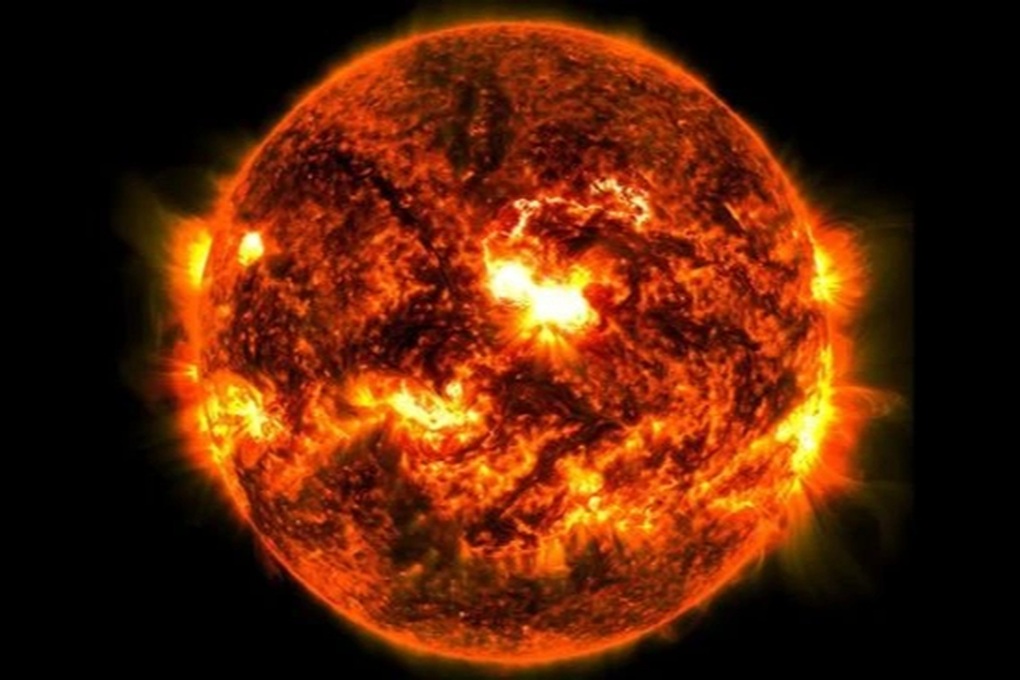

NASA's observatory captured images of solar flares occurring on October 8, 2024 (NASA).
The Sun has traditionally been seen as a symbol of stability, having existed and functioned for billions of years, but recent observations have painted a different picture.
According to analyses from the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), after solar cycle 24 (2008–2019) ended with record-low activity, a subsequent cycle (cycle 25) will continue without any significant disruption.
However, the reality is quite the opposite. The Sun's activity in the current cycle is not only exceeding expectations, but also showing signs of accelerating, breaking away from the familiar 11-year cycle pattern.
A unified analysis of long-term data by a team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory shows that from around 2008, shortly after the 24-cycle minimum, solar wind parameters tended to strengthen and have continued to increase steadily to this day.
This trend contradicts expectations of a prolonged period of "hibernation" and could lead to more extreme space weather events in the coming years.
Analysis shows a renewed upward trend has been observed since the 2008 minimum, a time when scientists believed the Sun was entering a "long sleep."
It's worth noting that while this trend is supported by many scientists, there are still many unclear aspects to the Sun's internal mechanisms.
Solar cycle reversal: Why are predictions wrong?
In science, the solar cycle is often described as an 11-year loop, comprising a peak phase (when the number of sunspots, bursts of energy, and eruptions of coronal mass increase) and a minimum phase (when activity decreases).
Astronomers have observed this phenomenon for hundreds of years, yet predicting the Sun's behavior remains extremely difficult due to the incredibly complex mechanisms within the star.
History has recorded unusual fluctuations, such as the Maunder Minimum (1645–1715) and the Dalton Minimum (1790–1830), when the number of sunspots almost disappeared for decades.
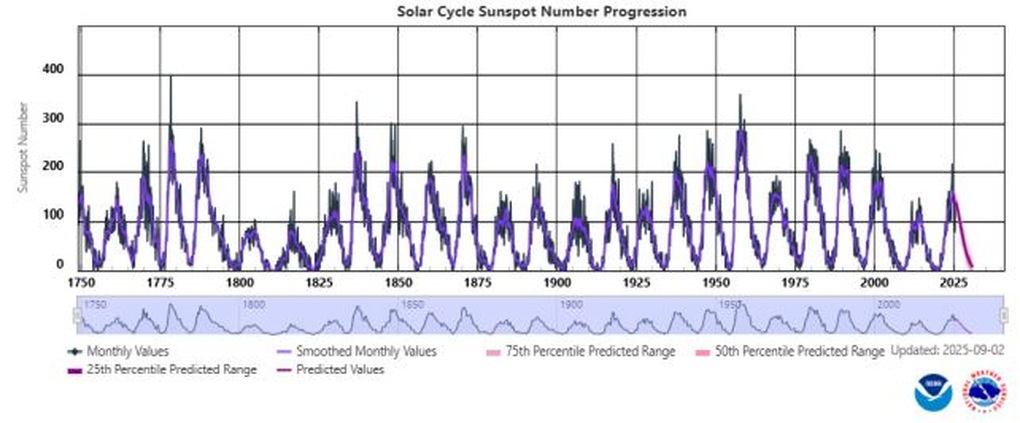
The graph shows the activity of sunspots since 1750 (Image: NOAA).
Therefore, as the solar wind continuously weakened for two consecutive cycles (1986–2008), many experts believed that Earth was entering a long-term "quiet" period.
However, new data from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) suggests the opposite. Since 2008, the solar wind has unexpectedly intensified, with its speed, density, temperature, and magnetic field strength all steadily increasing.
This signals an increase in energy inside the Sun, completely contrary to previous predictions.
The dangers of a chaotic universe.
According to plasma physicist Jamie Jasinski and colleague Marco Velli, this trend means that in the coming years, Earth could face more intense solar storms, more powerful coronal mass ejections, and even large-scale energy bursts.
