Otitis media is a disease caused by infection or bacteria in the ear. This is a common and recurring disease in young children, causing many parents to worry.
Causes of otitis media
Otitis media is divided into two main types, including acute otitis media and chronic otitis media.
- Acute otitis media is inflammation of the middle ear mucosa or a complication of impaired eustachian tube function due to a virus causing an upper respiratory tract infection.
- Chronic otitis media is a persistent infection that causes damage and may drain fluid through a hole in the eardrum.
Otitis media with effusion is a form of otitis media with effusion, often without obvious signs, fluid accumulates in the eardrum, creating a feeling of fullness in the ear. The patient may feel tension or pressure in the ear and have general health symptoms such as fever, earache, and ear discharge.
The cause of otitis media is usually an infection caused by viruses, bacteria or other diseases such as flu, colds, allergies. In children, otitis media can be due to the incomplete development of the structure and function of the Eustachian tube, as well as a weak immune system.
In addition, otitis media can be caused by adenoids, because the swollen adenoids will affect and block the Eustachian tube, causing infection. This phenomenon occurs more often in children than in adults.
Symptoms of otitis media
Otitis media in children is often accompanied by symptoms including:
- Earache, hearing loss, discomfort in the ear.
- Anorexia, difficulty sleeping, crying, vomiting in children.
- Hearing loss, poor response to sound.
- High fever up to 39 - 40 degrees Celsius, can cause convulsions.
- Loose stools, frequent bowel movements, digestive disorders.
Signs of otitis media in adults include:
- There is fluid coming out of the ear.
- Hard of hearing.
- Earache.
To diagnose otitis media, patients should go to medical facilities to be examined by doctors using endoscopy to detect any lesions in the ear. The doctor will also use an otoscope to check the eardrum and other areas such as the palate, sinuses, and throat. If the eardrum contains fluid or is inflamed, swollen, and congested, the middle ear is likely infected.
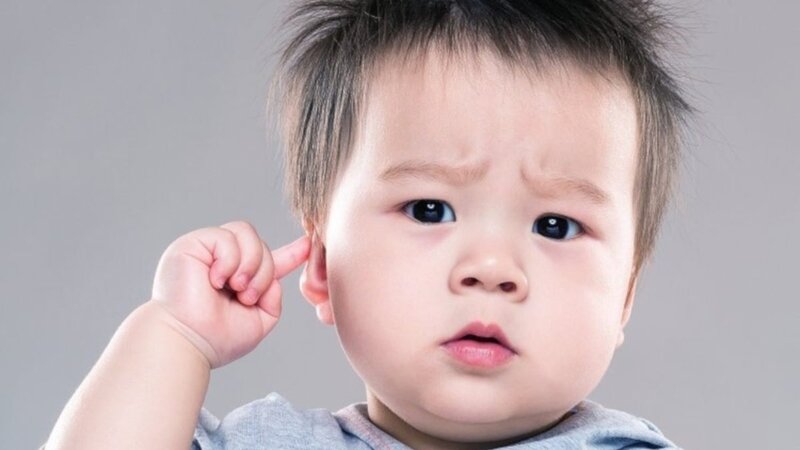

Otitis media can occur at any age, but is most common in children. Illustration photo.
Treatment of otitis media
Treatment of otitis media depends on the individual and the severity. Treatments prescribed by the doctor include the use of antibiotics, antihistamines, nasal drops, nasal sprays, eustachian tube insufflation, corticosteroids and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The use of antibiotics in the treatment of otitis media depends on the stage and cause of the disease. There are cases where antibiotics are used from the beginning. In cases where the patient does not need antibiotics, treatment will focus on symptoms and follow up after 48 - 72 hours to re-evaluate. If the disease progresses unfavorably, the patient can use antibiotics.
Patients should use saline, antiseptic solution and ear drops as directed by the doctor if the eardrum is perforated.
Adenoidectomy, tonsillectomy and ventilation tube placement are some of the surgical treatments that may be prescribed by your doctor in cases where the infection is widespread and medical treatment is no longer effective.
Additionally, with chronic otitis media, a CT scan or MRI may be recommended if there are signs of cholesteatoma and other complications including fever, dizziness, and ear pain. If there is recurrent or persistent granulation tissue, an ear biopsy may be required.
Medical advice
Otitis media can occur at any age, but is most common in children, because the ear structure of children is not fully developed, weak immunity. According to statistics, more than 80% of children have had at least one episode of otitis media by the age of 3. Although the subject of otitis media is mainly children, this disease can also appear in adults.
Therefore, to effectively prevent otitis media, each age group has different notes:
- For adults
Keep your ears clean by cleaning them regularly, being careful to do it gently, avoiding strong movements that can damage the ear mucosa, allowing bacteria to easily enter and cause ear infections. Avoid getting water in your ears (when bathing, washing your hair or swimming). If you have ear, nose or throat diseases, you need to treat them early.
- For children
Clean your hands and vaccinate your children with the right doses and at the right time as recommended by the health sector. Breastfeed your children until they are 2 years old, because breast milk helps strengthen their immune system. In addition, avoid exposing your children to smoke, dust, and tobacco. When your child shows signs of ear, nose, and throat diseases, they need to be treated immediately to avoid the condition progressing to otitis media.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/cach-dieu-tri-viem-tai-giua-can-biet-172241101213853459.htm




![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man holds talks with Speaker of the Malaysian House of Representatives](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/19/5cb954e3276c4c1587968acb4999262e)
![[Photo] Spreading Vietnamese culture to Russian children](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/19/0c3a3a23fc544b9c9b67f4e243f1e165)
![[Photo] Sea turtle midwives](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/19/9547200fdcea40bca323e59652c1d07e)
























































































Comment (0)