The Secretariat set a target of attracting 50-55% of high school students to the vocational education system by 2030. At the same time, it required the inclusion of vocational education development into the socio -economic development plans of the sector and locality.
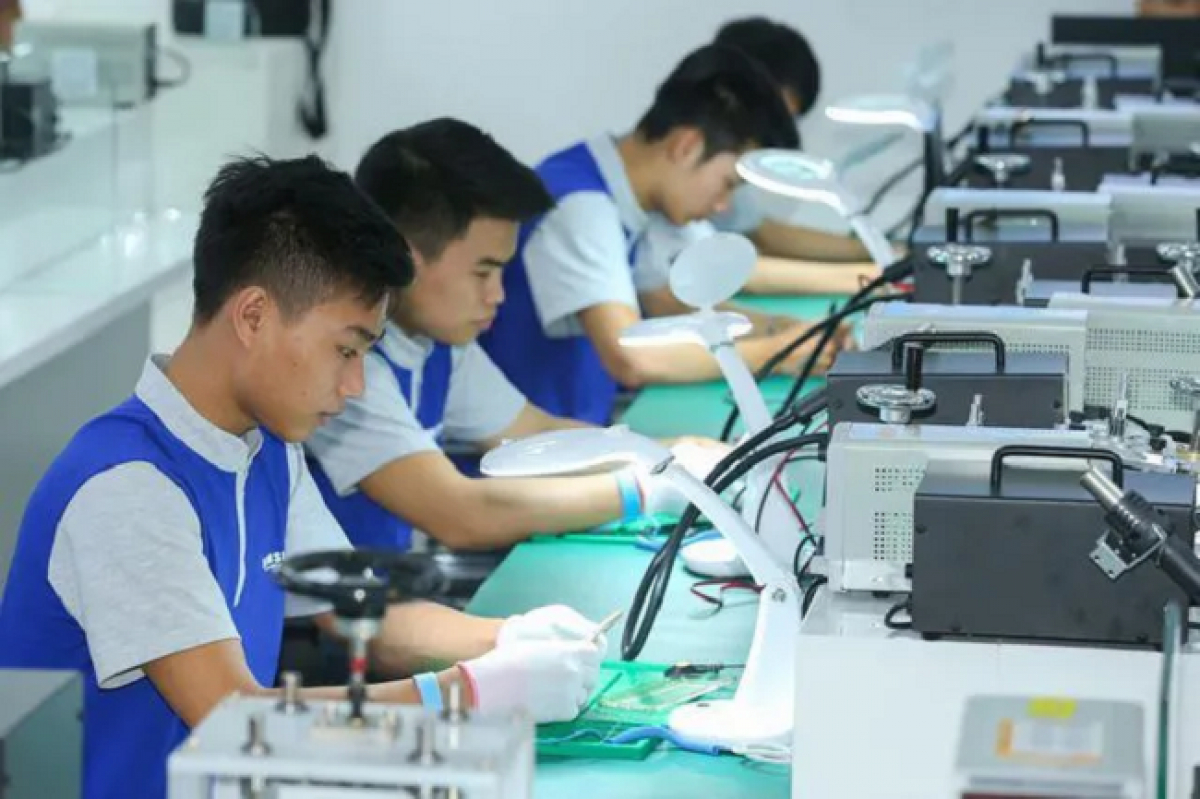

