Scientists have identified a plateau in Chile's Atacama Desert that receives as much solar radiation as Venus.
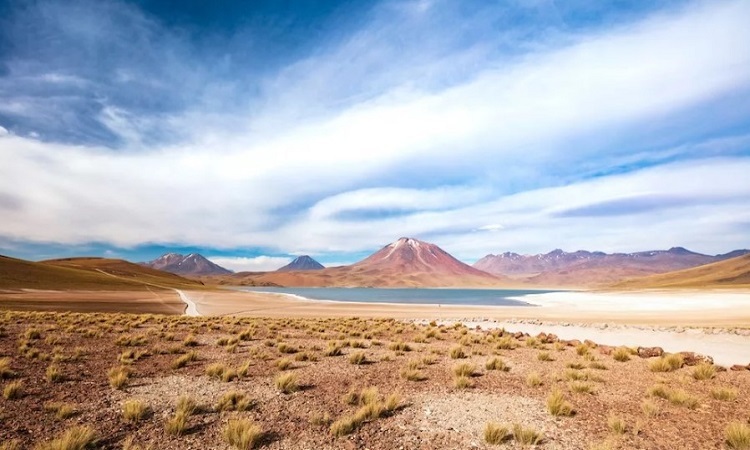
Altiplano plain in the Atacama Desert. Photo: Pawel Toczynski
The sunniest spot on Earth is the Altiplano in the Atacama Desert, an arid plain near the Andes Mountains in Chile that receives as much sunlight as Venus. Though typically cold and dry, this sun-drenched region at an altitude of 13,000 feet (4,000 meters) receives more sunlight than places closer to the equator or higher, according to a study published in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, Live Science reported on July 21.
The Atacama Desert is special for many reasons. It is the oldest desert on Earth, the driest outside the polar regions, and possibly the clearest place to observe the night sky. Chile's Altiplano is also notable for its solar radiation, the amount of light energy emitted by the Sun that reaches Earth. Scientists have measured a world record of 2,177 watts per square meter on the plateau. For comparison, radiation at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is about 1,360 watts per square meter.
“That's actually the amount of radiation you would get in the summer if you were standing on Venus,” said study leader Raul Cordero, a climate researcher at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands.
The comparison is remarkable because Venus is 28% closer to the Sun than Earth. The average solar radiation over the plains is 308 watts per square meter, another world record, more than twice as high as in central Europe and the East Coast of the United States.
“As solar radiation passes through the atmosphere, it is absorbed by water vapor and scattered by clouds and aerosols,” said Seiji Kato, an atmospheric scientist at NASA. “However, locations above the water vapor layer, where there are fewer clouds and aerosols, receive more sunlight.”
Another reason Chile is so hot is because of its location in the Southern Hemisphere. This is especially true in the summer when the Earth’s orbit is closer to the Sun, resulting in a spike in radiation levels, up to 7% higher than in the Northern Hemisphere. While satellite data suggests this is the sunniest region in the world, new research helps confirm and explain the reasons behind such high radiation levels.
According to VNE
Source



























































































Comment (0)