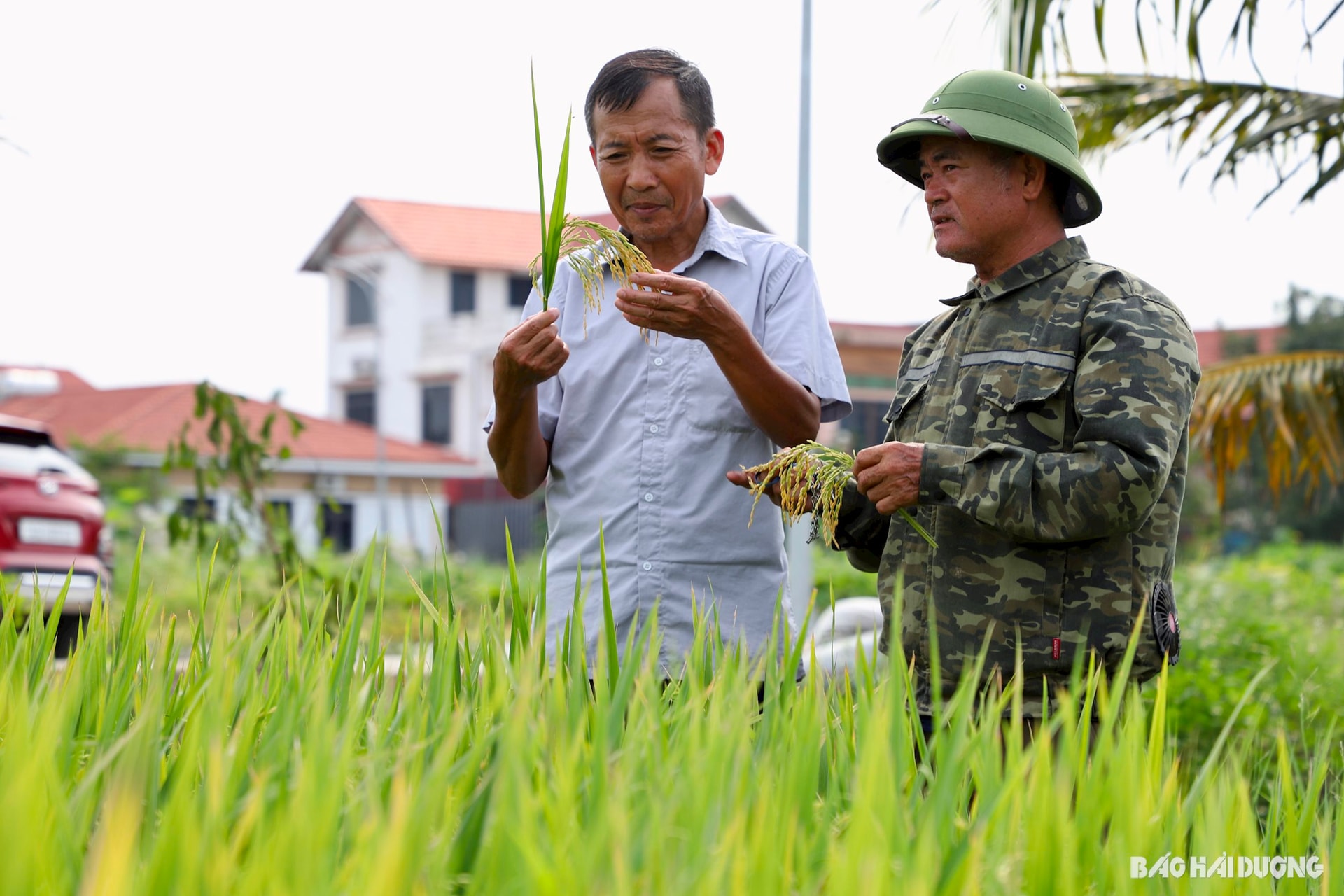

Greenhouse gases are gases that have the ability to absorb long-wave radiation (infrared) reflected from the Earth's surface after being illuminated by the sun, then disperse heat back to the Earth, causing the greenhouse effect.
This gas mainly includes Carbonic gas (CO 2 ), Methane (CH 4 ), Dinitrogen monoxide (N 2 O), Ozone (O 3 ). Greenhouse gases emitted by industrial and agricultural production activities, of which rice production has emitted a large amount of greenhouse gases, the most is CH 4 .
To produce rice to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and meet the requirements of creating carbon credits, farmers should implement the following technical measures:
Alternate flooding and drying for rice
- From transplanting to tillering: Keep a 3 - 5 cm layer of water on the field surface to limit weeds, keep the rice warm, and facilitate top dressing.
- From tillering to panicle formation, carry out alternating wet and dry irrigation: Let the water in the field dry naturally. When the water level drops below 15 cm below ground level (use a PVC pipe inserted into the field to measure the water level), then pump water to flood the field 3 - 5 cm.
- The period from when the rice begins to panicle until one week before flowering: When fertilizing the panicle, add water about 3 - 5 cm to fertilize. Then continue to water alternately wet and dry as above.
- One week before flowering to two weeks after flowering: Continue to maintain water in the field at 3 - 5 cm.
- Stage after two weeks of rice flowering until harvest: Let the water drain until harvest.
To apply this measure, it is also necessary to have a relatively complete irrigation system, proactive irrigation, and relatively flat fields. In addition, farmers need to apply the correct technical measures, noting that it should not be applied to active acid sulfate soil, saline irrigation water, or low-lying land.
Use fertilizer properly
The main cause of N2O emissions is due to excessive urea fertilizer application. Therefore, it is necessary to base on each rice variety, soil type and crop season to have the appropriate amount of fertilizer and application method. Do not apply too much urea fertilizer, or you can use other slow-release forms of nitrogen to reduce nitrogen loss when fertilizing crops.
Some other measures
- Using short-term varieties to have a short growing time in the field will limit CH4 emissions or using drought-tolerant varieties to limit flooding.
- Absolutely do not burn straw directly in the fields, causing CO2 emissions and other harmful effects. Biological products can be used to decompose straw and compost it into organic fertilizer.
TMSource: https://baohaiduong.vn/giai-phap-ky-thuat-canh-tac-lua-gop-phan-giam-phat-thai-khi-nha-kinh-414847.html




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives President of Cuba's Latin American News Agency](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F01%2F1764569497815_dsc-2890-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)







































































![[Photo] President Luong Cuong holds talks with Sultan of Brunei Darussalam Haji Hassanal Bolkiah](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/01/1764574719668_image.jpeg)





































Comment (0)