The 20th century was the period of the space race between countries around the world with a series of projects and research by state agencies such as the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA) or the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos)...
Entering the 21st century, the commercial space race has divided opportunities for private corporations to set their sights beyond Earth.
SpaceX
Founded in 2002 by billionaire Elon Musk, SpaceX has completely changed the way humanity views the rocket launch industry.
From Falcon 1 - the first private US rocket to reach orbit to Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy - a line of rockets that can be reused many times, SpaceX has reduced the cost of launching satellites dozens of times compared to before.
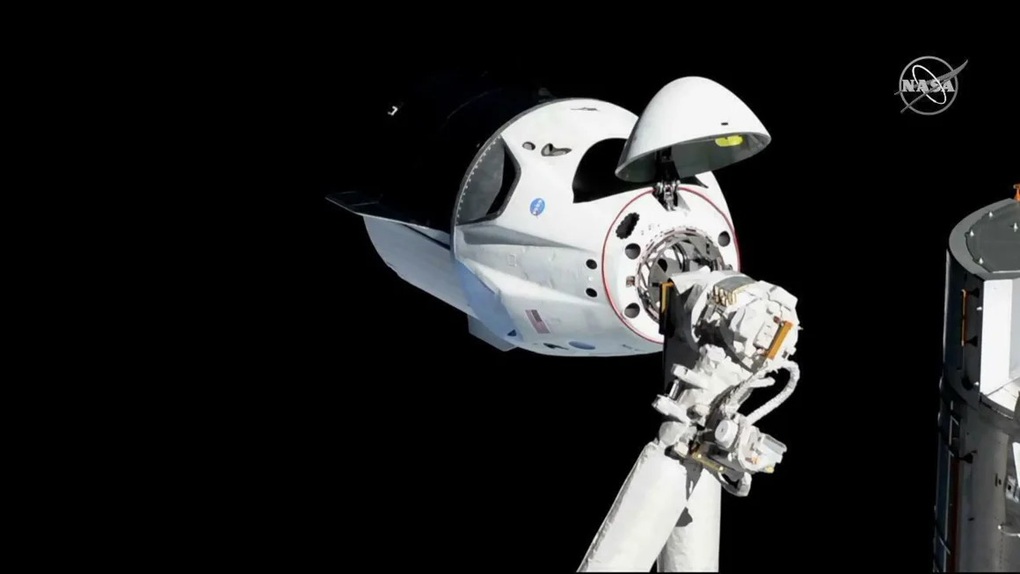

SpaceX's Dragon spacecraft docks with the International Space Station (Photo: NASA).
SpaceX's Dragon spacecraft is the first private spacecraft to carry cargo and astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS). SpaceX is now focusing on the Starship project - a giant rocket system aiming to take humans to Mars.
SpaceX currently holds the number one position in the global commercial satellite launch services sector.
Blue Origin
Billionaire Jeff Bezos also has ambitions to conquer space. In 2000, the Amazon founder invested in Blue Origin with a vision of a future where millions of people live and work in space.
Unlike SpaceX, Blue Origin follows a sustainable and long-term development direction, focusing on reusable systems and engine technology research.
Blue Origin's New Glenn rocket successfully reached orbit in early 2025. New Glenn is among the largest rockets in operation today, dwarfed only by SpaceX's Starship and NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) in height.
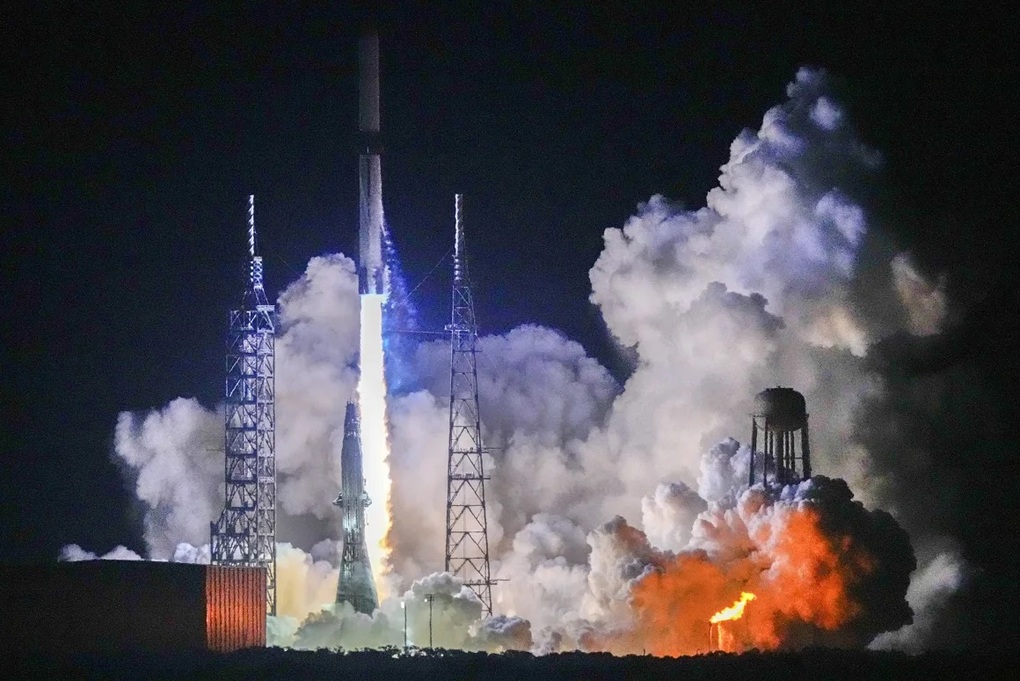

