Research has shown that people with an apple-shaped body - who store more belly fat - may be at risk of serious health problems including colon cancer, compared to people with a pear-shaped body - who store excess fat in the hips, buttocks and thighs, according to the Times of India.
Why are people with apple-shaped bodies at risk of colon cancer?
A large waistline indicates a dangerous accumulation of belly fat or visceral fat that surrounds internal organs like the liver, kidneys, or even the heart. This is not the usual fat that lies just under the skin, this hidden fat can wreak havoc on the heart and increase the risk of cancer, heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and sleep apnea, among other problems.
The apple-shaped body is more common in men and is associated with higher levels of visceral fat
ILLUSTRATION: AI
Even people who are not overweight but have an apple-shaped body - indicating more visceral fat - are still at higher risk of harmful chronic diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
The apple-shaped body is more common in men and is associated with higher levels of visceral fat and a higher risk of heart disease.
In women, pear-shaped obesity is more common and is considered metabolically healthy due to higher concentrations of subcutaneous adipose tissue.
One study found that people with an apple-shaped body had a significantly higher risk of death from all causes than people with a pear-shaped body.
Apple-shaped body and colon cancer risk
Research published in the scientific journal Science Advances found that people who are obese or have a body mass index (BMI) over 30 have a 10% higher risk of developing colon cancer than people of a healthy weight.
However, the study also showed that people who were not obese but had a lot of belly fat or had an apple-shaped body had a 12% higher risk of developing colon cancer than those with smaller waists, according to the Times of India.
Heart disease risk in people with apple-shaped bodies
Research published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that a large waistline is directly linked to a higher risk of heart disease. For every 10cm increase in waist circumference, the risk of heart disease increases by 3% in women and 4% in men.
Men are more likely to have an apple-shaped body, but some women can develop an apple shape after menopause. They are also at higher risk for heart problems even if they are a normal, healthy weight.
Too much belly fat is strongly linked to higher cholesterol levels, high blood pressure and a higher risk of heart disease, including heart attack and stroke.
According to some studies, a larger midsection is also linked to a higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
Too much belly fat also increases your risk of fatty liver disease, which can lead to liver damage or cirrhosis if left untreated.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/nguoi-nhieu-mo-bung-co-nguy-co-mac-benh-tim-ung-thu-dai-trang-cao-hon-185250211092046413.htm





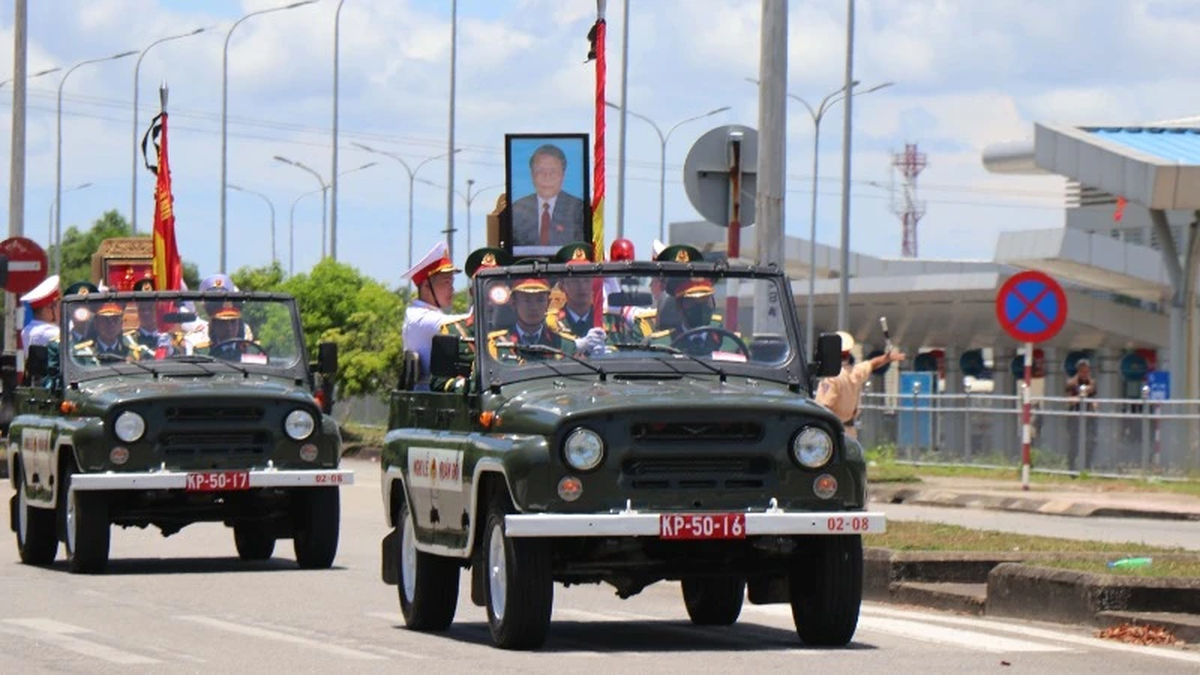
![[Photo] The coffin of former President Tran Duc Luong arrives in Quang Ngai](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/25/1f1aca0d92ab47deae07934e749b35e6)
![[Photo] Funeral of former President Tran Duc Luong in Quang Ngai](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/25/ccf19a3d8ea7450bb9afe81731b80995)
![[Photo] Welcoming ceremony for Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh and his wife on an official visit to Malaysia](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/25/dc30203c3ae24da3990266ec3b29bb2d)














































































Comment (0)