Normally, the amount of uric acid in the blood is always kept stable at a concentration below 7.0 mg/dl (420 micromol/l) and is kept at a constant level due to the balance between the synthesis and excretion of this substance.
Any cause that disrupts the balance between these two processes of synthesis and excretion, such as increased uric acid synthesis or decreased uric acid excretion, increases uric acid in the blood. Hyperuricemia is considered when the amount of uric acid in the blood in men is above 7.0 mg/dl (or above 420 micromol/l), in women is above 6.0 mg/dl (360 micromol/l).
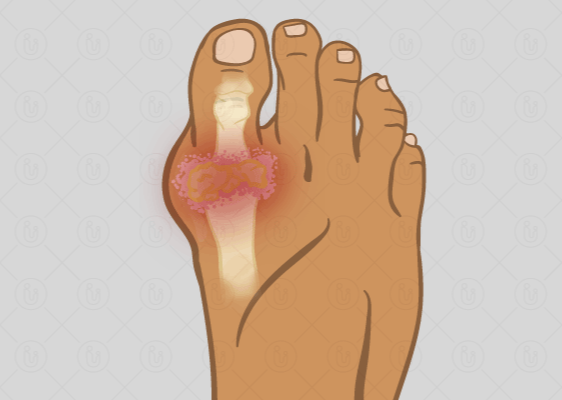
The gradual increase in uric acid levels in the blood in the body is associated with an unhealthy diet.
1. The importance of diet for people with hyperuricemia
Diet plays an important role for people with hyperuricemia. Adhering to a reasonable diet helps control uric acid levels in the blood, reduce the risk of acute gout attacks and prevent dangerous complications of the disease.
Limit the amount of purines in the body: Purines are compounds that, when metabolized, form uric acid. Some foods have high purine content such as: animal organs, red meat, seafood, beans, asparagus, etc. Limiting the consumption of these foods can help reduce the amount of purines in the body, thereby contributing to controlling uric acid levels in the blood.
Weight loss: Being overweight or obese is one of the high risk factors leading to increased uric acid in the blood. Reasonable weight loss helps to lower uric acid levels in the blood, reducing the risk of gout.
Reduce fructose intake: Fructose is a type of sugar found in fruits, soft drinks, canned fruit juices, etc. Fructose can increase uric acid production in the body. Therefore, people with hyperuricemia should limit their consumption of foods rich in fructose.
Drink plenty of water: Water helps to eliminate uric acid from the body through urine. Drinking enough water every day (about 2 liters) also helps to control uric acid levels in the blood.
Fiber supplements: Fiber can help reduce uric acid levels in the blood. Foods rich in fiber that are good for people with hyperuricemia include: green vegetables, fruits, whole grains,...
2. Vitamin supplements for people with hyperuricemia
Certain supplements for people with hyperuricemia can help ease gout symptoms and prevent flare-ups. People with gout are more likely to be deficient in both vitamin D and vitamin B12. Low levels of these and other nutrients may be due to dietary choices or health conditions commonly associated with gout.
Fish oil: A source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential polyunsaturated fats that are important for many different aspects of health. However, fish oil supplements alone have not been shown to reduce gout flare-ups, but there is benefit from consuming foods containing omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts, and certain vegetable oils.
Folic acid: A diet rich in folic acid (a B vitamin) may reduce uric acid levels and prevent gout. However, research on the direct effects of folic acid on gout is limited. Folate and folic acid are found in most plant foods such as spinach, beans, cereals, and avocados.
Vitamin C: Due to its antioxidant properties, vitamin C (found in bell peppers, citrus fruits, broccoli, strawberries, and many other foods) has been studied as a potential treatment option for gout.
Vitamin D: Vitamin D from foods or supplements is beneficial for preventing and controlling gout. Vitamin D is found in foods such as milk, some fish, mushrooms, and fortified foods.
Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 performs many important functions in the body. Vitamin B12 is found in many animal-based foods and fortified foods.
3. Vitamins to avoid when having hyperuricemia
Certain vitamins and other nutrients can make gout worse.
Niacin: Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is found in foods and supplements. This vitamin can increase uric acid levels and make gout worse.
Nicotinic acid: Nicotinic acid, a derivative of niacin, is also thought to increase uric acid levels and even cause gout.
Vitamin A: Although the evidence is uncertain, it is thought that vitamin A also affects uric acid levels or makes gout symptoms worse.
