Gout is a joint disease caused by a disorder of purine metabolism, leading to increased uric acid in the blood. When uric acid in the blood increases to a certain level (this level varies from individual to individual), it will be saturated in the extracellular fluid, leading to deposition in tissues, joints, and kidneys, causing clinical symptoms of gout.
The disease is common in middle-aged men, especially in those who are obese, drink alcohol, and eat a high-protein diet.
Diet is very important for people with gout because this is one of the causes of increased uric acid levels in the blood. Therefore, even during Tet, patients still need to follow a healthy, balanced diet.

Dr. Truong Hong Son, Director of the Vietnam Institute of Applied Medicine, said that people with gout need to limit foods such as:
- Animal organs (heart, liver, kidney, spleen, intestines, lungs): These foods have quite high levels of cholesterol and purines, so they can cause acute gout attacks at any time.
- Red meats (beef, horse meat, buffalo meat, goat meat): They contain high amounts of protein, so when patients eat a lot, it will lead to excess protein, producing and increasing uric acid in the blood, causing gout attacks.
- Seafood (crab, oysters, clams, shrimp, mussels, herring, tuna): They are rich in protein and fat, making gout more painful and severe.
- Nem chua: This is a very attractive snack during Tet, but the sour taste in nem is produced from rice bran and pork, which can also increase uric acid in the blood.
- Some vegetables (asparagus, bamboo shoots, mushrooms, bean sprouts, beans, elephant foot yam, spinach, cauliflower) also contain a lot of purines.
- Foods rich in fat (fat, animal skin, fried foods) and foods processed with fat (instant noodles, fast food).
- Banh chung, pickled onions, and braised meat: While banh chung increases inflammation, braised meat contains a lot of fat and pickled onions have a high salt content. These three foods are not good for people with gout.
- Wine, beer, carbonated drinks, and candy contain a lot of sugar.
Foods that people with gout should eat
- Some foods have low purine content such as: River fish (carp, tilapia), freshwater fish (perch), white meat (chicken breast) have low purine content, patients can still use them to provide necessary protein for the body.
- Prioritize green vegetables and fruits rich in fiber: Green mustard greens, celery, spinach, Malabar spinach, betel leaves, watercress, carrots, gac fruit, tomatoes, pumpkins, cucumbers, tomatoes and fruits such as watermelon, grapes, apples, pears, ripe papaya are low in purines and rich in vitamins C and E, very good for gout patients.
- Increase your intake of eggs and milk because these foods do not contain purines and are not harmful to people with gout.
- Drink at least 2 liters of water per day: Water helps excrete uric acid through urine and limits urate crystallization in tissues.
Risk factors that may increase your risk of hyperuricemia and gout include:
- Age
Gout is more common in older adults and rarely affects children.
- Gender
In people under 65 years of age, gout is four times more common in men than in women.
- Genetics
A family history of gout may increase a person's chances of developing the condition.
- Lifestyle choices
Drinking alcohol interferes with the removal of uric acid from the body. Eating a diet high in purines also increases the amount of uric acid in the body. Both of these can lead to gout.
- Medicine
Certain medications can increase uric acid levels in the body, such as some diuretics and medications containing salicylates.
- Weight
Being overweight, obese, and having high levels of visceral fat are associated with an increased risk of gout. However, being overweight or obese cannot directly cause the condition.
- Other health conditions
Kidney failure and other kidney conditions can reduce the body's ability to remove waste, leading to high uric acid levels. Other conditions associated with gout include high blood pressure and diabetes.
Symptoms of gout:
- Acute arthritis: Swelling and pain in the joints, especially the metatarsal joints and big toe.
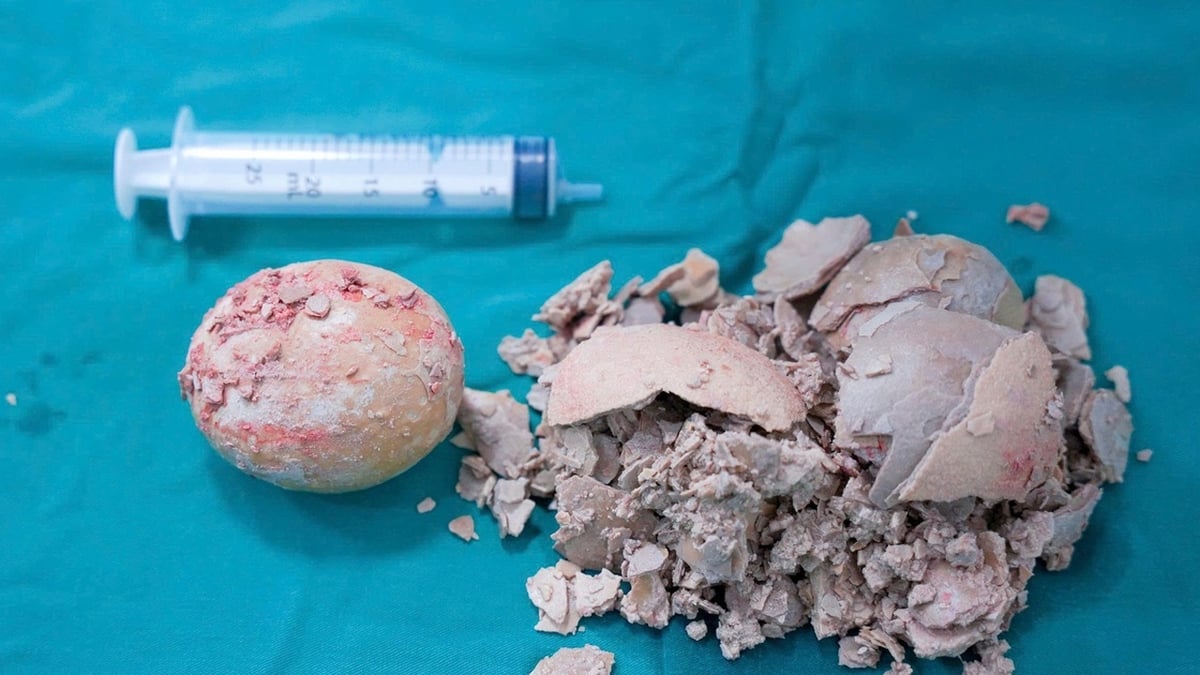
- Urate deposits: This is the case of mobile urate lumps or grains under the skin below the earlobe, elbow tip, patella or near the Achilles tendon.
- Urate stones, uric acid in the renal - urinary system, interstitial nephritis, renal failure.
- Blood test shows high uric acid.
Source link


















































![[Maritime News] More than 80% of global container shipping capacity is in the hands of MSC and major shipping alliances](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/16/6b4d586c984b4cbf8c5680352b9eaeb0)












































Comment (0)