Endometriosis, blocked fallopian tubes in women or enlarged prostate in men are causes of secondary infertility.
Secondary infertility is the inability to conceive despite having previously given birth. About one-third of secondary infertility cases are due to the woman, one-third are due to the man. In the remaining 30% of cases, secondary infertility involves both sexes or is of unknown cause.
Causes of secondary infertility in women include:
Age: Women's fertility begins to decline after age 30.
Endometriosis: A condition in which tissue that lines the uterus grows outside the uterus, causing problems getting and maintaining a pregnancy.
Blocked fallopian tubes: The fallopian tubes from the ovaries to the uterus can become blocked by a pelvic infection such as chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): This hormonal disorder causes high levels of male sex hormones, which prevent ovulation and cause irregular periods.
Excessive weight gain: Weight gain can lead to ovarian dysfunction in some women.
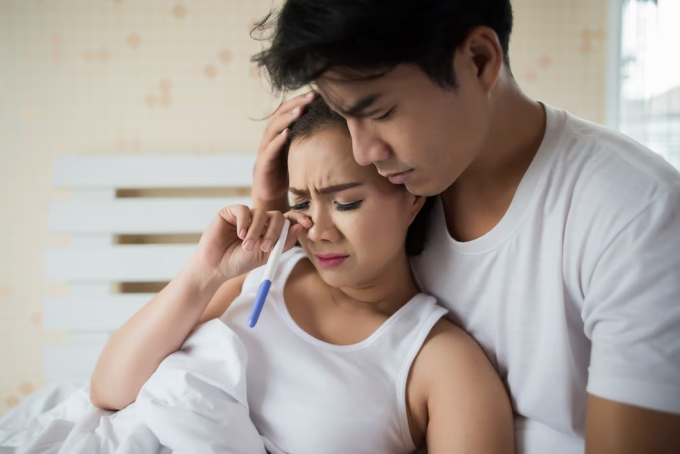

Causes of secondary infertility can come from both men and women. Photo: Freepik
Causes of secondary infertility in men include:
Age: Semen quality often declines after age 40.
Low testosterone levels: Testosterone is important for sperm production but can decrease due to aging or genital injury.
Prostate enlargement: Prostate enlargement reduces sperm count and limits ejaculation.
Prostatectomy: Removal of the prostate gland to treat cancer or other conditions can cause sperm to flow backward.
Hypogonadism: This is a condition of reduced male hormone secretion.
Excessive weight gain: Like women, overweight or obese men are also at increased risk of infertility.
Signs of secondary infertility
If you are under 35 and have had regular sex but have not become pregnant within a year, you should talk to your obstetrician. If you are over 35 or have fertility-related conditions such as irregular periods or endometriosis, it is best to see a doctor as soon as possible.
For men, if they cannot conceive after a year of unprotected intercourse, they should also have a health check-up. The doctor may request a semen analysis to check the quality and quantity of sperm in case the man does not experience any problems during sexual intercourse such as premature ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, etc.
Secondary infertility treatment
Treatment for secondary infertility will depend on the cause.
Treatment options for women include:
Medication: Women with ovulation problems will be prescribed medication by their doctor to stimulate egg production.
Hysterectomy: This surgery removes growths in the uterus such as scar tissue, polyps, and fibroids that affect fertility.
In vitro fertilization (IVF): This is a procedure in which eggs are removed from the ovaries, then fertilized in the laboratory with sperm to form embryos, which are then transferred back into the uterus for implantation.
Treatment options for men include:
Intrauterine insemination (IUI): IUI is a procedure that places sperm directly into a woman’s uterus. This procedure is often used when a man has a low sperm count or poor sperm quality. It is also an option for women with poor cervical mucus.
Testicular surgery can correct varicocele, a condition that can affect sperm quality and quantity.
Use supplements: Supplements such as antioxidants and anti-aging agents may increase male fertility, while drug therapy improves semen quality.
Weight loss: Infertility related to lifestyle factors such as excessive weight gain can be reversed with weight control measures.
As You Wish ( According to WebMD )
Source link





















![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man visits Vietnamese Heroic Mother Ta Thi Tran](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/20/765c0bd057dd44ad83ab89fe0255b783)











































































Comment (0)