Increasing multidrug-resistant infections in hospital patients
At the Infectious Diseases Conference held by Cho Ray Hospital last March, Dr. Le Quoc Hung, Head of the Department of Tropical Diseases, Cho Ray Hospital, presented alarming figures about the situation of drug-resistant microorganisms.
According to the report, multidrug-resistant infections, resistance of gram-negative bacteria, and drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus are spreading and are a global disaster. The mortality rate due to fungal invasion and antibiotic resistance is also increasing sharply.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are spreading around the world like a pandemic, causing about 5 million deaths each year and becoming one of the world's biggest killers.
According to Dr. Le Quoc Hung, the situation of multidrug-resistant infections in patients in hospitals is increasing "dizzily". In 2020 alone, it is estimated that there were more than 2 million cases of invasive fungal infections. At Cho Ray Hospital alone, there are an average of 480 cases of difficult-to-treat multidrug-resistant Gr(-) infections and about 200 cases of drug-resistant Gr(+) infections each month, mainly caused by community-acquired infections. Statistics show that more than 80% of parents do not know how to properly use antibiotics for children under 2 years old.
"This increases the mortality rate by 1.6 times, increases the total cost of treatment by nearly 2 times, and increases the cost of antibiotics by 3 times compared to normal," said Dr. Hung.
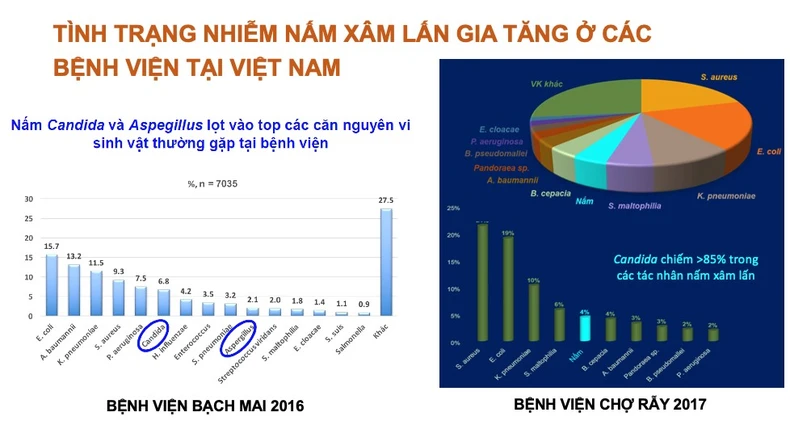
Dr. Le Quoc Hung, Head of the Department of Tropical Diseases, Cho Ray Hospital, shared that the situation of invasive fungal infections is increasing in hospitals in Vietnam. |
Of course, the consequences of drug resistance will lead to high mortality rates as well as a large financial burden for treatment costs. It can be said that in the end, all the consequences still fall on the patient.
There are many reasons for the increase in drug resistance, but the most important reason that experts warn is: Indiscriminate use and abuse of drugs.
Using drugs, especially antibiotics, improperly in life has many approaches, for example: Growing crops and raising livestock using a lot of antibiotics, causing the food we use to already have antibiotics, doctors prescribing antibiotics abusing or prescribing when not necessary....
However, according to the World Health Organization in Vietnam, the serious problem of antibiotic resistance is due to the purchase of drugs without prescription. It is very easy to buy antibiotics at pharmacies without a prescription. Pharmacists at pharmacies are arbitrarily selling drugs without a prescription even though they are not authorized to prescribe drugs.
Even doctors, who are only authorized to examine and treat patients and are not allowed to sell drugs at their clinics (if they do not register their pharmacy business), are often selling drugs in disguise to patients.
Need to strictly manage prescription drug sales
In 2021, the Ministry of Health issued Circular 27/2021/TT-BYT; Circular 04/2022/TT-BYT regulating electronic prescriptions and prescription drug sales, as well as a decision to operate the National Information System on prescription management and prescription drug sales (Decision 425/2025/QD-BYT), piloting from 2019 to 2024.
According to reports at conferences of the Ministry of Health, implementing the cycle of electronic prescription and prescription drug sales is good management of prescription drug sales.
Electronic prescriptions are a very small and essential component of electronic medical records. More broadly, electronic prescriptions also arise at medical facilities for patients who are not inpatients and do not have medical records.
Only by using electronic prescriptions nationwide to ensure monitoring and management of prescription and prescription drug sales at each medical facility can there be hope of gradually controlling drug resistance in the community.
Electronic prescriptions provide transparent information about each prescription (medical facility, prescribing doctor) and update the prescription status (partially sold, fully sold, expired...) to help both drug sellers and patients comply with regulations.
If using a paper prescription as before, it is difficult to know whether the prescription is real or not, whether it was prescribed by the correct doctor or not, whether the prescription has been sold or not, whether it is full or partial, and whether the prescription is still valid or expired (the prescription is only valid for 5 days according to Circular 52/2017/TT-BYT).
According to the report of the representative of the Medical Informatics Association, currently, 100% of hospitals nationwide have HIS hospital management software, and commune and ward health stations have applied V20 software of the Ministry of Health. Thus, 100% of the public health sector has been and is prescribing electronic drugs.
For the private health sector (specialized clinics), nearly 10,000 private facilities have connected electronic prescriptions. Clinics must also connect patient examination and treatment data to the VNeID electronic health record system of C06, Ministry of Public Security according to the provisions of Project 06.
As for the pharmacy sector, since 2019, the Drug Administration of Vietnam, Ministry of Health has required 100% of pharmacies to have computers with internet connection and software. These software have all received electronic prescriptions to carry out sales.
This means that at this time, medical facilities (medical examination, treatment and pharmaceutical business) can all do it.
According to the latest data provided by the Vietnam Medical Informatics Association, to date, about 21,287 medical examination and treatment facilities have been connected to the system, of which about 10,663 are public medical examination and treatment facilities (including 1,007 hospitals and 9,656 commune and ward health stations); 9,541 are private medical examination and treatment facilities (including general and specialized clinics). About 109 thousand doctors, nurses, and prescribers have been given identification codes. Only about 30% of medical facilities have connected their prescriptions to the National Prescription System.
However, there are only about 208.9 million prescriptions from this group of interconnected medical examination and treatment facilities. The number of prescriptions recorded as sold is about 63.4 million, of which more than 3 million are outpatient prescriptions purchased at pharmacies and more than 60 million are inpatient prescriptions.
In the trend of digital transformation, implementing the direction of the Politburo in Resolution No. 57-NQ/TW dated December 22, 2024 on breakthroughs in science and technology development, innovation and national digital transformation, the Ministry of Health needs to soon have more measures to strongly promote the health sector's digital transformation, implement electronic prescriptions and sell prescription drugs nationwide to improve people's health and promptly prevent and combat the pandemic of drug resistance.
Source: https://nhandan.vn/khong-quan-ly-chat-ke-don-thuoc-gia-tang-nguy-co-khang-khang-sinh-post871570.html




























![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man visits Vietnamese Heroic Mother Ta Thi Tran](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/20/765c0bd057dd44ad83ab89fe0255b783)





































































Comment (0)