The Directive clearly states that in recent years, vocational education has always received the attention of the Party and the State, leading and directing, achieving many important results. The vocational education system has been formed in an open and interconnected direction, basically in line with other countries in the world . The network of vocational education facilities has developed strongly... The rate of workers with vocational training degrees and certificates; the rate of workers with jobs suitable to their vocational skills and training level has increased; many students have won high awards in regional and international vocational competitions...
The results of vocational education have significantly contributed to forming a skilled workforce, building a modern and strong working class and farmers to serve socio-economic development, the cause of industrialization and modernization of the country.
However, the Secretariat also pointed out that the scale of vocational education is still small; the structure of industries, occupations, and training levels are not suitable; the quality and effectiveness of training are not high, especially in training high-quality human resources, new industries, occupations, and advanced skills. Policies and laws have not kept up with practical requirements; investment resources for vocational education development are not commensurate. State management capacity, especially at the local level, is still limited.
The connection between the State - schools - enterprises is not tight. The form and method of training organization is slow to innovate, not diversified and flexible enough to promptly meet the needs of the labor market; retraining and regular training for workers are not focused on, not creating opportunities and encouraging workers to participate in lifelong learning...
To continue to innovate, develop and improve the quality of vocational education by 2030, with a vision to 2045, creating a breakthrough in human resource development, especially high-quality human resources with vocational skills to meet the requirements of promoting industrialization, modernization of the country and international integration in the spirit of the Resolution of the 13th National Party Congress, the Secretariat requests Party committees, Party organizations, authorities, the Vietnam Fatherland Front and mass organizations at all levels to focus on leading, directing and implementing well a number of important goals, tasks and solutions:
Firstly, the goal is to attract 50-55% of high school students to the vocational education system by 2030; retrain and regularly train about 50% of the workforce; have about 90 high-quality vocational education institutions, including a number of vocational education institutions performing the functions of national and regional centers; a number of vocational education institutions approaching the level of ASEAN-4 and G20 countries; have about 200 key industries and occupations, including 15-20 industries and occupations with outstanding competitiveness in the ASEAN region and the world. By 2045, meet the demand for highly skilled human resources of developed countries, reaching the advanced level of the world.
Second, promoting propaganda and education work, raising awareness and responsibility among cadres and party members, especially leaders, managers, heads of agencies, organizations and enterprises on innovation and development of vocational education is a major and consistent policy of the Party and State; is an important, regular and long-term task; affirms the position, role and importance of vocational education in socio-economic development, contributing to creating sustainable jobs for workers and the young generation.
At the same time, create a strong change in the awareness of learners, families and society about the significance of vocational training, vocational skills in accessing jobs, increasing income and lifelong learning opportunities. Mobilize social participation in implementing goals, tasks and solutions for vocational education, contributing to the successful implementation of strategic breakthroughs in human resource development, especially high-quality human resources.
Third, review, supplement and perfect the system of policies and laws on vocational education, ensuring that it is linked to the labor market in an open, interconnected, modern, integrated and adaptive direction. Strengthen career guidance in general education, effectively carry out streaming, increase the proportion of post-secondary students entering vocational education; implement both vocational training and cultural teaching at vocational education institutions, so that graduates have both a high school diploma and a vocational diploma that ensures quality, has the conditions to participate in the labor market and the opportunity to continue studying and improve their qualifications; have policies to encourage good and excellent students to enter the vocational education system.
Fourth , accelerate the roadmap for vocational training for youth, workers, farmers and laborers through appropriate forms of support. Honor skilled and highly skilled workers; prioritize vocational training for youth who have completed military service, police service, youth volunteers, people with disabilities and vulnerable groups. Develop vocational education in rural areas, especially difficult areas, ethnic minority areas, mountainous areas, border areas, and islands; prioritize clean land funds for vocational education. Encourage the development of private vocational education facilities with foreign investment.
Fifth, continue to review and arrange vocational training institutions under central and local agencies, ministries and branches in the spirit of Resolution 6 of the 12th Central Committee on continuing to innovate the organization and management system, improve the quality and efficiency of public service units, ensure the scale, structure and rationality of industries, occupations, training levels, standardization, modernization, quality stratification, linked to the requirements and development trends of the labor market. Focus on industries, occupations and training fields with strengths linked to the needs of the labor market. Complete the state management apparatus in the direction of streamlining, effectiveness and efficiency. Strengthen supervision, inspection and examination; periodically evaluate and classify the quality of vocational training institutions.
Sixth, innovate training content, programs, and methods, ensuring "learning goes hand in hand with practice"; upgrade and standardize training facilities, equipment, and means. Pay attention to training and fostering teachers, vocational trainers, and experts for key industries and occupations; improve the capacity of teachers and vocational education managers in a modern, high-quality direction, approaching the standards of advanced countries. Focus on vocational skills training associated with ethics education, lifestyle, discipline, soft skills, industrial style, improving foreign language proficiency, and digital skills for learners; regularly update and retrain the workforce to improve the ability to adapt to the requirements of technological innovation, digital economy development, green economy, and circular economy... Innovate the assessment of knowledge and skills of learners and workers; develop a system for assessing and certifying the quality of vocational education.
Seventh, improve the effectiveness of linkage and cooperation in vocational education between the State - schools - enterprises. Vocational training institutions proactively cooperate in training with enterprises, increase training and practice time for learners in enterprises. Encourage enterprises to participate in vocational education from recruitment, training to use, and establish practice facilities at vocational training institutions. Complete the labor market information system, linking labor supply and demand with vocational education.
Eighth, increase resources, prioritize state budget for vocational education in total state budget expenditure for education and training commensurate with the position and role of vocational education, especially for training high-quality human resources, key and spearhead industries and occupations. Quickly shift the budget allocation mechanism to ordering and assigning tasks to improve the operational efficiency of vocational education institutions. Promote socialization and public-private partnership to mobilize and effectively use many resources for vocational education development, especially for industries, fields and localities where the non-public sector can participate. Ensure equal policies for public and non-public vocational education institutions.
Ninth, proactively and actively integrate into international vocational education; enhance the exchange of information, experience, training cooperation, experts, teachers, and learners with other countries. Summarize practices, research theories, expand high-quality vocational training models through the training systems of advanced countries; absorb international experience in vocational education; promptly update new standards and technologies in vocational education. Improve the quality and effectiveness of regional and international vocational skills competitions.
To achieve the above objectives and tasks, the Secretariat requests that provincial and municipal Party Committees, Party committees, Party executive committees, Party delegations, and Party committees directly under the Central Committee organize research, disseminate, and widely disseminate the Directive to cadres, Party members, and people. Develop programs and plans to implement the Directive in accordance with the situation of the industry, locality, agency, and unit.
Strengthen Party building work in vocational training institutions; incorporate vocational training development into the socio-economic development plans of the sector and locality.
The Party Delegation of the National Assembly leads the revision, supplementation and completion of the legal system on vocational education, creating a unified and synchronous legal basis for the implementation and supervision of the implementation of the Directive; ensuring the state budget for innovation, development and improvement of the quality of vocational education.
The Government Party Committee shall lead the development of a plan to implement the Directive; review and complete sub-law documents, mechanisms and policies on vocational education; regularly monitor, inspect and evaluate the implementation situation; summarize the pilot program of training according to the curriculum sets transferred from developed countries; strengthen coordination between ministries, branches, localities and enterprises in implementing the Directive.
The Vietnam Fatherland Front and organizations at all levels shall step up the work of mobilizing people, members and union members to actively implement and supervise the implementation of the Directive.
The Central Propaganda Department shall preside over and coordinate with the Party Committee of the Ministry of Labor, War Invalids and Social Affairs and relevant agencies to organize the implementation of the Directive; propagate, guide, inspect, urge and periodically summarize and report to the Secretariat on the results of the Directive's implementation.
At the same time, disseminate this Directive to Party cells.
PV







![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the second meeting of the Steering Committee on private economic development.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/01/1762006716873_dsc-9145-jpg.webp)































































































Comment (0)