Cassava is an important food source in many parts of the world , including Africa, the Caribbean and is also quite familiar to Vietnamese people. This food contains resistant starch and many vitamins and minerals essential in the modern diet, such as potassium and vitamin C.
Cassava itself is not fattening, but like any food, its impact on weight depends on how much you eat and your overall diet. Read on to learn more about the benefits and how to use cassava properly to improve your health and your weight loss (if any).
Health benefits of cassava
One cup of cooked cassava can provide 10% of your daily potassium needs - a mineral essential for fluid balance, cell function and blood pressure regulation, maintaining heart and kidney health...
Cassava is also rich in vitamin C and folate. Vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant in the body, protecting cells from oxidative damage that can lead to disease.
Due to its cell-protective effects, consuming a diet rich in vitamin C may reduce the risk of certain health conditions, such as cancer.
Weight loss support
The health benefits of cassava do not stop there, cassava is also very good for intestinal health and supports weight loss because it contains resistant starch - a type of carbohydrate that resists digestion in the small intestine.

Resistant starch passes into the large intestine, where it is broken down or fermented by gut bacteria. This fermentation results in the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate.
SCFAs promote gut health in several ways. They act as a fuel source for the cells lining the large intestine, maintain the integrity of the intestinal mucosa, and regulate inflammation and mucus production.
Additionally, one cup of cooked cassava provides 3.04 grams of fiber, which can help support healthy bowel movements, increase feelings of fullness, and promote overall bowel health and function. Adding sources of resistant starch like cassava to your diet can be a great weight loss aid.
However, despite containing resistant starch, consuming too much cassava can still lead to weight gain, as cassava contains nearly twice as many calories as potatoes and is perhaps one of the most calorically dense of the tropical starchy roots and tubers.
100 grams of cooked cassava contains about 160 calories, Their caloric value comes mainly from sucrose which accounts for more than 69% of the total sugar content. Amylase (16–17%) is another major source of complex carbohydrates.
According to nutritionists, cassava should only be enjoyed in moderation, about 73–113 grams/day. This helps provide the necessary energy without exceeding daily calorie needs, thereby supporting weight maintenance and overall health.
When should I eat cassava?
Do not eat cassava when hungry, consuming cassava when hungry can cause digestive discomfort and affect blood sugar levels.
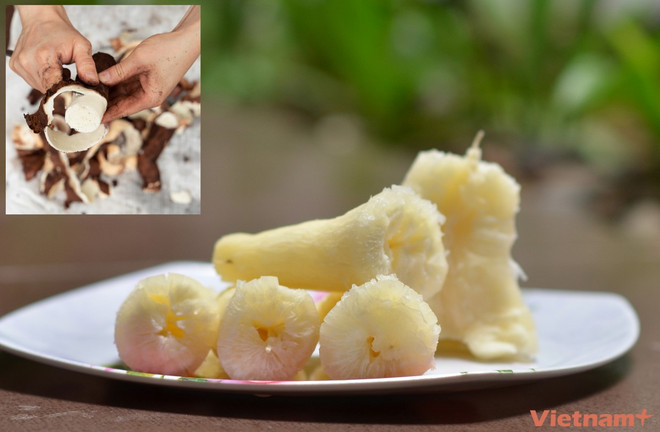

