I am pregnant and have hepatitis B, the virus level is not dangerous. Can the disease be transmitted to the baby? How can I prevent the disease for my child? (An Thao, 28 years old, Hue )
Reply
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnavirus family. Acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection does not affect fetal development. Pregnant women with untreated hepatitis B have a 90% chance of transmitting the virus from mother to child. If the mother is positive for HBeAg antigen and has a high level of hepatitis B virus (HBV DNA), the risk of transmission to the child is higher. About 90% of children infected with hepatitis B virus from their mothers during the perinatal period (from the 28th week of pregnancy to the end of the first week after birth) will develop chronic hepatitis.
In case you are infected with hepatitis B virus but the virus level is not dangerous, it is completely possible to prevent infection to your child by:
During the last 3 months of pregnancy, pregnant women need to be tested, monitored and given short-term medication to reduce the amount of hepatitis B virus in the blood, in order to reduce the possibility of transmitting hepatitis B virus from mother to child during labor and delivery.
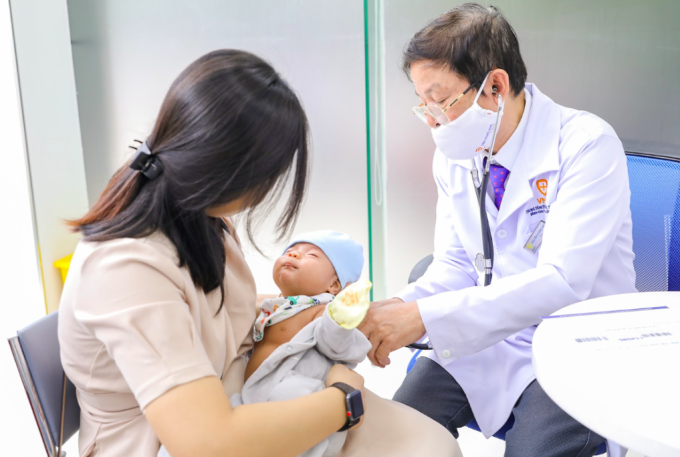

Children are screened before vaccination at VNVC. Photo: Moc Thao
Immediately after birth, the baby needs to be injected with hepatitis B immune serum (preferably within the first 6 hours) and vaccinated with hepatitis B vaccine within the first 24 hours - the sooner the better. After that, continue to give the baby a single dose of hepatitis B vaccine or the hepatitis B vaccine component in the combined vaccine doses in full and on schedule from the second month of age onwards.
After that, it is necessary to monitor and test the child's serology including HBsAg and anti HBs when the child is 9-12 months old (best at 12 months old or 1-2 months after the full hepatitis B regimen if the child is vaccinated late) to assess the child's health status.
Vietnam is a country with a high prevalence of hepatitis B virus, while hepatitis B is very likely to progress to cirrhosis and liver cancer, so it is very important to pay attention to vaccination on schedule and with enough doses. For newborns (including those whose mothers are infected with hepatitis B), hepatitis B vaccination will not require testing because the vaccine has a 95% protection rate.
The VNVC Vaccination Center system has a full range of 6-in-1 vaccines Infanrix Hexa (Belgium)/ Hexaxim (France) to prevent 6 diseases: Whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus, polio, hepatitis B and diseases caused by HIB; hepatitis A vaccine Havax (Vietnam), hepatitis B vaccine Heberbiovac (Cuba), Gene-HBvax (Vietnam) and Euvax B (France). In particular, Twinrix vaccine (Belgium) helps prevent both hepatitis A and hepatitis B in just one injection, providing long-term immunity.
You can contact the hotline or go directly to VNVC Centers nationwide for advice and to schedule vaccination for your child.
Dr. Pham Hong Thuyet
Medical Management, VNVC Vaccination Center System
Source link






























![[Infographic] Vietnam-Senegal traditional friendship](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/23/4c96a604979345adb452af1d439d457b)









































































Comment (0)