According to nutritionist Nguyen Thi Thu Huyen from Tam Anh General Hospital in Hanoi , foodborne infections are one of the leading causes of gastrointestinal diseases and food poisoning.
Many families have a habit of storing food in the refrigerator to extend its shelf life, but doing so incorrectly can increase the risk of bacterial contamination.
Do not wash food before putting it in the refrigerator.
Unwashed raw vegetables, fruits, meat, and fish contain many harmful bacteria such as E. coli, which causes urinary tract infections, severe diarrhea, and blood infections; and Listeria, Clostridium, and Salmonella, which cause stomach and head pain, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, and fever.
To avoid cross-contamination of bacteria to other foods, before refrigerating, families should wash food thoroughly and place it in specialized food bags or containers. Food should also be patted dry, as any remaining moisture (especially in vegetables) creates a suitable environment for bacteria and mold to grow.
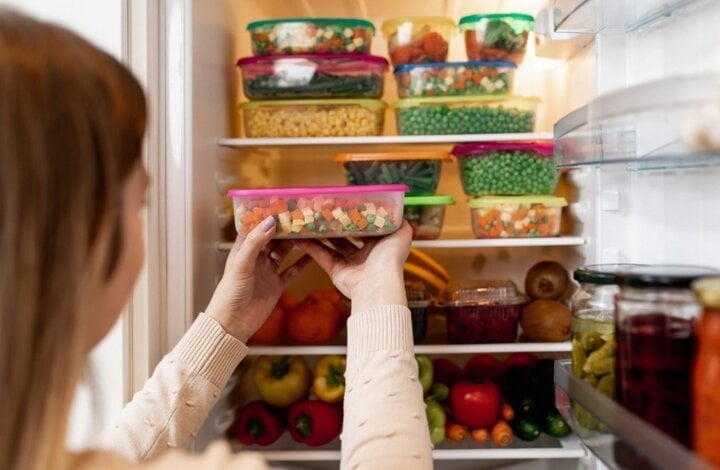

Failing to clean food before refrigerating it can easily lead to bacterial growth, increasing the risk of intestinal diseases. (Illustrative image)
Improper food arrangement
The most common mistake is storing eggs and milk in the refrigerator door. Opening and closing the door causes the temperature in that area to fluctuate frequently, making it unsuitable for preserving these two foods.
Refrigerator doors are only suitable for foods with a long shelf life and that can withstand temperature fluctuations, such as spices and dried goods.
Mixing raw and cooked foods also increases the risk of food poisoning. Bacteria from uncooked meat, fish, and vegetables can easily contaminate cooked food.
Families should categorize food items such as raw meat, uncooked vegetables, and cooked food into separate, designated compartments. Raw meat, fresh seafood, and eggs should be stored in the coldest compartments to keep them fresh longer. Regularly check the refrigerator to remove expired food and prevent bacterial contamination.
Do not cover leftover food.
Unsealed food is more likely to contaminate other foods. Wrap food in airtight packaging or food storage containers before refrigerating to prevent bacterial contamination, maintain moisture, and prevent odors from mixing with other foods in the refrigerator.
Improperly storing food overnight
Storing food in the refrigerator for too long can compromise food safety and hygiene. Some foods, such as vegetables and mushrooms, should not be stored overnight because their nitrite content increases significantly. Adults can absorb nitrite at levels as low as 0.01 mg/l, which can be toxic, and long-term consumption can lead to cancer.
Salads and mixed vegetable dishes are not processed at high temperatures, so bacteria or parasites can easily remain. These continue to multiply and thrive when left for a long time, even in the refrigerator.
Wait until the food has completely cooled before putting it in the refrigerator.
After cooking, food gradually cools down from 100°C. When the food temperature drops to 60°C, bacteria begin to grow. At temperatures of 30-40°C, bacteria multiply rapidly. If not preserved promptly, food spoils easily and contains many harmful bacteria.
Adults should refrigerate food at a temperature of 70-80 degrees Celsius, wrapping it tightly in plastic wrap or a food container to prevent bacterial contamination.
Use plastic bags to store food.
Plastic bags are convenient but can contain many harmful substances, such as dyes that pose a risk of cancer. These bags also harbor many bacteria that can easily harm your health.
Families should use bags specifically designed for food or glass or plastic containers with lids.
Refreeze after thawing.
Refreezing food creates conditions that allow any remaining bacteria to thrive. Families should divide food into appropriate portions and consume it all after thawing.
If you accidentally thaw too much food, put the excess in a sealed food container, set it aside, and use it as soon as possible. Food that has been completely thawed and then reheated to room temperature, or that has been left out of the refrigerator for more than two hours, should not be used.
Foods that are thawed and frozen multiple times can lose their texture, flavor, appearance, and quality, resulting in reduced taste.
Not cleaning the refrigerator regularly.
After a period of use, food accumulates a large amount of bacteria in the refrigerator, causing unpleasant odors and posing a risk of digestive illnesses.
Families should clean their refrigerators at least once a month or more, removing spoiled food and thoroughly wiping down each compartment and nook. Cleaning up food stains immediately not only reduces the growth of Listeria bacteria but also helps prevent cross-contamination from one food item to another.
Nutritionists say that gastrointestinal infections rarely affect adults, but the risk of serious complications is higher in people with weakened immune systems, such as young children and the elderly.
If left untreated, gastrointestinal infections can lead to many problems such as irritable bowel syndrome, intestinal bleeding causing severe infections, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, and chronic gastritis.
Patients should see a doctor if they experience symptoms of foodborne infection such as loss of appetite, headache, nausea, and diarrhea. These symptoms usually begin within 24 hours of eating contaminated food, but may appear later, after a few days or weeks, depending on the type of bacteria causing the illness.
Source: https://vtcnews.vn/8-sai-lam-khi-bao-quan-thuc-pham-trong-tu-lanh-ar872951.html


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives the Governor of Tochigi Province (Japan)](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765892133176_dsc-8082-6425-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Image] The tenacious fighting spirit of Vietnamese women's football](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F17%2F1765990260956_ndo_br_4224760955870434771-copy-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Lao Minister of Education and Sports Thongsalith Mangnormek](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765876834721_dsc-7519-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Live] 2025 Community Action Awards Gala](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765899631650_ndo_tr_z7334013144784-9f9fe10a6d63584c85aff40f2957c250-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Image] Leaked images ahead of the 2025 Community Action Awards gala.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765882828720_ndo_br_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-45-png.webp&w=3840&q=75)









































































![[Live] Closing Ceremony and Award Presentation for the "Impressive Vietnam Tourism" Video/Clip Creation Contest 2025](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/17/1765974650260_z7273498850699-00d2fd6b0972cb39494cfa2559bf85ac-1765959338756946072104-627-0-1338-1138-crop-1765959347256801551121.jpeg)



























Comment (0)