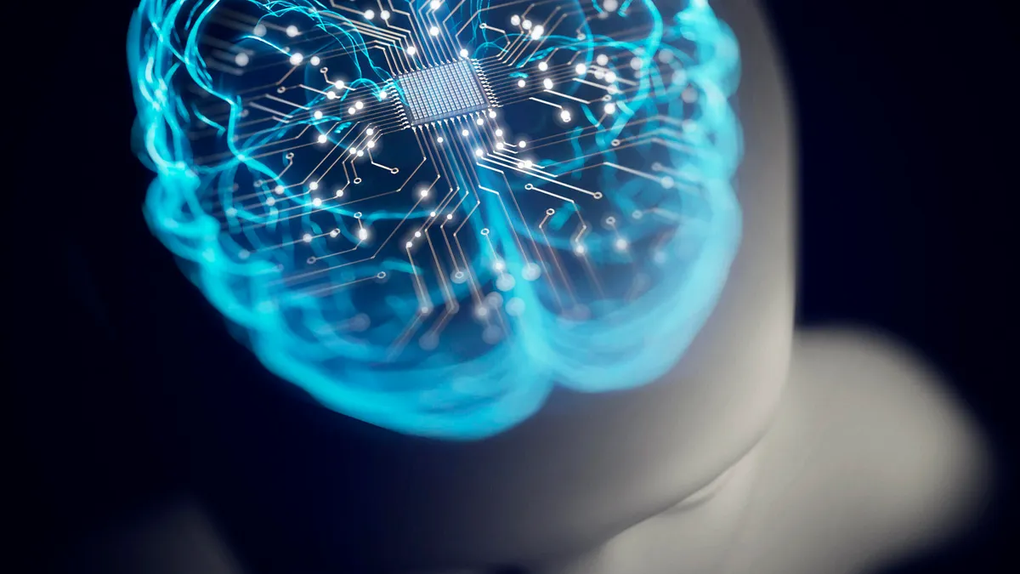

Frequent use of ChatGPT may be associated with lower levels of brain activity in users (Illustrative image: ST).
Dr. Nataliya Kosmyna, head of the research team at the Media Lab (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), wanted to understand the impact of using AI in learning, as more and more students are using this tool.
The research team created an experiment in which participants wrote an essay in 20 minutes on an SAT-style (Scholastic Assessment Test) prompt, with topics such as philanthropic ethics or the consequences of too many choices.
54 people (aged 18-39) were divided into three groups: one group used ChatGPT, one group used Google search, and the remaining group did not use any tools.
Researchers used electroencephalography (EEG) to record brain activity in 32 different regions of the study participants throughout the essay writing process.
The results showed that, compared to the other two groups, the group using ChatGPT had the lowest levels of brain activity and consistently performed poorly in neurological, linguistic, and behavioral aspects.
Over the course of the study, the level of effort put in by the ChatGPT users gradually decreased with each essay, as they typically only performed copy and paste operations.
The essays were incredibly similar, lacking independent ideas and repeating similar expressions and arguments.
By the third essay, many people simply input the prompt into ChatGPT and let the tool do almost all the work.
Conversely, the group that only used brain-based thinking showed the highest levels of neural connectivity, particularly in the alpha, theta, and delta wavelengths—associated with creativity, memory, and word processing.
This group was judged to be more actively involved, demonstrating a greater sense of ownership over their writing and greater satisfaction with their results.
The final group, using Google search, also showed a high level of satisfaction with the essay and active brain activity.
This is a notable difference in the context of an increasing number of people tending to search for information through AI chatbots instead of traditional search engines like Google.
After the three groups completed their essays, the research team asked them to rewrite one of the previous essays.
This time, the team that had used ChatGPT had to redo the task without the tool's assistance, while the team that "used their brains" was allowed to use ChatGPT.
The results showed that the first group could barely remember the content of their own essays and had weaker alpha and theta brainwaves, reflecting poorer deep memory retention.
Conversely, the second group showed positive results, significantly increasing brain connectivity across all EEG frequency bands.
As of July, ChatGPT was processing over 2.5 billion queries per day, reflecting its growing popularity and the changing way people interact with technology.
If used correctly, AI chatbots can support and enhance learning rather than hinder it.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/khoa-hoc/quet-nao-nguoi-dung-chat-gpt-phat-hien-dieu-khong-ai-ngo-toi-20250804124522554.htm


































![[Image] Vietnam's colorful journey of innovation](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F14%2F1765703036409_image-1.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)



































































Comment (0)