Blue Origin's New Glenn rocket takes off on its first launch from Cape Canaveral Space Station in Florida (Photo: AP).
Blue Origin's New Shepard rocket has successfully launched and returned tourists to space multiple times, and Blue Origin is also working with NASA on the Artemis program, which includes the Blue Moon lander project.
Arianespace SA
Founded in 1980, Arianespace SA is the world's first commercial satellite launch company, operating under the coordination and supervision of the European Space Agency (ESA) and non-state enterprises.

The Ariane 6 rocket seen before its first launch at the Guiana Space Centre (Photo: AFP).
Over the past 40 years, Arianespace SA has carried out more than 350 missions, launching over 1,100 satellites for more than 60 countries and organizations, serving as the launch provider for many major telecommunications satellites and ESA missions.
Arianespace SA's flagship medium-to-heavy-lift rockets Ariane 4, Ariane 5 and upcoming Ariane 6 have also achieved great success in the space race, becoming famous in the aerospace industry for their consecutive launch success rate records.
Virgin Galactic
Unlike other satellite launch corporations, Virgin Galactic - founded in 2004 by British business tycoon Richard Branson - has chosen a different direction: space tourism.
In 2018, the company conducted the first manned flight to an altitude of more than 80km with the VSS Unity spacecraft and has been conducting commercial flights continuously since 2021.
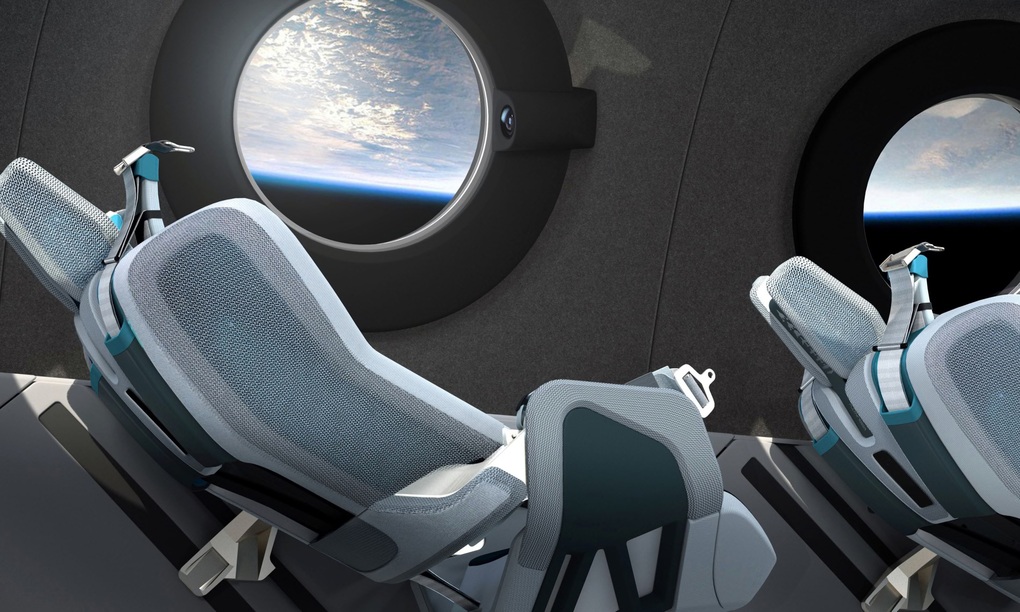

View from the cabin inside Virgin Galactic's VSS Unity (Photo: Virgin Galactic).
In June 2024, Virgin Galactic's last passenger spaceflight landed safely before pausing for two years for upgrades.
Two new Delta-class ships will replace the VSS Unity, which is expected to fly commercially in 2026. Each seat will cost $600,000 and there will be up to 125 flights per year for the elite who want to travel to space.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/khoa-hoc/nhung-doanh-nghiep-tu-nhan-nao-da-chinh-phuc-vu-tru-thanh-cong-20251107195359263.htm





![[Photo] Cutting hills to make way for people to travel on route 14E that suffered landslides](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/08/1762599969318_ndo_br_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-2025-11-08t154639923-png.webp)





























![[Photo] "Ship graveyard" on Xuan Dai Bay](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/08/1762577162805_ndo_br_tb5-jpg.webp)








![[Video] Hue Monuments reopen to welcome visitors](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/05/1762301089171_dung01-05-43-09still013-jpg.webp)
































































Comment (0)