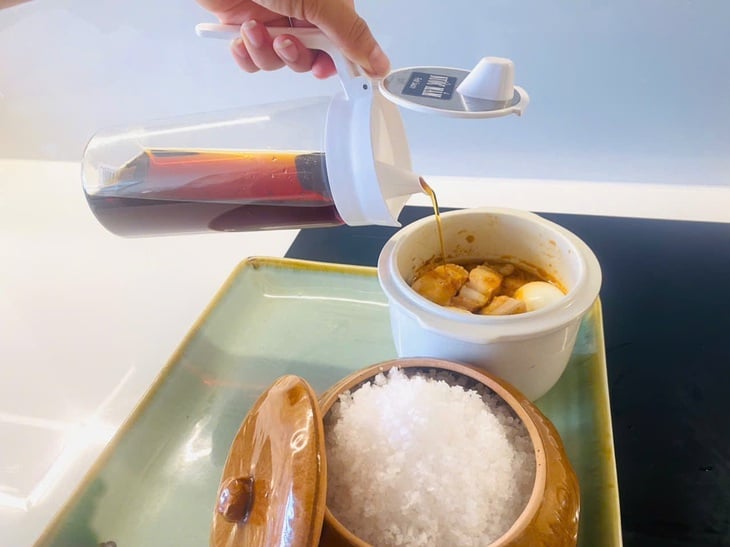

Traditional fish sauce and coarse salt are increasingly appearing in modern kitchens - Photo: CHAU SA
This trend has been widely shared on cooking groups, spreading from urban to rural areas with the belief that eating food in its original form is healthier.
"Detox" your kitchen with fish sauce and coarse salt.
For about two months now, Ms. An Vy (Da Nang) has been clearing out her jars of commercially produced seasonings and replacing them with traditional fish sauce, coarse salt, and homemade dry spices. The change began after she happened to watch a video analyzing the ingredients of commercially produced fish sauce.
"I was surprised to see that my hometown is where fish sauce is made, yet for so many years I've only been using industrially produced fish sauce. That's why I switched to pure, undiluted fish sauce – intensely salty but with a strong fishy aroma – a very authentic feeling. Using coarse salt makes the dishes less flavorful than before, but it gives me peace of mind," said Ms. Vy.
On social media, more and more people are sharing their "kitchen detox" journeys, switching back to fish sauce concentrate and coarse salt, abandoning artificial seasonings and flavorings. Some people stock up on coarse salt for use, while others source fish sauce from traditional craft villages.
For Ms. Kim Phuong ( Quang Ngai ), coarse salt, once only used for making fish sauce or lime salt, has now become her main seasoning. She even bought earthenware jars to store the salt because she believes that the longer the salt is stored and properly preserved, the more subtly sweet its aftertaste will become, without the bitterness she imagined.
Which salt and fish sauce are good for your health?
Dr. Tran Ba Thoai - a member of the executive board of the Vietnam Endocrinology and Diabetes Association, and a professional advisor at Hospital 199 ( Ministry of Public Security ) - believes that consumers need to clearly distinguish between traditionally handcrafted fish sauce, traditionally produced fish sauce on a large scale, and industrially produced fish sauce.
"To put it simply, industrial fish sauce is a type of dipping sauce that's simply labeled as fish sauce. It's a product made from water, salt, a portion of anchovy extract (the exact amount is unknown), along with various chemicals, flavor enhancers, colorings, and fragrances," Mr. Thoai said.
Dr. Nguyen Thi Thuy, deputy head of the nutrition department at Da Nang Hospital, observes that the trend of switching to using coarse salt and traditional fish sauce instead of refined salt and industrial fish sauce reflects the increasingly meticulous food choices of housewives today.
According to Dr. Thuy, while the food industry offers many conveniences and choices, it also harbors numerous health risks. "The overuse of industrial, refined, and processed foods with unbalanced nutritional content, lacking essential micronutrients and minerals, and containing many additives, preservatives, flavorings, and sweeteners can easily lead to nutritional imbalances and long-term health problems," Dr. Thuy warned.
Regarding fish sauce, Dr. Thuy stated that according to Vietnamese Standard TCVN 5107:2003, fish sauce is classified based on its total nitrogen content, reflecting protein levels from 10 to over 25g/l, corresponding to grades 2 to special. Meanwhile, industrially produced fish sauce (also known as dipping sauce) is usually made from fermented fish extract (or plant protein such as soybeans), diluted with additives.
"One thing is certain: fish sauce always has a higher protein content than dipping sauces. Traditional fish sauce typically has a protein content of around 25-28°N. Some special types, such as concentrated fish sauce, can reach 40-50°N, but these are premium products and less common in the market."
According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), only products with a protein content above 10°N should be called fish sauce; anything below this threshold should only be called dipping sauce," Dr. Thuy emphasized.
In addition, Dr. Thuy also analyzed the difference between refined salt and coarse salt. Refined salt is salt that has been refined, has a high purity (97-99% sodium chloride), and contains almost no natural minerals – although it is often supplemented with iodine. This type of salt usually has a harsh, salty taste and lacks a sweet aftertaste.
Conversely, coarse salt (sea salt) is a product obtained from the evaporation of seawater. Besides sodium chloride (>80%), coarse salt also contains many trace minerals such as sulfates, carbonates, calcium, potassium, magnesium, iron, zinc, etc., which create its characteristic sweet aftertaste.
Based on the above analysis, Dr. Thuy affirmed that prioritizing the use of traditional fish sauce and coarse salt will help supplement the body with essential micronutrients such as magnesium, manganese, iron, and zinc, even in low amounts.
This also helps limit the intake of unnecessary chemicals and additives from industrial products. "For meticulous homemakers, this is also a more acceptable option thanks to the natural, pure flavor in family meals," added Dr. Thuy.
Salt and seasonings containing salt should be limited.
Dr. Nguyen Thi Thuy noted that salt and salt-containing seasonings like fish sauce are familiar components in meals, contributing to the flavor of dishes. However, salt contains up to 40% sodium – a substance proven to be linked to high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and kidney disease. According to the Ministry of Health's recommendations, a normal person should consume less than 6g of salt per day.
People with cardiovascular or kidney disease need to limit their salt intake depending on their health condition. In daily practice, it is advisable to limit the use of salt and salt-containing seasonings: reduce seasoning when cooking, and limit sauces on the table. At the same time, choose products from reputable brands and carefully read labels to ensure quality and safety.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/muoi-mam-nao-tot-hon-cho-suc-khoe-20250710230422272.htm













































































































Comment (0)