodical, practical approach and based on the availability of data, connectivity and synchronization of infrastructure between agencies in the political system to review and propose reductions to ensure effectiveness, substance, and in accordance with the assigned schedule. Promote the role of coordinating and urging ministries and branches; proactively propose and report to the Steering Committee on difficult and complicated issues that need to be handled promptly and thoroughly.
8. On implementation organization
a) Establish an inter-sectoral working group headed by comrade Nguyen Huy Dung, full-time member of the Steering Committee, with the participation of representatives from the Ministries and agencies: Science and Technology, Finance, Justice, the Central Party Office and relevant agencies. The specific composition will be proposed and assigned by the Head of the working group. The working group has the following tasks:
(i) Work with a number of ministries, localities and enterprises to identify specific problems (due to mechanisms or implementation organizations) related to the registration and disbursement of state budget capital for science, technology, innovation and digital transformation. Set up and operate a support hotline, operating continuously to receive, answer and promptly guide the difficulties and problems of agencies, localities and enterprises related to this content.
(ii) Take the lead in urging the public disclosure and transparency of all processes, procedures, and related guidance documents for registration, allocation, and disbursement of funds for science, technology, innovation, and digital transformation on the VNeID application and other information systems so that relevant agencies, organizations, and individuals can easily look up and access them.
(iii) Timely synthesize and request the Ministries of Science and Technology, Finance and relevant ministries and branches to promptly resolve issues related to registration, allocation and disbursement of funds; report to the Standing Steering Committee on implementation results.
The Working Group urgently conducts preparatory work to ensure that the above tasks are deployed from October 25, 2025 .
b) Ministries and agencies: Public Security, Home Affairs, Government Office, Central Party Office and ministries, branches and localities closely coordinate with the Ministry of Justice to perform the task of reviewing and re-evaluating all administrative procedures at the provincial and communal levels to propose plans for reduction and simplification in substance and efficiency, and report to competent authorities for consideration and decision before November 15, 2025 (Clause 8, Section III of Conclusion Notice No. 07-TB/CQTTBCD dated October 15, 2025).
c ) Ministries, branches and localities seriously implement the task of developing an Action Plan according to the requirements in Clause 3, Section IV of Conclusion Notice No. 07-TB/CQTTBCD dated October 15, 2025 and the tasks in this Notice.
------------
[1] Industrial property.
Source: https://nhandan.vn/thao-go-nhung-ton-tai-han-che-diem-nghen-ve-khoa-hoc-cong-nghe-doi-moi-sang-tao-va-chuyen-doi-so-post916680.html



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with Speaker of the Hungarian National Assembly Kover Laszlo](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760970413415_dsc-8111-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Solemn opening of the 10th Session, 15th National Assembly](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760937111622_ndo_br_1-202-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man holds talks with Hungarian National Assembly Chairman Kover Laszlo](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760952711347_ndo_br_bnd-1603-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Chairman of the Hungarian Parliament visits President Ho Chi Minh's Mausoleum](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760941009023_ndo_br_hungary-jpg.webp)
















![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with Speaker of the Hungarian National Assembly Kover Laszlo](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760970413415_dsc-8111-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] The Steering Committee of the 2025 Fall Fair checks the progress of the organization](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760918203241_nam-5371-jpg.webp)







































































Comment (0)