These phenomena have the potential to directly affect satellite systems, telecommunication signals, GPS navigation, and the global power grid.
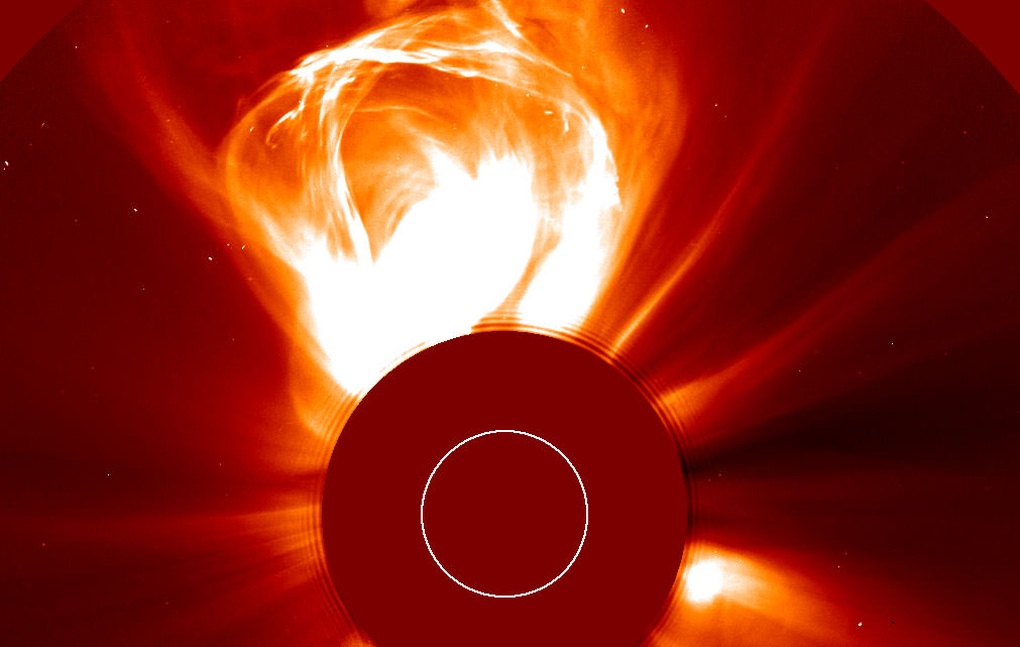

Satellite images captured a massive burst of solar radiation released from the Sun in February 2000 (Photo: NASA).
Notably, the research results are also consistent with the Hale cycle, or the 22-year magnetic loop, which is considered the "mother cycle" that governs two consecutive solar cycles. Clearly, there is growing evidence that relying solely on the 11-year cycle is insufficient to accurately assess the influence of this star.
If this assessment is correct, what is happening in cycle 25 may be just one part of a more profound transformation taking place inside the Sun.
Researchers suggest that while current solar wind pressure remains lower than it was at the beginning of the 20th century, the steady increase over the past nearly two decades raises a major question: Are we entering a prolonged period of unusual activity, or merely short-term fluctuations in the Sun's natural patterns?
Experts believe the answer can only come from continued long-term monitoring and expanding the scope of observation. This is because, while the data on sunspots is useful, it is still an incomplete piece of the puzzle.
To truly understand this "giant energy machine," humanity needs to study many other parameters simultaneously, specifically from solar wind, radiation, magnetic fields to internal motion.
As the source of life for the entire solar system, understanding its laws is not only scientifically significant but can also determine the level of safety for modern civilizations that are increasingly dependent on electronic and space technologies.
According to a NOAA report published in August 2025, the average monthly number of sunspots has reached its highest level since 2002, indicating that cycle 25 is entering its peak phase sooner than expected.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/khoa-hoc/chu-ky-mat-troi-dao-chieu-20250917073356700.htm



![[Photo] Thousands of tourists visit the Quang Trung Emperor Temple in Nghe An during the early spring season.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/02/26/1772095410680_img-9305-3882-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man inspects election preparations in Hai Phong city.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/02/26/1772095420401_ndo_br_bnd-8016-jpg.webp)



![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man working with the Hai Phong City Election Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/02/26/1772103806795_ndo_br_bnd-8224-jpg.webp)





































































































Comment (0)