Summer Solstice June 21: Vietnam enters the longest day of the year
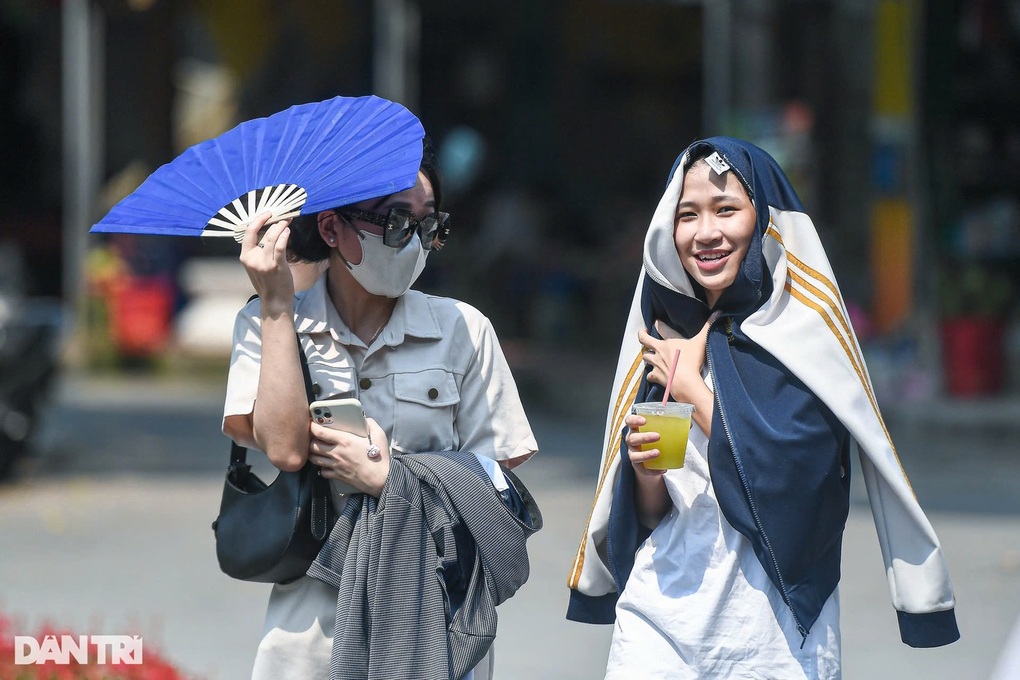

On June 21, Vietnam and many countries in the Northern Hemisphere entered the summer solstice (Photo: Toan Vu).
At 9:42 a.m. on June 21 (Vietnam time), the summer solstice officially takes place, marking the longest day of the year for countries in the Northern Hemisphere, including Vietnam.
The summer solstice is an astronomical phenomenon with a fixed cycle that occurs once a year around June 20-21, not only officially opening summer according to the astronomical calendar, but also expressing the laws of Earth's movement in the solar system.
This event occurs when the Earth's axis of rotation is tilted 23.5 degrees, causing the Sun to shine perpendicularly at noon at the Tropic of Cancer, 23.5 degrees north latitude – the northernmost point where the Sun can shine directly.
At the summer solstice, the Sun reaches its highest position in the sky for the year for observers in the Northern Hemisphere, resulting in the longest daylight hours.
For cities as far north as Oslo, Norway, the Sun may not even set for 24 hours, explaining the phenomenon known as "white nights".
In Hanoi , the sunlight can last more than 13 hours, while Ho Chi Minh City also records longer than average daytime hours throughout the year, according to TimeandDate .
In contrast, countries in the Southern Hemisphere such as Australia, New Zealand and South Africa are entering the winter solstice, when the Sun is at its lowest position in the sky and daylight hours are reduced to a minimum.
The Earth's tilt axis and the law of seasonal change

Graphic showing the tilt of the Earth relative to the Sun during the summer and winter solstices (Image: NASA).
The summer solstice is caused by a change in Earth's tilt, which was caused by a collision billions of years ago between the early Earth and a Mars-sized body. The event created both the Moon and its characteristic tilt.
It is thanks to the 23.5-degree tilt that regions outside the equator have four distinct seasons in a year, with the vernal equinox, autumnal equinox, summer solstice and winter solstice (while regions near the equator have two main seasons: rainy and dry). These are clear transitions in the climate and light cycle.
Since ancient times, people have recognized this rule and left impressive marks such as giant astronomical structures: Stonehenge (England) was built to face the rising point of the Sun on the summer solstice; or the Chichén Itzá Pyramid (Mexico) where the shadow forms the shape of the snake god Kukulkan on the spring and autumn equinoxes.
These legacies prove that humans have long observed, calculated and been deeply attached to astronomical phenomena.
For modern people, the summer solstice is not only a milestone in astronomy but also has significance in daily life, especially in agriculture , culture and industries that depend on light.
In addition, astronomers also take advantage of the summer months to observe the summer constellations such as Asteroid, Lyra and Draco, as well as the upcoming June full moon and meteor showers.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/khoa-hoc/vi-sao-216-la-ngay-dai-nhat-trong-nam-o-viet-nam-20250621075737724.htm




























![[Photo] Nghe An: Provincial Road 543D seriously eroded due to floods](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/5/5759d3837c26428799f6d929fa274493)
![[Photo] Discover the "wonder" under the sea of Gia Lai](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/6/befd4a58bb1245419e86ebe353525f97)


































































Comment (0)