Fiber offers many health benefits, but consuming too much can cause bloating, abdominal distension, constipation, and in more severe cases, intestinal obstruction.
Fiber is an important nutrient for health, consisting of two types: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber helps lower bad LDL cholesterol levels and is found in bananas, apples, oats, berries, and avocados. Insoluble fiber helps control constipation by acting as a laxative, helping stool move through the intestines, and has a stabilizing effect on blood sugar. Some sources of insoluble fiber include nuts, corn, whole grains, and the peels of some fruits and vegetables.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends consuming 22-34 grams of fiber per day, depending on age and gender. Because everyone's fiber tolerance varies, a sudden increase in fiber intake can sometimes cause symptoms.
Bloating
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is difficult to digest. Therefore, eating too much or increasing fiber intake too quickly can lead to unpleasant gastrointestinal side effects, such as bloating and gas. People who need to increase their fiber intake should do so gradually, adding a few grams each week.
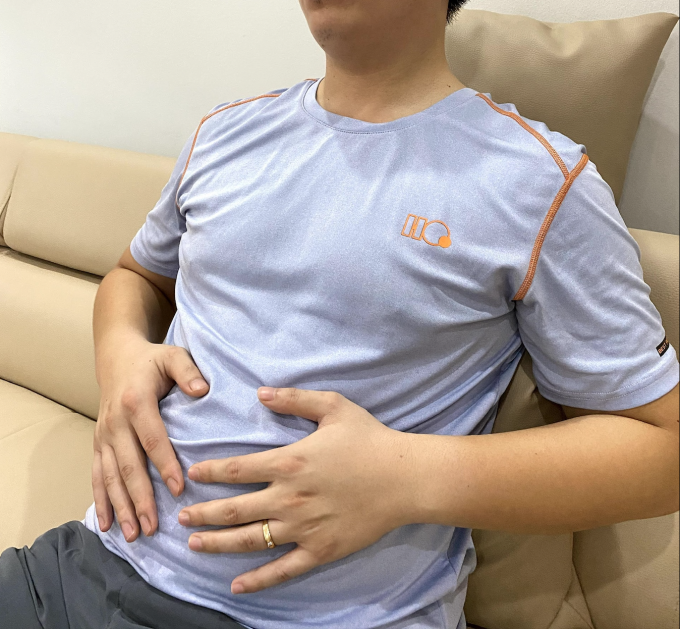
Eating too much fiber can cause bloating and gas. Photo: Bao Bao
Constipation
Fiber has a laxative effect; however, it can cause constipation if the amount of fiber accumulates excessively, overloading the digestive system. To reduce constipation, fiber intake should be slow and steady, and plenty of water should be drunk.
Fiber combines with water to help stool move through the digestive tract easily. Without enough water, stool forms but is difficult to move, causing constipation.
Stomach-ache
Increasing fiber intake too quickly and excessively can cause stomach cramps and bloating, leading to severe abdominal pain. Usually, this subsides after the body has digested the fiber-rich foods. If excess fiber is identified as the cause of the abdominal pain, it's advisable to limit fiber intake for about 1-2 weeks afterward.
Intestinal obstruction
Some people may experience intestinal blockages if they consume too much fiber. This occurs when fiber accumulates in the intestines, clumps together, and interferes with digestion. Intestinal blockages due to high fiber intake are rare, usually occurring in older adults or those with certain digestive conditions. This is because the efficiency of digestion and the elasticity of the intestinal wall decrease.
Symptoms of consuming too much fiber can range from mild to severe. Severe cases, such as nausea, vomiting, fever, severe abdominal pain, or constipation, should be treated with medical attention. For mild to moderate cases, some of the following methods may help alleviate the condition.
Drinking extra water helps reduce bloating and prevents dehydration caused by eating a lot of fiber.
Limit your intake of high-fiber foods to give your body time to digest what you've consumed until your symptoms subside.
Performing some exercises such as walking and gentle stretching can improve bloating and constipation.
Avoid carbonated drinks or chewing gum, as these can introduce extra air into the digestive system, leading to bloating and abdominal discomfort.
Bao Bao (According to Eating Well )
| Readers can ask questions about nutrition here for the doctor to answer. |
Source link














































































































Comment (0)