What is collagen and why is it important?
According to Healthline , collagen is made up primarily of the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These amino acids form three strands, creating the characteristic triple-helical structure of collagen.
Collagen is found in connective tissue, skin, tendons, bones and cartilage. It provides structural support to tissues and plays an important role in cellular processes, including tissue repair, immune response...
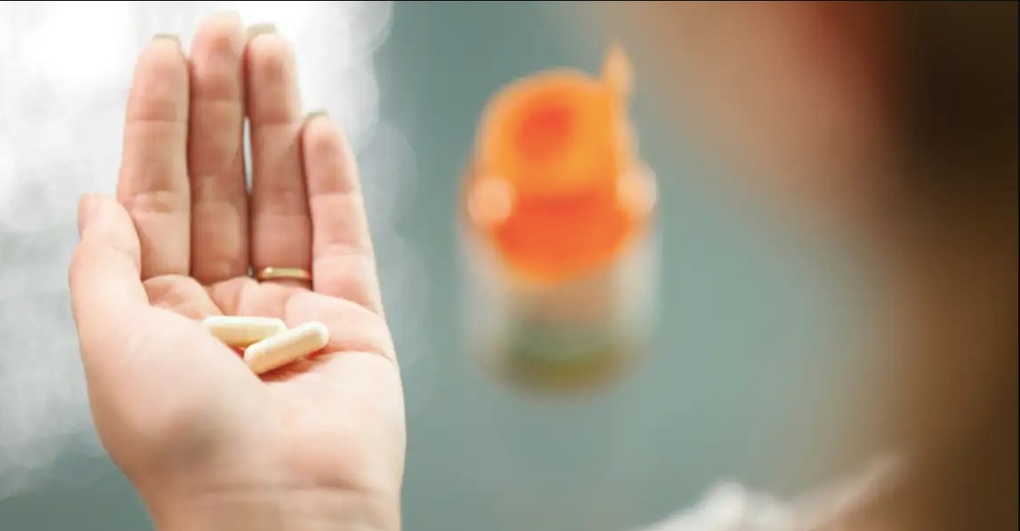

More and more people are supplementing collagen daily with the hope of improving their skin, hair and joints (Photo: Health.Osu).
Connective tissue cells called fibroblasts produce and maintain collagen. As people age, collagen becomes fragmented, fibroblast function declines, and collagen production slows.
These changes, along with the loss of another important structural protein called elastin, lead to signs of aging like sagging skin and wrinkles.
What causes collagen loss?
As you age, collagen production naturally decreases. In addition, collagen becomes fragmented and more loosely distributed. These changes lead to typical signs of aging, such as wrinkles and dry, sagging skin. Collagen integrity in the skeletal system also decreases with age, leading to decreased bone strength.
Collagen loss and damage as you age is inevitable, but certain dietary and lifestyle factors can accelerate this process.
For example, smoking breaks down collagen and causes skin aging, wrinkles, and loss of elasticity. Excessive alcohol consumption has also been shown to accelerate skin aging by reducing collagen production and damaging the skin's repair mechanisms.
Additionally, diets high in added sugars and ultra-processed foods can lead to premature aging by contributing to a process called glycation, which reduces collagen metabolism and interferes with collagen's ability to interact with surrounding cells and proteins.
Too much sun exposure also reduces collagen production, so wearing sunscreen and avoiding too much sun exposure can help prevent signs of premature skin aging.
What foods are rich in collagen?

Foods that provide collagen for the body (Illustration: Istock).
The body naturally produces collagen. Alternatively, you can get it through food sources. Collagen is found in all animals and is concentrated in certain parts of the body, such as the skin and joints.
Here are a few examples of collagen-rich foods:
- Animal bones, skin and tendons, such as chicken skin and pork legs.
- Some seafood, such as fish skin and jellyfish.
- Products made from animal parts such as bones and tendons, including bone broth.
Since your body naturally produces collagen from amino acids, you can support collagen production by making sure you eat enough protein from foods like poultry, fish, beans, and eggs.
In addition to amino acids, your body needs other nutrients to produce and maintain collagen.
For example, vitamin C is needed for collagen synthesis, so a deficiency can lead to impaired collagen production. Eating plenty of foods rich in vitamin C can help support healthy collagen production. For example, try eating citrus fruits, bell peppers, green vegetables, and berries.
Furthermore, consuming a diet rich in beneficial plant compounds may also help improve skin health by reducing inflammation and protecting the skin from collagen degradation.
What are the benefits of collagen supplements?
According to the Cleveland Clinic , there is currently a lack of randomized controlled trials of dietary supplements (the gold standard for testing the effectiveness of medications).
A small amount of research has been done showing that collagen peptides may be effective in improving skin moisture and elasticity. It may also be effective in reducing pain and improving joint function in people with knee osteoarthritis.
Important things to know about the science behind supplements.
First, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate collagen supplements as drugs. The FDA does not require randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials like drugs must undergo to be approved.
Dietary supplement manufacturers do not have to prove their products are safe or effective before they go to market.
Second, many studies conducted with dietary supplements are funded by the dietary supplement industry or the study authors have financial ties to the dietary supplement industry.
Third, it is not yet known whether collagen supplements are as effective as advertised on the label.
Finally, remember that consuming collagen peptides—from food or supplements—cannot be directed to their intended use. Your body uses these peptides for its needs, be it as collagen or protein.
More research is needed before any firm conclusions can be drawn about the effectiveness of supplements in promoting healthier skin.
It's important to note that you don't necessarily need to take collagen supplements to support your body's collagen levels or bone health.
In fact, you can help your body produce collagen and maintain healthy collagen and bone tissue simply by getting enough high-quality protein, vitamin D, calcium, vitamin C, and zinc in your diet.
A balanced diet with a little more protein is especially helpful for maintaining muscle and bone tissue as you age. Researchers recommend consuming about 0.8g per kg of body weight for this purpose.
To support this, combine this high-protein diet with physical activity, especially resistance training and weight-bearing exercises.

Source: https://dantri.com.vn/suc-khoe/bo-sung-collagen-co-thuc-su-hieu-qua-20251020113847139.htm


![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man holds talks with Hungarian National Assembly Chairman Kover Laszlo](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760952711347_ndo_br_bnd-1603-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Chairman of the Hungarian Parliament visits President Ho Chi Minh's Mausoleum](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760941009023_ndo_br_hungary-jpg.webp)



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with Speaker of the Hungarian National Assembly Kover Laszlo](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760970413415_dsc-8111-jpg.webp)




































































































Comment (0)