Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that plays an important role in many bodily functions, including boosting the immune system, collagen production, acting as an antioxidant, and iron absorption...
Vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid) is one of the vitamins that can boost immunity. Because the body cannot produce this antioxidant on its own, it must be supplemented from foods rich in vitamin C.
1. Vitamin C stimulates collagen synthesis
The body relies on vitamin C to synthesize collagen. Health experts say that adequate vitamin C levels are necessary for collagen production. Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body and plays an important role in connective tissues such as those found in our organs and also in hair, skin, and nails.
According to Oregon State University, increased collagen synthesis also means vitamin C helps wounds heal faster.
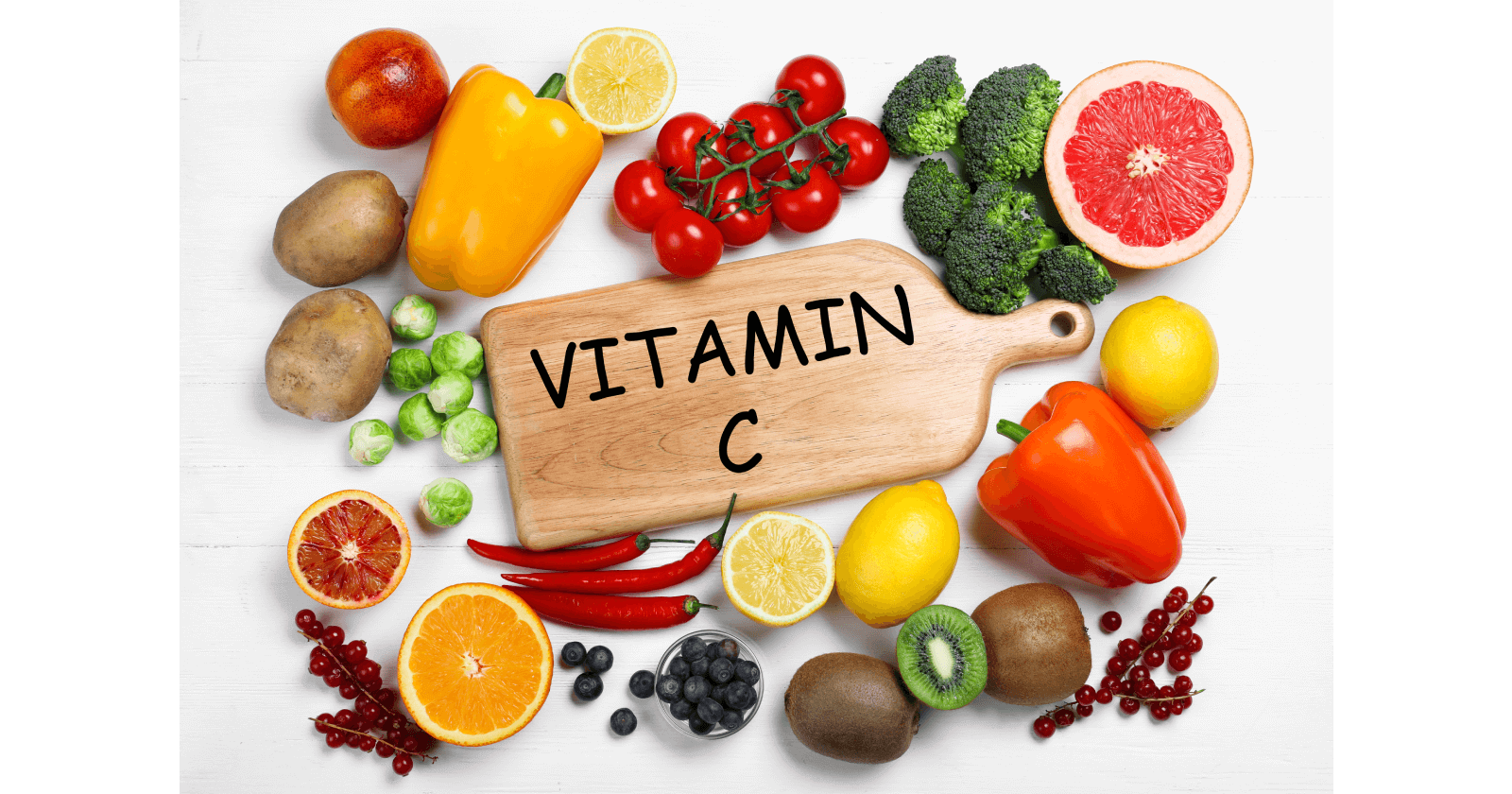
Vitamin C is important for health.
