Bananas - the number 1 candidate for supporting good intestinal health
Bananas contain many nutrients that are good for the intestines, such as:
Rich in fiber : Both soluble and insoluble fiber in bananas help promote elimination, soften stools, and make bowel movements easier. A small ripe banana contains about 2 grams of fiber, while a medium ripe banana can contain about 4.5 grams of fiber, according to Verywell Health (USA).
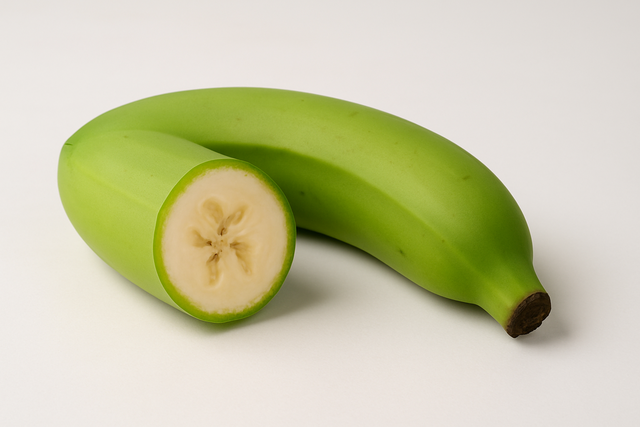

Green bananas contain up to 21g of resistant starch, suitable for people who need to control blood sugar.
Photo: AI
Contains prebiotics : Prebiotics support the digestive system, improve mineral absorption and regulate blood sugar. Supplementing about 5g of prebiotics per day can help improve gut health.
Source of resistant starch : Green bananas are a rich source of resistant starch, which cannot be broken down by the digestive system. Instead, resistant starch is fermented in the colon, helping to feed beneficial bacteria. They also play a role in preventing diseases and cancers related to the digestive system.
In particular, bananas help stimulate mucus production from the stomach lining, creating a protective barrier against acids that cause reflux and nausea. Eating bananas when you feel nauseous is also a way to provide essential vitamins and minerals without causing stomach upset.
Choose bananas according to the ripeness suitable for your physical condition.
Unripe bananas are high in resistant starch and low in sugar, so they are often more suitable for people who need to control their blood sugar levels.
In contrast, fully ripe bananas (brown skin) are soft and slightly crumbly. Ripe bananas are also sweeter and contain less starch than their unripe counterparts.
According to one report, a small unripe banana can contain up to 21 grams of resistant starch, while a fully ripe banana contains only about 1 gram.
Who should limit eating bananas?
Some of the following people may be sensitive to certain ingredients in bananas:
People with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Ripe bananas contain a lot of oligofructan fiber, which can cause intestinal discomfort and aggravate symptoms in people with IBS. If you have IBS, choose bananas that are slightly green because they contain less oligofructan, making them easier to digest.
Heart failure : People with heart failure often take medications that are associated with increased blood potassium levels. Therefore, they should control their potassium intake from foods, including bananas.
End-stage renal disease : At this stage, the kidneys are no longer able to regulate the amount of potassium in the blood. Therefore, patients may be advised to limit potassium-rich foods such as bananas.
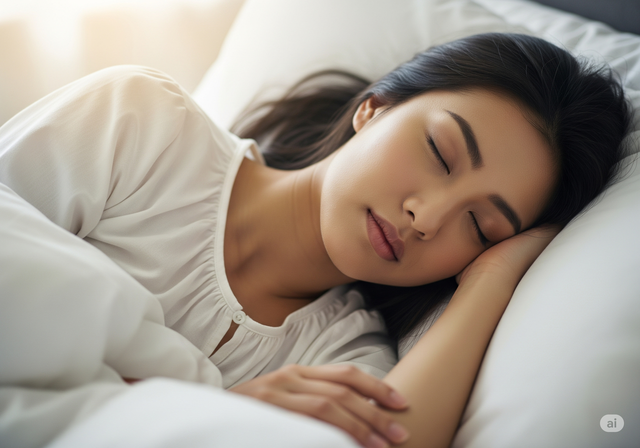

A small study found that eating two bananas a day helps you sleep better.
Photo: AI
What time of day is best to eat bananas?
There is no “right” time to eat bananas, however, you can choose the time to eat them that suits your specific goals or activities.
Before exercise : Bananas provide easily digestible starch, providing a quick source of energy for more effective exercise.
After exercise : Bananas help restore physical strength thanks to containing starch, electrolytes such as magnesium and potassium, replenishing lost energy and supporting muscle recovery.
Before bed : A small study found that older adults slept better when they ate two bananas a day. This is because bananas contain a substance that can be converted into serotonin and melatonin - two hormones that aid sleep.
Accordingly, the study noted that eating 2 bananas a day helps increase melatonin levels in the blood by more than 500%. In addition, magnesium and potassium in bananas are also said to be related to improving sleep quality. However, more research is still needed to determine this role clearly.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/thoi-diem-va-cach-an-chuoi-tot-cho-suc-khoe-185250711230307948.htm






![[Photo] Dan Mountain Ginseng, a precious gift from nature to Kinh Bac land](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F11%2F30%2F1764493588163_ndo_br_anh-longform-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)





























































































Comment (0)