The system of cultural values is stable and sustainable, lasting over time, especially intangible culture. Today, facing the mission of integration in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, that system of sustainable and unified cultural values becomes a bridge connecting the past with the present and the future, an endogenous strength to build and protect the Fatherland.
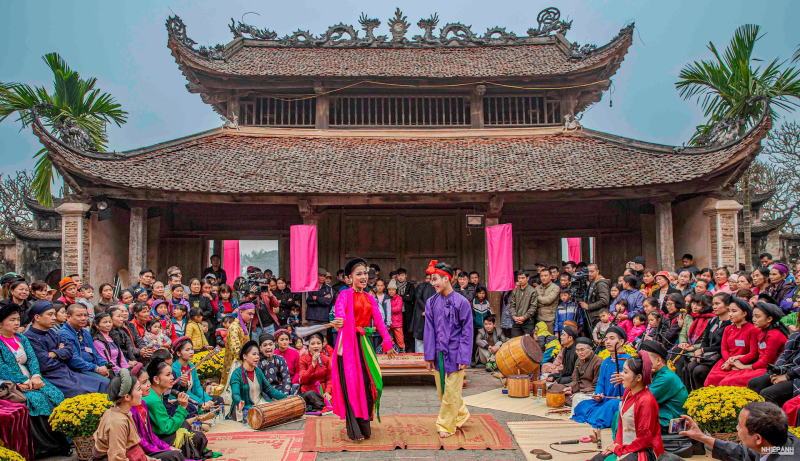
Cheo art is being submitted for consideration for inclusion in UNESCO's List of Intangible Cultural Heritage_Photo: Document
Looking back at the historical origins of the formation of the multi-ethnic Vietnamese national community, it can be seen that the system of customs, practices and forms of cultural, artistic, and fine arts practices, and activities of thousands of traditional craft villages have accumulated, creating a huge treasure of indigenous cultural knowledge of 54 ethnic groups (including more than 700 local ethnic groups). All of these cultural resources are mainly based on the consciousness - psychology of gratitude, worship of the supporting power of natural forces that help people preserve life (such as land, trees, water and other essential resources for life) along with the gratitude and admiration of successive generations for their ancestors, building cultural values with profound human significance. From the centripetal consciousness and the psychology of worship, gratitude, and honoring the historical past, in ethnic and racial communities, spiritual "products" associated with the community or individuals, objects and related cultural spaces have been formed/created, with historical, cultural, scientific value, expressing the identity of the community, constantly being recreated and passed down from generation to generation by word of mouth, craft, performance and other forms (1) . In which, there exist vividly customs, practices and countless ways of practicing rituals, festivals, and beliefs, expressing the community's awareness, views and behavior towards the natural ecological environment, the humanistic ecological environment and the socio-cultural environment. That is the "support" for the birth of a series of historical - cultural relics, forms of practicing intangible cultural heritage, creating the identity and cultural traditions of each community in the multi-ethnic Vietnamese national community. The "flow" of the treasure trove of intangible cultural heritage of Vietnam, built up through generations, has formed a system of traditional cultural values, seamlessly expressing the centripetal psychology of small communities, creating the basis for the formation of village culture, from which to reach a large community (region - area - country), in the system of the multi-ethnic Vietnamese national community. Following the footsteps of previous generations, dozens of ethnic groups and ethnic groups have come down from the North or upstream from the South to live together, share the same fate, share the same sympathy, and work towards consensus in the process of coexistence, and are attached to the destiny of a nation, a multi-ethnic community. From there, it contributes to creating cultural products and shaping/building/enhancing cultural values, making the system of national cultural treasures increasingly diverse and vivid, although each nation and ethnic group still preserves cultural features with their own national identity.
The intangible cultural treasure of Vietnam is rich and diverse in the forms of written language culture and the forms of modern art, fine arts, theater, cinema, and other forms of cultural expression of contemporary life. The presence of folk cultural heritage alongside the official, written cultural heritage and especially the flourishing of the contemporary intangible cultural treasure has made the diverse culture in the multi-ethnic community of Vietnam even richer and more prosperous, contributing to the world's cultural treasure with values that both bear the cultural identity of the nation and ethnic groups, and are in harmony with the common cultural values of the international community in the context of exchange and integration.