2. Vitamin C combined with iron helps better absorption
Another plus for vitamin C is how it interacts with other vitamins and minerals in the body, such as iron. Iron supports proper growth and development, supports the body's ability to transport oxygen throughout the body, and helps make certain hormones. Nonheme iron, the type found in plants, can be difficult for the body to absorb, but eating vitamin C (and ideally heme iron, which is found in meat and seafood) at the same time as nonheme iron helps with absorption, according to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health .
3. Plays a role in enhancing brain function
Vitamin C also plays a role in neurotransmitter synthesis and cognitive function. Neurotransmitters are important in sending messages from the brain to the rest of the body, according to the University of Queensland in Australia. More vitamin C may be linked to improved brain function. A systematic review in Nutrients found higher vitamin C levels in study participants with intact cognition compared to those with impaired cognition.
4. Antioxidants prevent chronic diseases
Many of the benefits of vitamin C can be attributed to its antioxidant properties. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals, which are volatile and harmful substances produced in the body that cause damage to cells and tissues.
According to the Mayo Clinic, antioxidants may help protect against the development of serious health conditions like cancer or heart disease. However, more research, especially studies involving humans, is needed to show whether vitamin C can prevent cancer or heart disease, according to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
5. Vitamin C boosts the immune system
Perhaps the most well-known benefit of vitamin C is its positive effect on the immune system. In a review of studies, vitamin C was found to support the immune system by protecting against oxidative stress, helping to kill bacteria, and reducing tissue damage. Deficiencies in this vitamin have been shown to increase the risk of infection. Adequate vitamin C may help you recover more quickly from a cold.
6. Vitamin C can help treat cancer
According to the Mayo Clinic, vitamin C can make radiation and chemotherapy more effective when given intravenously. A study in Anticancer Research found that high doses of vitamin C helped fight breast cancer cells when combined with anticancer drugs. Study participants received extremely high doses of vitamin C that people cannot get through diet and home supplements. However, it is absolutely not recommended to take high doses of vitamin C supplements on your own without consulting a specialist. Usually, treatment results depend on the type of cancer, the severity of the cancer, and the overall health of each individual.
