On the morning of June 20, with the majority of delegates in favor (94.94% of the total number of National Assembly delegates), the National Assembly officially passed the Law on Civil Defense.
The Law on Civil Defense prescribes principles and activities of civil defense; rights, obligations and responsibilities of agencies, organizations and individuals in civil defense activities; state management and resources to ensure the implementation of civil defense.
Civil defense must be prepared early, from afar, prevention is key.
The Law on Civil Defense also clearly defines the principles of civil defense operations. That is: Civil defense must be prepared early, from afar, and primarily based on prevention; implement the "4 on-site" motto in combination with support from the Central Government, other localities, and the international community; proactively assess the risk of incidents and disasters, determine the level of civil defense, and apply appropriate civil defense measures to promptly respond to and overcome the consequences of war, incidents, disasters, natural disasters, epidemics, protect people, agencies, organizations, and the national economy , minimize human and property damage, and stabilize people's lives.
At the same time, combine civil defense with ensuring national defense, security, socio-economic development, protecting people's lives, health and property, protecting the environment and ecosystems, and adapting to climate change.
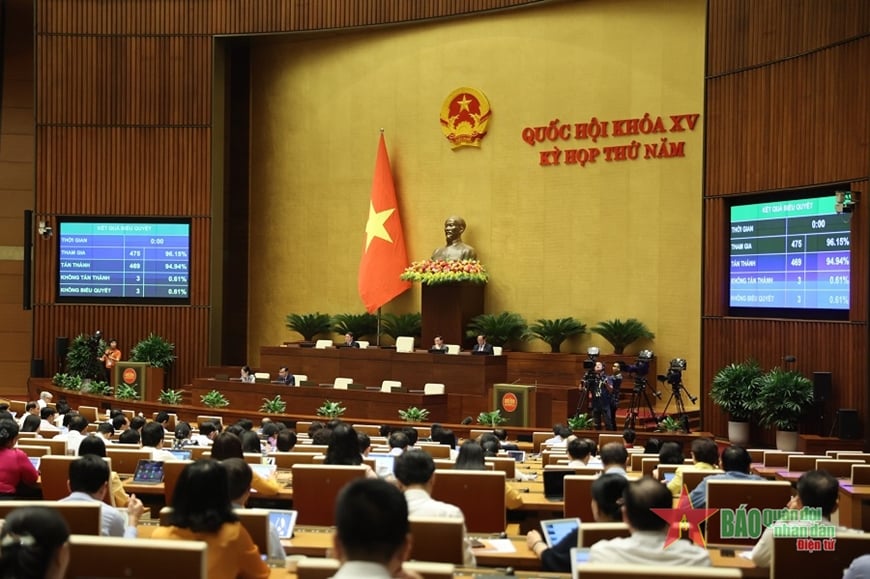 |
The National Assembly passed the draft Law on Civil Defense with a high approval rate. Photo: Tuan Huy |
The Ministry of National Defense is the standing agency of the National Civil Defense Steering Committee.
Notably, Article 34 of the law clearly stipulates the national steering agency and the civil defense command agency. Accordingly, the Ministry of National Defense is the standing agency of the National Civil Defense Steering Committee. Members of the National Civil Defense Steering Committee are responsible for presiding over and advising the Steering Committee in organizing, directing, and operating civil defense in the management field according to the provisions of law.
Article 35 of the law also stipulates that civil defense forces include core forces and broad forces.
The core forces include: Militia, Self-Defense Force, Civil Defense Force; specialized and part-time forces of the People's Army, People's Police, and of Central Ministries, branches, ministerial-level agencies, and localities. The broad force is participated by the entire population.
Previously, during the discussion, some delegates suggested clearly defining the scope and relationship between civil defense forces and forces for natural disaster and epidemic prevention and control and other fields so that the Government has a basis for specific regulations, avoiding possible problems during application.
At the meeting, clarifying this content, Chairman of the National Assembly's Committee on National Defense and Security Le Tan Toi said that civil defense activities have a very wide scope, related to many fields such as: Prevention, combat, and overcoming the consequences of war; prevention, combat, and overcoming the consequences of incidents, disasters, natural disasters, and epidemics. Therefore, the forces participating in these activities are all civil defense forces.
