Major health benefits of mangoes
Improves digestive function
Mango is a great fruit to help relieve constipation, as it is rich in soluble fiber, which works by absorbing water from the digestive tract, forming a gel that helps regulate bowel movements. Additionally, mangiferin found in mangoes acts as a natural laxative, increasing bowel movements.
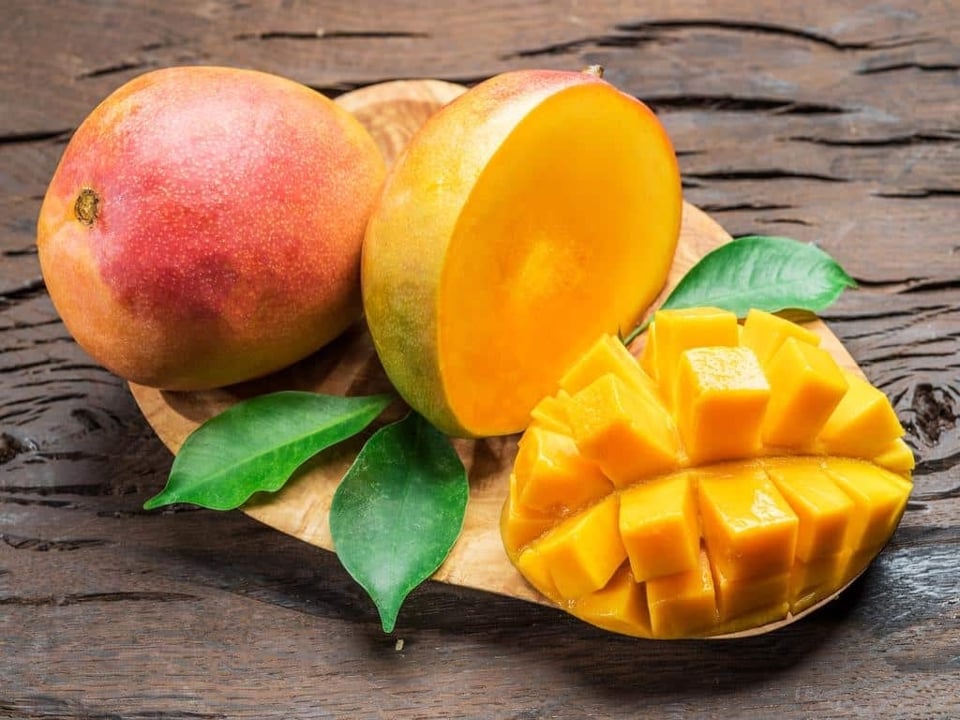

Mangiferin also protects the liver, improves the activity of bile salts which are important for fat digestion and helps treat worms and intestinal infections.
Anti-gastritis
Mango has mangiferin and benzophenone in its composition, which protects the stomach by having antioxidant effects, reducing damage to stomach cells, and also helps reduce stomach acid production and thus, can help treat gastritis or stomach ulcers.
Helps control blood sugar
Some studies show that polyphenols such as gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, and ferulic acid can stimulate insulin production and reduce blood sugar and glycated hemoglobin levels, which are indicators of diabetes and may be an important ally in diabetes treatment.
However, mangoes should be consumed in moderation and in small portions or it can be used along with other fiber-rich foods. Also, the best way to take advantage of mangoes' blood sugar-controlling properties is to consume green mangoes, as ripe mangoes can have the opposite effect and increase blood sugar levels.
Has anti-inflammatory effects
Mangiferin, gallic acid and benzophenone present in mango have anti-inflammatory properties and are useful in treating inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease, as it reduces the production of inflammatory substances such as prostaglandins and cytokines.
Additionally, the anti-inflammatory effects of mango on the gut help prevent cell damage that can lead to cancer in the colon and rectum.
Has antioxidant effects
Vitamin C and polyphenolic compounds such as mangiferin, quercetin, kaempferol, gallic acid and caffeic acid have antioxidant properties, fight free radicals and reduce cell damage. Therefore, mangoes help prevent and fight diseases related to oxidative stress caused by free radicals such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke, diabetes or cancer.
Anti-cancer
Several studies using leukemia and breast, prostate, and colon cancer cells have shown that polyphenols, especially mangiferin, found in mangoes have antiproliferative effects, reducing the growth of cancer cells.
Additionally, polyphenols have antioxidant effects, which work by fighting free radicals that cause cell damage.
Protection against cardiovascular disease
The soluble fiber present in mangoes helps reduce bad cholesterol and triglycerides, which are responsible for the formation of fatty plaques in the arteries, as it reduces the absorption of fat from food. Therefore, mangoes improve the function of the arteries and help prevent heart attacks, heart failure and strokes.
Additionally, mangiferin and vitamin C have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects that help reduce cell damage, keeping blood vessels healthy, and polyphenols, magnesium, and potassium help relax blood vessels and control blood pressure.
Strengthen the immune system
Mangoes are rich in nutrients like vitamins A, B, C, E and K and folate which stimulate the production of white blood cells which are essential defense cells to prevent and fight infections and thus, mangoes help boost the immune system.
Additionally, mangiferin stimulates the body's defense cells to fight infection.
Maintain eye health
Mangoes maintain eye health by having antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin that act as sun blockers, preventing eye damage caused by sunlight.
Additionally, vitamin A in mangoes helps prevent the onset of eye problems like dry eyes or night blindness.
Improve skin quality
Mangoes contain vitamins C and A, which are antioxidants that help fight free radicals that cause skin aging. Vitamin C also works by increasing collagen production, which is important for preventing sagging and wrinkling of the skin, improving the quality and appearance of the skin.
Source: https://kinhtedothi.vn/loi-ich-suc-khoe-cua-xoai-ma-khong-phai-ai-cung-biet.html



![[Photo] Closing of the 1st Congress of Party Delegates of Central Party Agencies](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/24/b419f67738854f85bad6dbefa40f3040)






















![[Photo] Editor-in-Chief of Nhan Dan Newspaper Le Quoc Minh received the working delegation of Pasaxon Newspaper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/23/da79369d8d2849318c3fe8e792f4ce16)































































Comment (0)