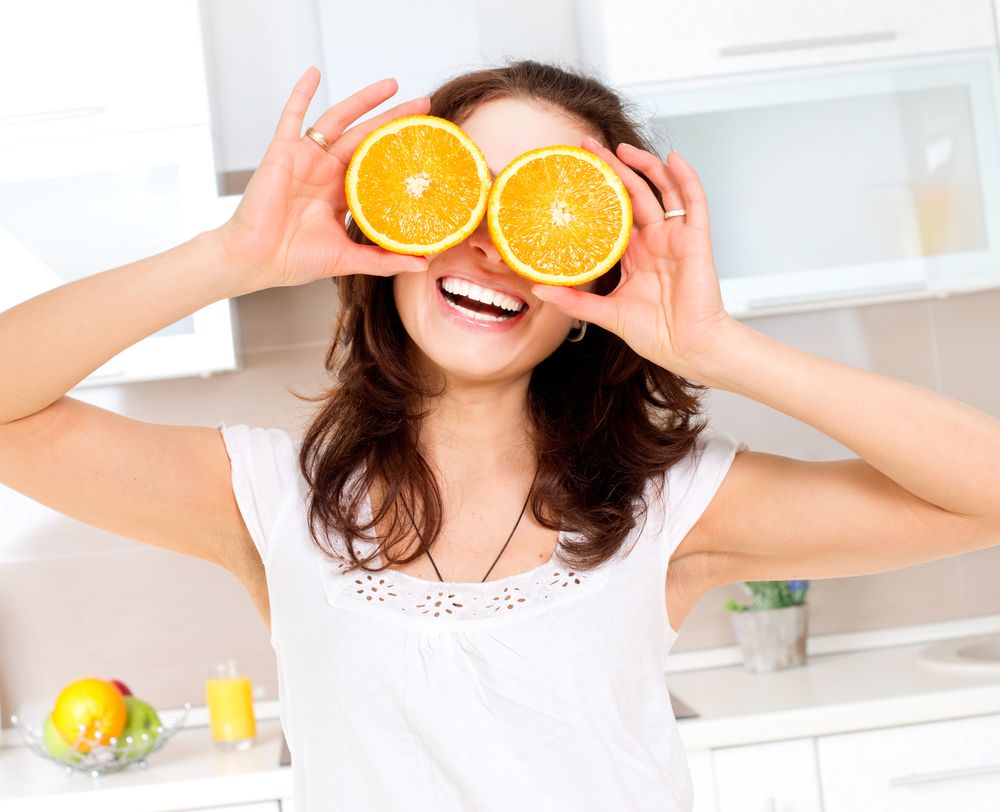

Foods rich in vitamin C boost antioxidants.
7. Vitamin C is rich in antioxidants that protect the eyes
The American Optometric Association notes that vitamin C may reduce the risk of developing cataracts and slow the progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Specifically, research has found that taking 500 mg per day as part of a daily supplement slowed the progression of the disease in people with moderate AMD, possibly due to its antioxidant properties. However, it is advisable to discuss any supplements with your ophthalmologist before taking them long-term.
8. Some foods rich in vitamin C
Fruits:
Guava: Guava is an excellent source of vitamin C, even more than oranges. It is also rich in antioxidants, vitamins A, B, and other minerals.
Oranges, lemons, tangerines, and other citrus fruits: These are common sources of vitamin C. One medium orange contains about 83 mg of vitamin C.
Kiwi: One medium kiwi contains about 70 mg of vitamin C.
Strawberries: Strawberries are also a good source of vitamin C, along with antioxidants and fiber.
Papaya: One cup of papaya can provide all the vitamin C you need in a day.
Black grapes: Black grapes also contain a significant amount of vitamin C.
Other fruits: Cherry, lychee, persimmon, pineapple, star fruit, mango, green mango, grapefruit, passion fruit...
Vegetables:
Bell peppers (especially red bell peppers): These are one of the vegetables highest in vitamin C. Half a cup of red bell peppers can contain up to 95 mg of vitamin C.
Broccoli: Half a cup of cooked broccoli contains about 50 mg of vitamin C.
Kale: Kale is also a good source of vitamin C, along with many other vitamins and minerals.
Tomatoes: One medium tomato contains about 20 mg of vitamin C.
Other vegetables: Spinach, purple cabbage, cauliflower, parsley...
Notes when supplementing vitamin C
Vitamin C is easily destroyed by high temperatures, so it is best to eat fruits and vegetables raw or cooked at low temperatures. Getting vitamin C from natural foods is always preferable to taking supplements. According to the Office of Dietary Supplements of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), adult women need 75 mg of vitamin C per day and adult men need 90 mg.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/7-loi-ich-suc-khoe-cua-vitamin-c-172250118215719441.htm




![[Photo] Solemn opening of the 1st Government Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/13/1760337945186_ndo_br_img-0787-jpg.webp)






















![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the opening of the 1st Government Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/13/1760321055249_ndo_br_cover-9284-jpg.webp)












































































Comment (0)