Neck and back pain are very common and can have many causes. In some cases, your doctor will prescribe muscle relaxants to treat the condition.
Stiffness and pain in the neck and back can cause insomnia and affect the quality of life of the sufferer. In some cases, muscle relaxants can help relieve the pain.
Muscle relaxants work by reducing muscle tension in a variety of ways, including acting on muscles, nerves, or the central nervous system, helping to relieve neck and back pain.
Some of the best muscle relaxants for neck pain and back pain
There are many types of muscle relaxants on the market, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The doctor can choose the right medicine for the individual patient:
- Muscle relaxant methocarbamol
Methocarbamol is generally a well-tolerated option for people with new neck and back pain. It works by blocking nerve impulses (or pain sensations) sent to the brain, providing pain relief. Methocarbamol is used in combination with rest and physical therapy to treat painful musculoskeletal conditions or injuries.
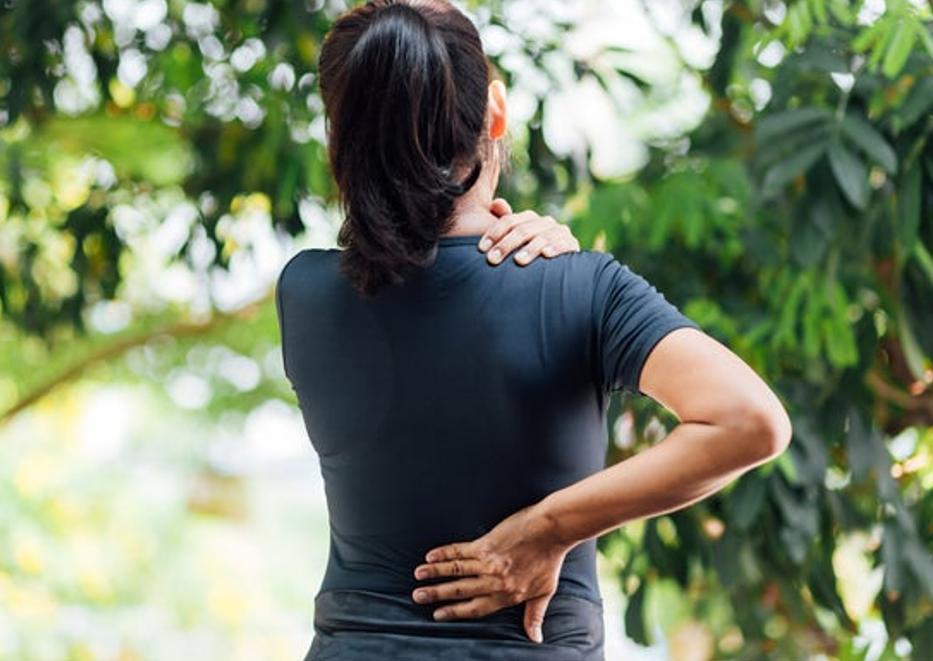

Neck and back pain have many causes, and in some cases muscle relaxants may be used.
Common side effects of methocarbamol may include:
- Headache, dizziness, drowsiness;
- Confusion, memory problems;
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain;
- Blurred vision, double vision;
- Sleep problems (insomnia);
- Lack of coordination…
- Muscle relaxant cyclobenzaprine
Cyclobenzaprine works in a similar way to methocarbamol and is used along with rest and physical therapy to relieve muscle pain. Cyclobenzaprine is more likely to cause drowsiness as a side effect, which is a concern when used during the day (it may be best to choose a non-sedating daytime medication).
Cyclobenzaprine can also cause dry mouth (especially in older adults), headache, dizziness, constipation…
- Muscle relaxant carisoprodol
Carisoprodol is used in conjunction with rest and physical therapy to temporarily relieve muscle pain. However, it is classified as a drug with a potential for abuse. It should not be used by patients with a history of substance abuse. When prescribed, it should only be used for a short period of time (2-3 weeks).
Carisoprodol can also cause drowsiness and dizziness, so it is not a good choice for people over 65. Because of the potential side effects, carisoprodol should not be used as a first-line treatment and may be replaced with better alternatives.
- Muscle relaxant metaxalone
Metaxalone works by slowing down activity in the nervous system to allow the body to relax; it is used in combination with rest, physical therapy, and other measures to relax muscles and relieve pain and discomfort caused by strains, sprains, or other muscle injuries.
This muscle relaxant has the fewest reported side effects and is less sedative. However, it works better for recurrent chronic low back pain than for new pain.
There are many types of muscle relaxants, and your doctor can choose the right one for your individual needs.
2. Notes when using muscle relaxants
Muscle relaxants can cause some side effects, users should read the instructions carefully before use. If side effects occur, notify the doctor for appropriate and timely treatment. Muscle relaxants often cause drowsiness, patients may need to avoid activities that require alertness while using these drugs.
The issue of interactions with other drugs and substances that the patient is using also needs attention and this is why muscle relaxants need to be prescribed by a doctor after examining the patient.
Common medications that may interact with muscle relaxants include:
- Drugs with sedative effects (drowsiness): Many muscle relaxants have sedative effects, slowing down brain activity. People who are taking drugs that affect the brain such as (zolpidem, gabapentin, opioid pain relievers, etc.) will have a higher risk of experiencing these side effects.
- Antidepressants: Some muscle relaxants can also affect serotonin levels in the brain - a hormone that affects mood. If you are taking mood-stabilizing drugs, muscle relaxants can cause serotonin levels to rise too much. Some antidepressants can interact with muscle relaxants such as amitriptyline, venlafaxine, sertraline, fluoxetine...
- Anticholinergics: Anticholinergics are commonly used to treat a variety of conditions from overactive bladder (overactive bladder) to digestive conditions and movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease. These drugs can cause difficulty urinating, constipation or dry mouth… if taken with muscle relaxants, these side effects will be more severe.
Some anticholinergic drugs such as: Diphenhydramine (treats allergies), hyoscyamine (treats stomach and intestinal diseases, irritable bowel syndrome), benztropine (treats Parkinson's, drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms), scopolamine (antispasmodic, used to reduce nausea, vomiting, dizziness due to motion sickness)...
Dr. Nguyen Phuong Thu
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/thuoc-gian-co-nao-tot-nhat-cho-chung-dau-co-va-dau-lung-172241125155048913.htm





![[Photo] Opening of the 14th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/05/1762310995216_a5-bnd-5742-5255-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Panorama of the Patriotic Emulation Congress of Nhan Dan Newspaper for the period 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762252775462_ndo_br_dhthiduayeuncbaond-6125-jpg.webp)




























































































Comment (0)