Eating more protein than your body needs can lead to side effects and does not provide any additional health benefits.
Protein is one of three macronutrients that the body needs in large amounts, along with fat and carbohydrates.
High protein diets are often considered beneficial for weight loss, muscle gain... Although meeting daily protein needs is important, is eating too much protein harmful?
According to Associate Professor, Dr. Nguyen Thi Lam - former Deputy Director of the National Institute of Nutrition, protein plays an extremely important role. Protein is one of three substances involved in cell structures, and is a basic component that creates antibodies to help the body fight disease. Protein also participates in hormones that help with development, weight control, and immune support.
1. How much protein do you need?
Protein is the building block of life but few people pay attention to how much they actually need each day, mostly eating according to habits, preferences and feelings.
The current Dietary Reference Intakes for Protein suggest a minimum daily protein intake of 0.8 g protein per kg body weight. To calculate your daily protein requirement, multiply your body weight by 0.8. For example, for a person weighing 68 kg, the daily protein requirement is 68 x 0.8 = 54.4 g protein per day.
Refer to the number of grams of protein in 100 grams of common foods below:
- Pork tenderloin: 26.2 g
- Sliced pork: 24.7 g
- Ground pork: 25.7 g
- Chicken breast: 32 g
- Turkey breast: 30.1 g
- Chicken thigh: 23.9 g
- Chicken wings: 30.5 g
- Tilapia: 26.2 g
- Canned tuna in water: 23.6 g
- Canned sardines in oil: 24.6 g
- Flounder: 22.5 g
- Salmon: 24.6 g
- Shrimp: 24 g
- Eggs: 12.6 g
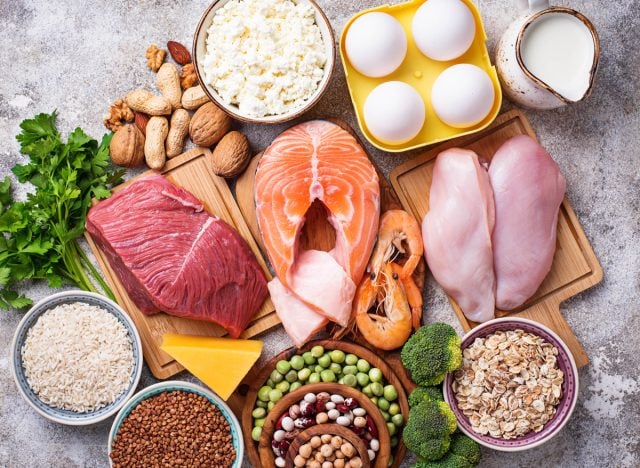

Protein sources from eggs, beef, poultry, fish and milk are generally considered good sources of protein.
It is important to remember that this recommendation is a starting point for the average healthy, inactive adult and that certain populations may need more. In particular, protein needs may be higher during pregnancy, in people who are more active, or when recovering from injury or critical illness. Protein needs may also be higher for older adults to reduce the loss of skeletal muscle due to aging.
Factors such as age, activity level and health status should be considered when determining individual protein needs. Always consult a doctor or dietitian for personal guidance on nutritional needs.
2. What are the consequences of too much protein?
Experts generally recommend that protein intake should not exceed 2 grams per kilogram of body weight per day due to potential side effects. Consistently exceeding this amount can lead to digestive problems, stress on the kidneys, increased risk of cardiovascular disease, and weight gain. It is important to focus more on getting your protein intake evenly throughout the day rather than consuming too much.
Additionally, consuming too much protein, especially from high-fat animal sources, may increase your risk of health problems over time. Here are some specific risks to be aware of when eating too much protein:
Digestive problems: Consuming too much protein, especially red meat, can lead to constipation. Not only does red meat cause constipation due to its high fat content, but eating too much protein from any source can displace nutrients that promote healthy, regular digestion, such as fiber.
Too much protein can put extra pressure on the kidneys to remove protein byproducts from the body, especially for people with pre-existing kidney disease. Therefore, too much protein over time can increase the risk of kidney damage or worsen existing problems.
Heart health: Some studies have shown that diets high in certain proteins, such as red meat and processed meat, are linked to an increased risk of heart disease. A 2022 study found that gut bacteria produce chemicals that are consumed after eating red meat that may increase the risk of heart disease.

Red meat is high in protein, which takes longer to digest, and can contribute to digestive problems.
Weight Gain: Eating more protein than your body needs can also lead to weight gain. Just like consuming too much of other macronutrients like carbohydrates and fats, excess protein is stored as fat. The bottom line is that if your protein intake exceeds your daily calorie needs for maintenance, it can lead to weight gain.
By choosing lean protein sources, including plant-based options, and watching portion sizes, you can meet your protein needs while avoiding potential negative health effects. You can support your overall health by meeting your individual protein needs through a regular intake of your favorite protein-rich foods every day.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/4-he-luy-suc-khoe-khi-an-qua-nhieu-protein-17224120623042582.htm





















































































![[OCOP REVIEW] Tu Duyen Syrup - The essence of herbs from the mountains and forests of Nhu Thanh](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/5/58ca32fce4ec44039e444fbfae7e75ec)







Comment (0)