4. Foods to eat and avoid when having high uric acid in the blood
Foods to eat
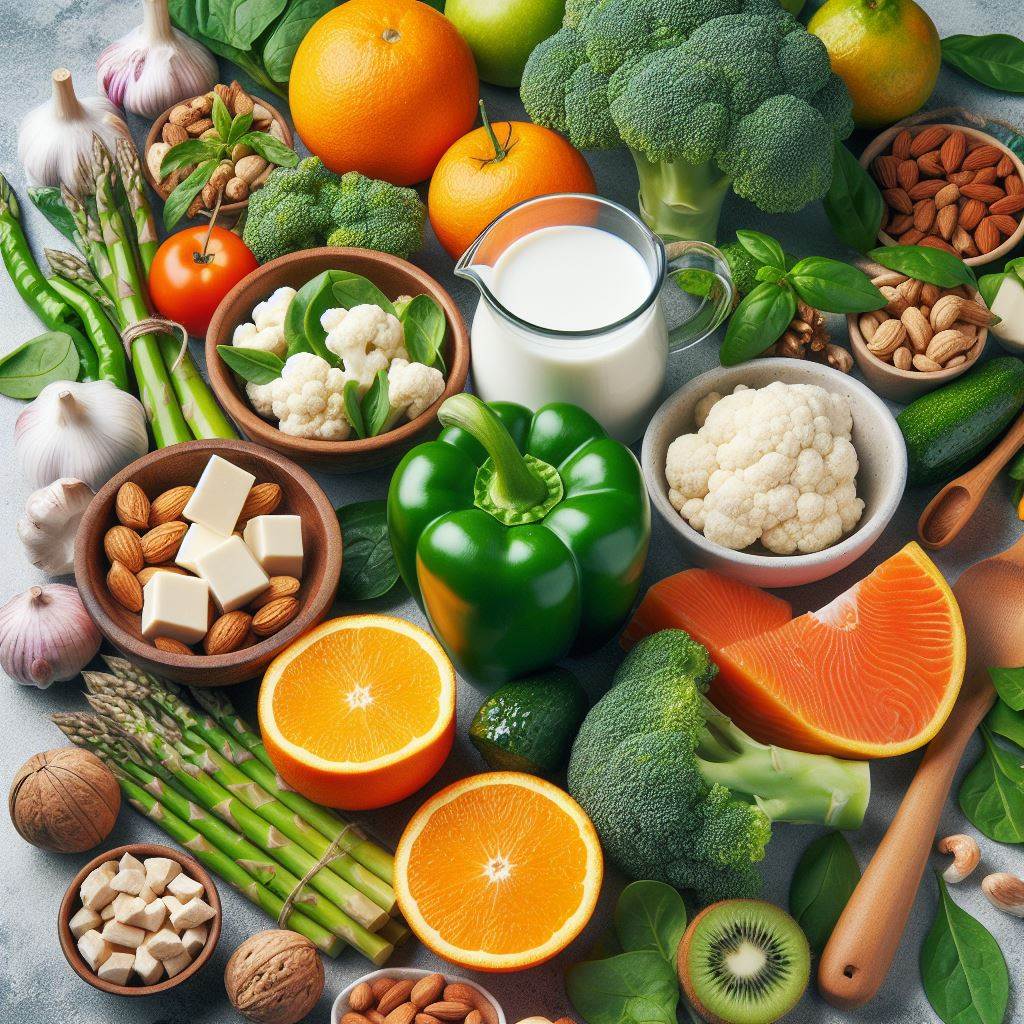

Foods that help control hyperuricemia.
Vegetables: Consuming purine-rich vegetables such as green peppers, asparagus, spinach, and cauliflower does not affect uric acid levels or increase the risk of gout attacks. In addition, eating vegetables helps achieve and maintain a healthy, reasonable weight. Provides the body with important vitamins and minerals.
Garlic and onions: Members of the allium family, they contain the antioxidant quercetin. According to the Arthritis Foundation, alliums also contain diallyl disulfide, which can reduce enzymes that damage cartilage. They also add flavor to dishes, making them easy to incorporate into your diet.
Dairy products: The protein in dairy products helps naturally reduce uric acid levels. Choosing low-fat products like skim milk or low-fat yogurt will also help maintain a healthy weight.
Tofu, whole grains, beans and lentils: Plant-based proteins will help maintain a balanced diet while managing the condition.
Citrus fruits: Choose fruits lower in fructose such as grapefruit, oranges or pineapple as this natural sugar can increase uric acid levels.
Cherries: Cherries, 100% tart cherry juice reduces serum uric acid levels and contributes to reducing the risk of flare-ups in gout patients.
Coffee: Drinking moderate amounts of coffee does not appear to increase uric acid levels and may reduce the risk of developing gout.
Green tea: A component of green tea called epigallocatechin-3-gallate helps reduce inflammation.
Avocados: Avocados are naturally low in purines and contain monounsaturated fats and vitamin E. These components have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can help reduce pain and inflammation. Diets high in these compounds have also been linked to a reduced risk of joint damage.
Oily fish: Oily or fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, mackerel, herring… as part of a regular diet, the fatty acids in these fish also help reduce overall inflammation.
