After storms and floods, the humid environment creates favorable conditions for mosquitoes to develop. People need to equip themselves with knowledge to prevent mosquito-borne diseases.
Mosquitoes are vectors of dangerous diseases.
Dengue fever
The vector of dengue fever is the female Aedes mosquito carrying the virus. The virus has four different serotypes: DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3 and DEN-4. Patients infected with a particular strain of the virus will only develop lifelong immunity to that strain. Therefore, people living in areas where dengue fever is endemic can contract dengue fever more than once in their lifetime.
When infected, the patient has symptoms: Headache, loss of appetite, burning eyes, sudden fever and rash in the upper and lower limbs, pain in the right hypochondrium, more severe symptoms include: subcutaneous hemorrhage, bleeding gums.
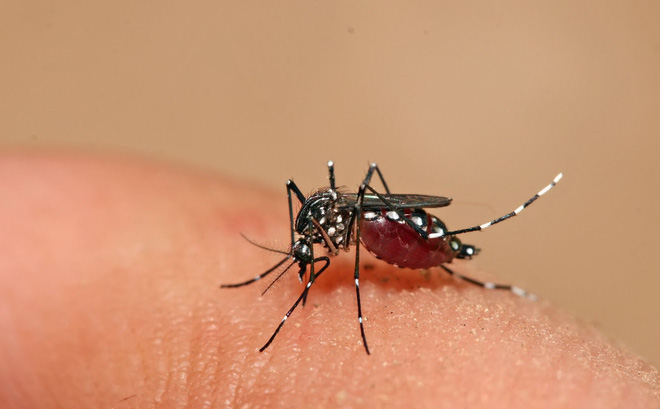

Mosquitoes are vectors of dangerous diseases.
Japanese encephalitis is caused by the Culex tritaeniorhynchus mosquito carrying the virus. The disease was first discovered in Japan, Japanese scientists isolated the virus in 1935, so the disease was named Japanese encephalitis.
Japanese encephalitis virus belongs to the Arbovirus group, Togaviridae family, Flavivirus genus, transmitted by Culex mosquitoes. This virus belongs to the flavivirus family related to dengue fever, yellow fever and West Nile virus infection, spread by mosquito bites.
When infected with Japanese encephalitis, the patient has symptoms of high fever, headache in the forehead, convulsions, coma and severe headache. The patient has meningitis syndrome and mild disturbance of consciousness.
Malaria
Malaria is caused by a parasite carried by mosquitoes called Anopheles. When causing the disease, there will be different symptoms and complications and require separate treatment methods.
The cause of malaria is the malaria parasite scientifically known as Plasmodium, mainly transmitted through the Anopheles mosquito with typical symptoms such as fever (cyclical), chills, sweating, anemia... Malaria occurs frequently all year round, but the disease will break out during the rainy season in mountainous areas...
When sick, the patient has chills, vomiting, fever, sweating, fainting and dry cough...
Diagnosis of mosquito-borne diseases
Depending on the symptoms, doctors will order tests. If dengue fever is suspected, antigen and antibody tests will be performed to diagnose the disease.
If Japanese encephalitis is suspected, a test for JEV-specific IgM antibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid will be performed.
If malaria is suspected, a blood smear will be examined under a microscope for malaria parasites.
How to prevent mosquito-borne diseases
Prevention of Dengue Fever
The Ministry of Health recommends the following:
- Check, detect and destroy mosquito larvae in domestic water containers by regularly washing, covering tanks and water containers tightly, and releasing fish to destroy mosquito larvae.
- Regularly change the water in vases, add salt or mosquito larvae killer chemicals to bowls of water placed under cupboards, aquariums, rockeries...
- Remove waste materials, natural water holes, and turn over unused water containers to prevent mosquitoes from laying eggs.
- Sleep under mosquito nets to prevent mosquito bites even during the day, wear long-sleeved clothes, use mosquito spray, mosquito coils, mosquito repellent cream, electric mosquito racket... to kill mosquitoes and prevent mosquito bites.
- Actively coordinate with the health sector in mosquito larvae eradication campaigns and chemical spraying campaigns to prevent and control epidemics.
- If you have a fever, go to a medical facility immediately for examination and treatment advice. Do not self-treat at home.
Prevention of Japanese encephalitis

Practice good environmental hygiene and keep your home clean to prevent disease.
- Practice good environmental hygiene, keep houses and livestock pens clean to limit habitats for grass mosquitoes. Move livestock pens away from the house and eliminate mosquito larvae nests.
- When sleeping, use mosquito nets, regularly use mosquito repellents in households, and do not let children play near livestock pens to prevent mosquito bites.
- Getting vaccinated against Japanese encephalitis fully and on schedule is the most important and effective way to prevent the disease. Note that only one dose of vaccine is not enough to protect, two doses of vaccine provide over 80% protection, three doses provide 90% - 95% protection for about 3 years.
Malaria prevention
To prevent malaria, patients need to sleep under mosquito nets whether at home, in the fields or in the forest. Preventing disease-carrying mosquitoes is still considered the most effective measure, specifically:
- Kill mosquitoes by spraying residual chemicals on the inside of walls and impregnating mosquito nets with mosquito repellent chemicals once a year before the rainy season.
- Apply mosquito repellent.
- Clear bushes, unclog drains around the house, build houses far from forests and water sources, wear long clothes at night.
- Limit mosquito larvae: clear the flow, remove algae to clear the water surface;
- Taking preventive medication: countries with high malaria prevalence have a policy of taking preventive medication for people entering malaria areas for a short time, pregnant women in malaria areas, and people newly settling in malaria areas.
In our country today, because malaria has decreased significantly, we do not take preventive medicine but only provide medicine for the above subjects to self-treat when they have malaria; Safe blood transfusion, especially for people with a history of malaria or who have lived in a malaria area.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/3-benh-do-muoi-truyen-can-chu-dong-phong-chong-sau-mua-bao-172240916233402312.htm



























































































Comment (0)