We have trillions of biological clocks in our bodies. So how do they work, and what role do they play in our health?

Morning sunbathing is good for your health - Photo: virtusan.com
Exposure to light and the timing of light exposure are important to human health. They signal our bodies to wake up in the morning, when to go to the bathroom, and what times of day we need to be most focused or alert.
So how does our body know when to do these things? And what does light have to do with it?
The answer lies in the biological clock.
One of the main roles of light is to set the human body's biological clock. This clock consists of a network of genes and proteins that regulate each other. The network sends signals to organs through hormones and the nervous system.
The central biological clock is located in the hypothalamus of the brain, and each cell has its own clock. According to LiveScience , these clocks work together to help us adapt to the daily light-dark cycle, adjusting our body functions according to the time of day.
However, the human body clock does not operate exactly on a 24-hour cycle (on average, 24 hours and 30 minutes). Therefore, the central clock needs to be reset every morning to start a new day. That is why light is important.
The central clock is directly connected to the light-sensing cells in the retina of the eye. Resetting the clock with light each morning helps our body function properly, in sync with the surrounding environment.
Additionally, the time we eat also plays a role in setting our biological clocks. However, this time it is the clocks in organs other than the brain, such as the liver, kidneys, or intestines.
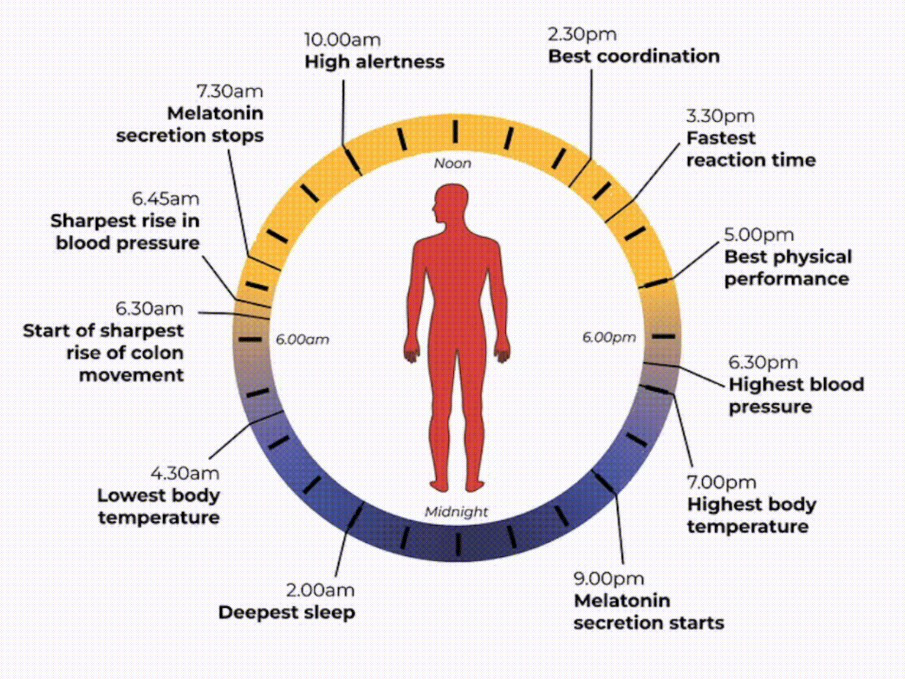
A person's biological clock - Photo: The Conversation
For sleep: The hormone melatonin, which is produced naturally in the brain, is linked to the central biological clock and makes us feel sleepy at certain times of the day. When it gets light, our bodies stop producing melatonin and we feel awake. As bedtime approaches, the hormone is released, making us feel sleepy.
Therefore, exposure to light at night when we should be sleeping can be harmful to our health. The main reason for these harmful effects is that exposure to light at the "wrong time" disrupts the body clock, which is most evident in people who tend to stay up late.
With the bowels: Digestion also follows a circadian rhythm. The muscles in the colon that help move waste through the body are more active during the day and slow down at night. A significant increase in bowel movements begins at 6:30 a.m. and is the reason many people have frequent bowel movements around this time.
The gut's circadian rhythm is a direct result of the gut's internal clock and the central clock, and is also influenced by when we eat.
Alertness and concentration: Our body clock also helps us control our levels of focus and alertness by changing the way our brains function at certain times of the day. Our levels of focus and alertness improve in the afternoon and evening, but decrease in the evening and early morning.
This affects productivity and can lead to accidents or mistakes during hours when we have low levels of concentration and alertness.
In short, exposure to light, especially in the morning, is important for synchronizing our body clocks with our bodily functions. In addition to helping us sleep better, increased exposure to morning light is also beneficial for mental health and reduces the risk of obesity.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/con-nguoi-co-hang-nghin-ti-dong-ho-sinh-hoc-chung-co-vai-tro-gi-20241225231103869.htm
































































































Comment (0)