Foods to avoid
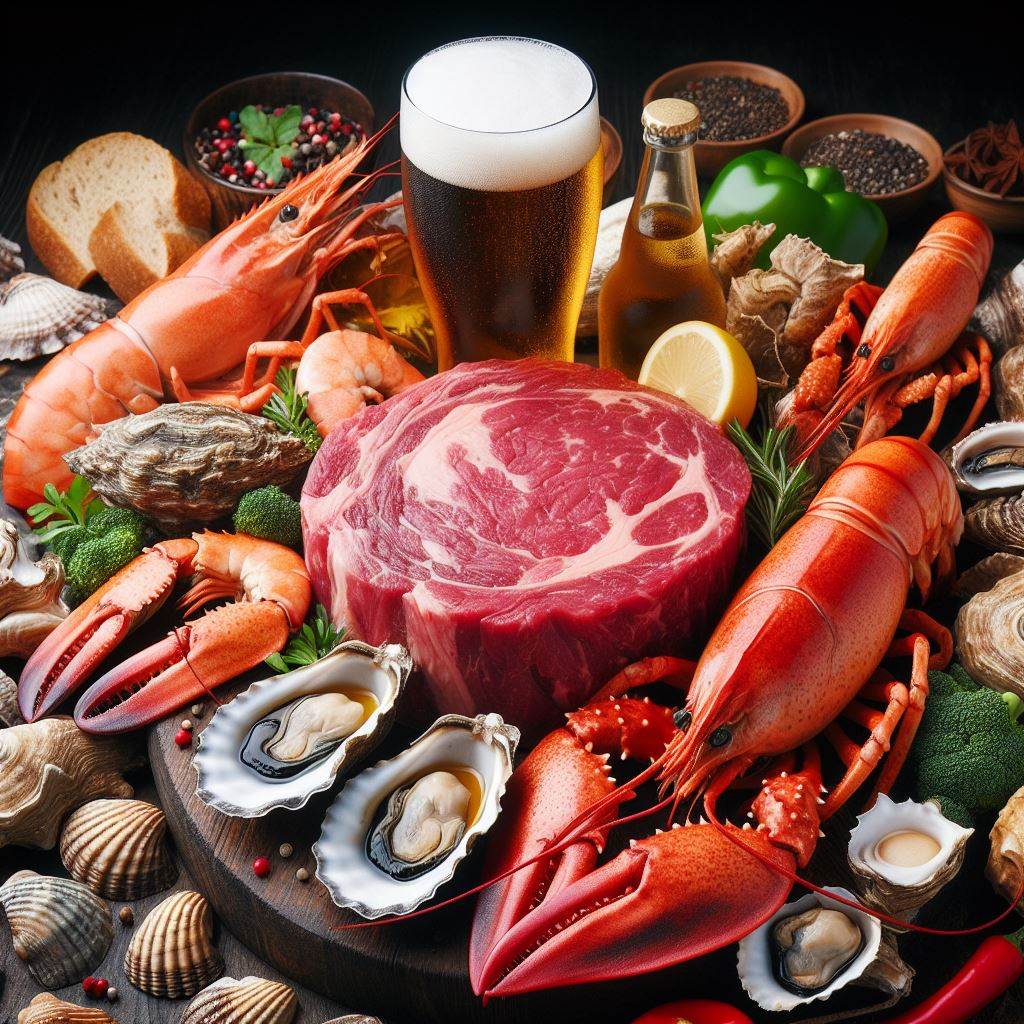

People with hyperuricemia should avoid foods such as red meat, offal, seafood, beer, alcohol, sugary drinks...
Red meat and organ meats: Red meats are higher in purines than white meats. Consuming a lot of red meat (such as beef, venison); organ meats (liver, tongue, testicles) increases the risk of gout attacks.
Shellfish: Some animals have higher purine content and should be limited, such as shrimp, oysters, crabs, etc.
Alcohol: Most alcoholic beverages are not recommended in the diet of people with hyperuricemia or gout. Beer and wine slow down the excretion of uric acid. However, drinking a little wine is not associated with a higher incidence of gout.
Sugary foods and drinks: Avoid foods and drinks that contain fructose — especially those containing high-fructose corn syrup. Keep uric acid levels low by limiting or avoiding your intake of soft drinks and other sugary drinks, canned fruit or fruit juice, high-sugar products such as donuts, cakes, candy, and some breakfast cereals.
Refined Carbs: Carbs are digested and absorbed quickly, which can increase blood sugar levels, which can increase uric acid levels. Stay away from refined carbs like white bread, white rice, cookies, and cakes. Although honey is a natural sweetener, it is high in fructose. When the body breaks down fructose, it releases purines.
In addition, people with hyperuricemia should also note:
- Divide meals into several small meals during the day.
- You should consult your doctor or nutritionist to develop a diet suitable for your health condition.
- By following a proper diet and combining it with taking medication as prescribed by your doctor, people with gout can increase their chances of controlling their disease well and improving their quality of life.
Dr. Vu Hoang
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/che-do-an-cho-nguoi-bi-tang-acid-uric-mau-172240524091549029.htm




























































































![[Infographic] In 2025, 47 products will achieve national OCOP](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/16/5d672398b0744db3ab920e05db8e5b7d)





Comment (0)