Avoid eating cassava early in the morning because at this time, the body needs energy quickly from more easily digestible food sources. Cassava contains complex starch, which takes time to digest, so it is not the optimal choice for breakfast.
You should also not eat cassava late at night because it can cause bloating and affect sleep quality.
The best time to eat cassava is about 1 hour after a main meal, helping the body absorb nutrients effectively and supporting the digestive system to function better.
In addition, cassava can be used as a snack between main meals to reduce hunger and provide fiber for the body.
Note that raw cassava contains compounds that can be converted into cyanide, which is harmful to the body. Therefore, it is necessary to peel, wash and cook thoroughly before eating to remove toxins./.
Source: https://www.vietnamplus.vn/vi-sao-cu-san-chua-tinh-bot-khang-nhung-van-de-gay-tang-can-post1019766.vnp
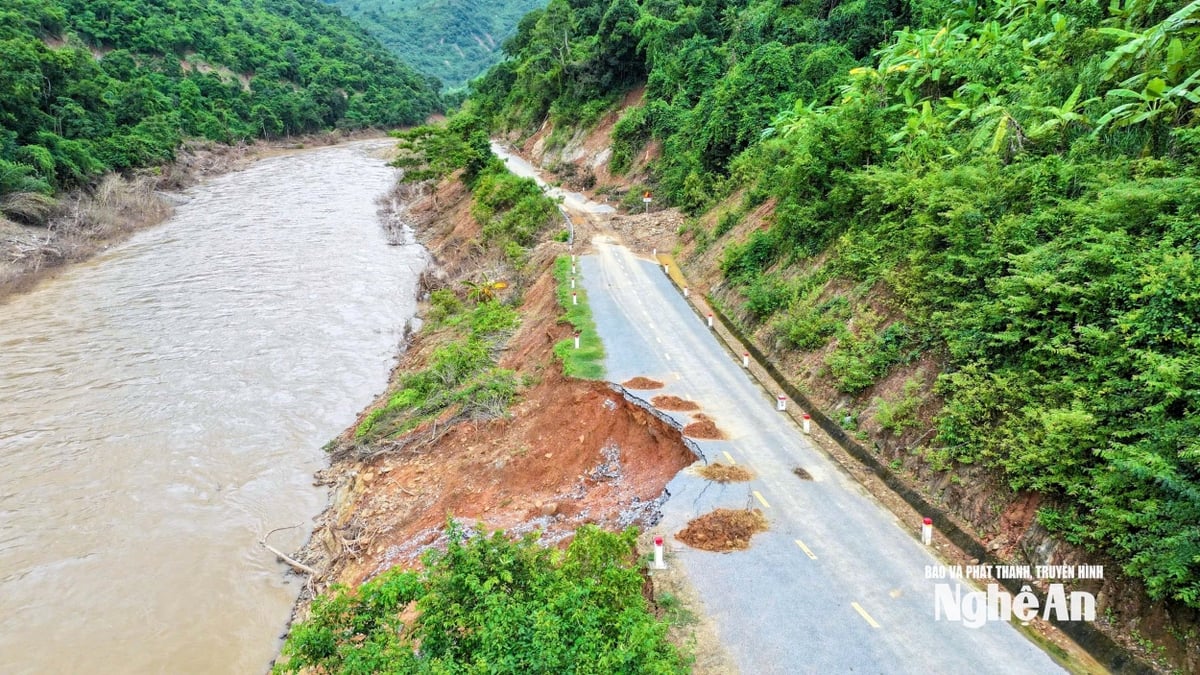























![[Photo] Nghe An: Provincial Road 543D seriously eroded due to floods](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/5/5759d3837c26428799f6d929fa274493)



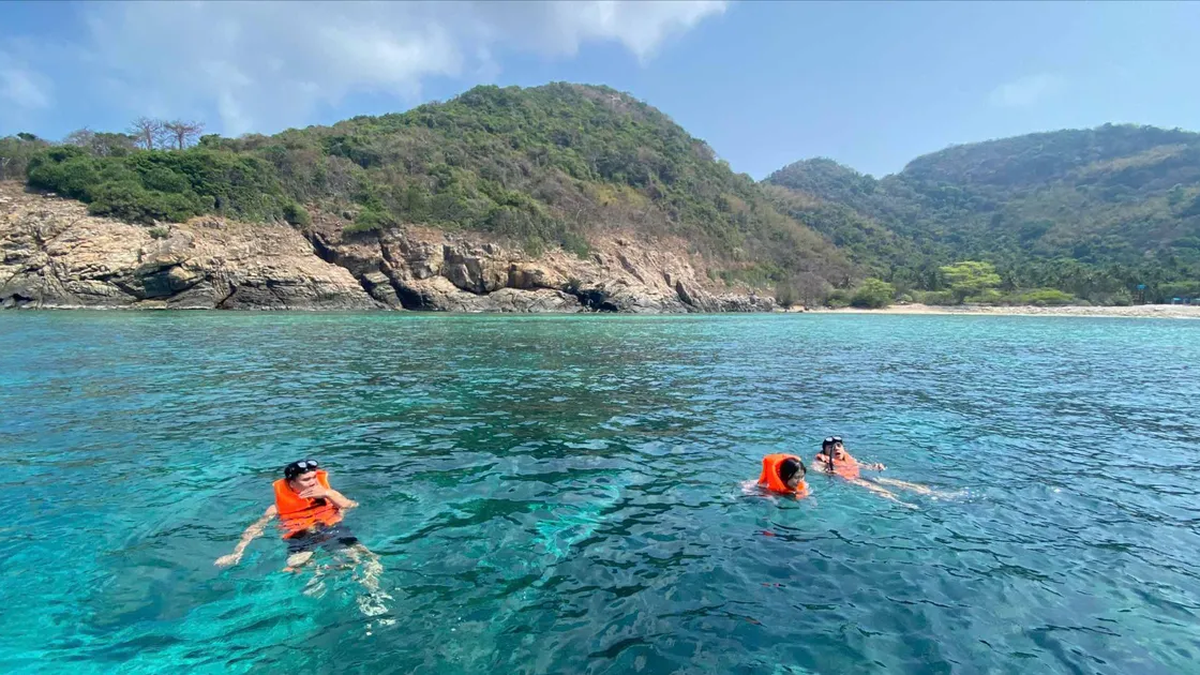
![[Photo] Discover the "wonder" under the sea of Gia Lai](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/6/befd4a58bb1245419e86ebe353525f97)



































































Comment (0)