On the other hand, Resolution No. 22-NQ/TW dated August 30, 2022 of the Politburo on civil defense until 2030 and the following years has determined: “Civil defense activities must rely on the people, the people are the root. The core forces are: Militia and self-defense forces; commune, ward and town police; specialized or part-time forces of the People's Army, People's Police and ministries, branches and localities. The broad force is participated by the entire people”.
"The mobilization and use of forces to prevent and combat natural disasters and epidemics in particular and in civil defense activities in general must be based on the actual situation and according to the authority prescribed by law. Therefore, the provisions in the draft law have ensured specificity and feasibility," said Le Tan Toi, Chairman of the National Assembly's Defense and Security Committee.
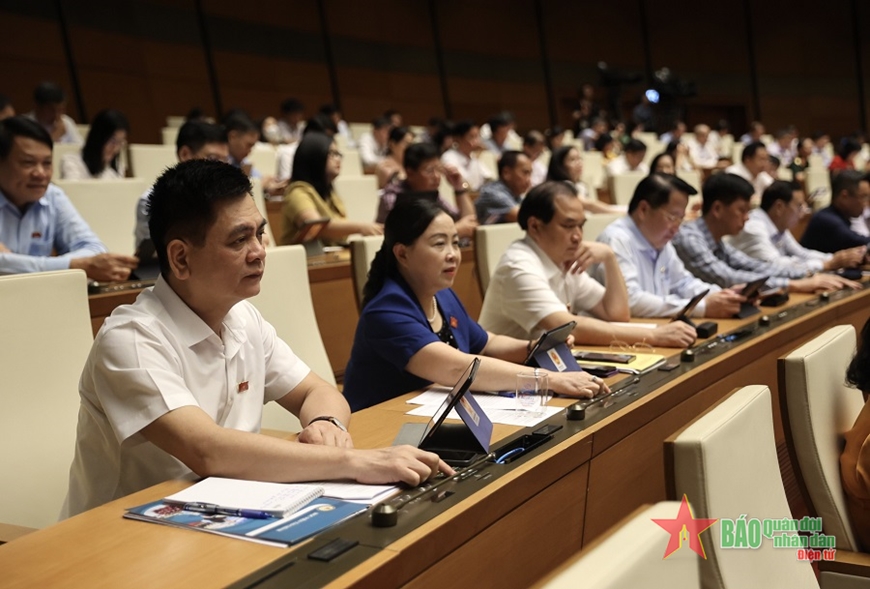 |
| National Assembly deputies voted to pass the draft Law on Civil Defense. |
The establishment of a Civil Defense Fund is necessary.
Notably, regarding the Civil Defense Fund (Article 40), based on the discussion and the results of the above consultation, Chairman of the National Assembly's Defense and Security Committee Le Tan Toi said that the vast majority of National Assembly deputies agreed with the existence of a Civil Defense Fund (both options 1 and 2 identify the existence of a fund), therefore, the establishment of a Civil Defense Fund is necessary.
Based on the results of the consultation, the National Assembly Standing Committee would like to accept and regulate the content of Option 1 as shown in Article 40; at the same time, accepting the opinions of delegates, members of the National Assembly Standing Committee and the opinions of relevant agencies at the 24th Session, the National Assembly Standing Committee proposes that the National Assembly supplement regulations on the principles of regulation between the Civil Defense Fund and non-budgetary state financial funds related to the activities of responding to and overcoming the consequences of incidents and disasters to be carried out in urgent cases and assign the Government to regulate the regulation between these funds as in the draft law.
PRAGUE
Source




![[Photo] Flooding on the right side of the gate, entrance to Hue Citadel](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761660788143_ndo_br_gen-h-z7165069467254-74c71c36d0cb396744b678cec80552f0-2-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chaired a meeting to discuss solutions to overcome the consequences of floods in the central provinces.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/29/1761716305524_dsc-7735-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man received a delegation of the Social Democratic Party of Germany](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761652150406_ndo_br_cover-3345-jpg.webp)



























![[Photo] Draft documents of the 14th Party Congress reach people at the Commune Cultural Post Offices](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761642182616_du-thao-tai-tinh-hung-yen-4070-5235-jpg.webp)








































































Comment (0)