In a broad sense, Vietnamese intangible culture is a diverse and rich part of the ethnic groups and peoples that have entered the process of exchange and integration very early. Right from the initial prehistoric stage of the formation of the Van Lang state in the Hung Kings' era, through relics found underground and comparing the existence of lifestyles, customs, practices, beliefs and local knowledge, archaeologists have affirmed that the Viet Muong culture from about three or four thousand years ago had exchange, integration, and even spread to regions and areas south of the Yangtze River of the Bai Viet or entered some countries in southern Southeast Asia. In the years before and after the Common Era, the exchange and cultural integration between the residents of the Au Lac land and foreign countries became more evident. First of all, it was the introduction of Buddhist culture from India by sea into Giao Chau (present-day North), which was the introduction through China before entering Vietnam, along with the introduction of Taoism with new and attractive forms and conditions for integration with indigenous intangible culture, especially religious practices in regions. Although it was influenced by foreign cultures, with the existence of "strongholds" of village culture and ethnic cultures..., our country's culture still stood firm, was preserved, created, transmitted, and continued through generations. Until the end of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century, the intangible cultural heritage of Vietnamese ethnic groups continued to adapt and receive positive features from Western culture with the presence of writing, newspapers, urban lifestyle and other cultural products of the industrialization process. In the second half of the 20th century, there was the introduction and integration of Western culture (from American imperialism) and socialist culture (focusing on the culture of the Soviet Union and modern China).
In the past two decades or so, Vietnamese intangible culture has been integrating into the flow and gradually integrating deeply with human culture, creating momentum at all levels, degrees and scopes to gradually integrate deeply into world culture. Along with global economic relations, the expansion of cultural cooperation has also been developing deeply. A series of bilateral cultural weeks between countries with strategic partnerships or good friendship relations with Vietnam have been organized. Many agreements on cultural and tourism development between Vietnam and other countries have been signed, the effectiveness of which is reflected in the number of Vietnamese tourists traveling to other countries and vice versa. Many international scientific conferences on Vietnamese cultural heritage have been organized in the country and in some countries. Many intangible cultural heritages of many ethnic groups in Vietnam have been listed in the List of Cultural Heritage of Humanity by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
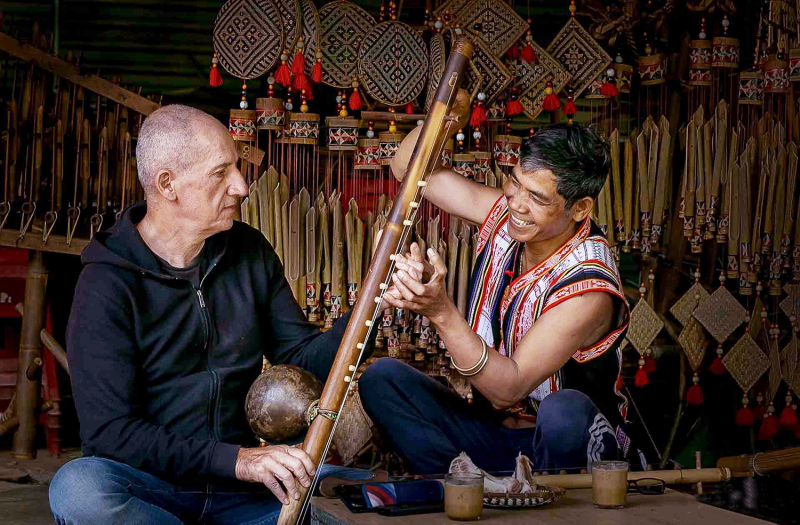
Tourists learn to play musical instruments of ethnic minorities in the Central Highlands_Source: nhiepanhdoisong.vn
In the context of cultural exchange and integration, Vietnamese intangible culture has been and is an important resource and energy playing a leading role in the strategy of developing the domestic cultural industry, creating soft power to attract and promote tourism development in almost all provinces and cities. It can be said that in the history of the nation, Vietnamese culture has never had the opportunity to absorb the quintessence of many cultures like today, and never before has the Vietnamese cultural environment been affected by so many negative factors like today. Therefore, it is not by chance that when recalling the existence of the system of tangible and intangible cultural heritage of the multi-ethnic Vietnamese national community at the National Cultural Conference to implement the Party's 13th Resolution on the cultural field held in Hanoi in November 2021, General Secretary Nguyen Phu Trong emphasized: "Vietnam is a country with more than 4,000 years of history, having undergone countless changes and ups and downs caused by nature and humans, it has accumulated, created and promoted many values and cultural identities of the nation, forming the soul of the nation; at the same time absorbing and contributing to the common culture of humanity" (2) ; and requiring everyone who wants to move towards a cultured nation to focus on building a healthy culture of behavior in society, promoting positive values of traditions and customs; upholding the spirit of mutual love, solidarity; respecting sentiment, justice and social morality, and paying more attention to preserving, embellishing and promoting national cultural values, tangible and intangible cultural values of regions, areas, and ethnic minorities, combined with absorbing the cultural quintessence of the times; building and developing the "soft power" of Vietnamese culture, contributing to enhancing the overall national strength./.
Professor, Dr. BUI QUANG THANH
Vietnam National Institute of Culture and Arts Studies
16:34, April 14, 2024
Source





































































































Comment (0)