According to a report from the Pasteur Institute in Ho Chi Minh City, the southern region recorded 12 cases of meningococcal disease in the first four months of this year, spread across eight of the 20 provinces and cities. Compared to the same period last year, the number of cases increased by nine, showing a worrying increase in the disease.
Cases appear sporadically in the community, but are mainly concentrated in high-risk areas such as densely populated areas, cramped living environments, poor sanitation conditions, and places with large concentrations of people with continuous movement between new and old people.
Experts warn that if drastic measures to control the epidemic are not implemented promptly and strictly following the instructions of the Ministry of Health , there is a possibility that more new cases will appear in the coming time. This is a strong reminder for the authorities and the community to proactively repel the risk of a wider outbreak.
What is meningococcal meningitis?
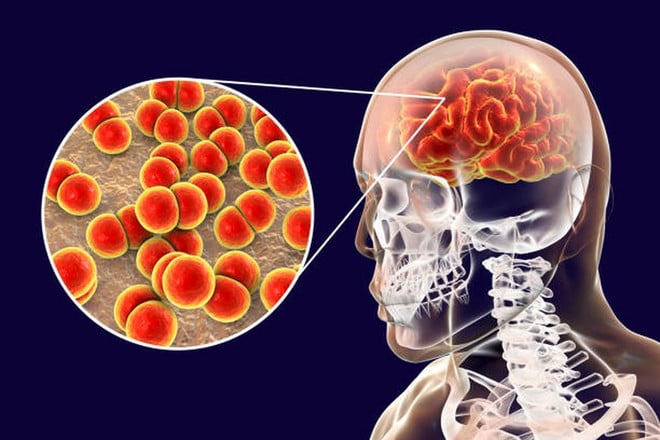
Meningococcal meningitis is an acute bacterial infection that develops rapidly, with symptoms such as high fever, severe headache, nausea with vomiting, stiff neck, and often the appearance of star-shaped hemorrhagic rash or blisters on the skin. The patient may fall into a state of drowsiness or coma. In some cases, the disease progresses rapidly with symptoms of sudden fatigue and exhaustion, accompanied by hemorrhagic patches and severe shock. Currently, if diagnosed early and treated actively, the mortality rate can be reduced to 5% to 15%.
Meningococcal disease has a wide range of clinical manifestations, including acute purulent meningitis, meningococcemia, arthritis, and meningococcal endocarditis. In addition, many cases of meningococcal infection are manifested by fever and/or mild nasopharyngitis. In endemic areas, the proportion of people carrying the pathogen in the throat but without clinical symptoms ranges from 5% to 10%.
Notably, asymptomatic infections are common during outbreaks and serve as a significant source of community spread.
(Photo: Getty images)
The natural reservoir of meningococcus is humans. Therefore, the main source of infection comes from patients and asymptomatic carriers. In the context of an epidemic, the proportion of people infected with the bacteria without showing typical clinical symptoms can exceed 25%, while the number of healthy people carrying meningococcus bacteria can account for over 50%. These sources of infection play an important role in the spread of the disease in the community.
The incubation period of the disease ranges from 2 to 10 days, but most commonly from 3 to 4 days. In most cases, the bacteria cause inflammation only in the pharyngeal mucosa. However, more serious conditions, when the bacteria invade the blood and spinal meninges, causing typical pathology, rarely occur.
The duration of infectiousness depends on the presence of meningococcal bacteria in the infected person's nasopharynx. After starting antibiotic treatment, the bacteria usually disappear from the nasopharynx within 24 hours. Once outside the body, the bacteria do not survive long in nasopharyngeal secretions.
Although Penicillin can limit the growth of meningococcal bacteria, it cannot completely eliminate them in the nasopharynx.
What are the symptoms of meningococcal disease?
The early symptoms of meningococcal disease can be easily confused with common infections or the flu, making early diagnosis a challenge. During the first 4-12 hours, warning signs may include:
- Symptoms begin with a sudden high fever, which can reach up to 41 degrees Celsius and does not subside despite using common fever-reducing medications.
- Accompanied by severe headaches, muscle aches and pains that make the body feel tired.
- The patient may feel a sore throat or develop a mild cough, along with nausea, vomiting, or even diarrhea.
- Patients often become sensitive to light, accompanied by cold hands and feet, and pale or ashen skin.
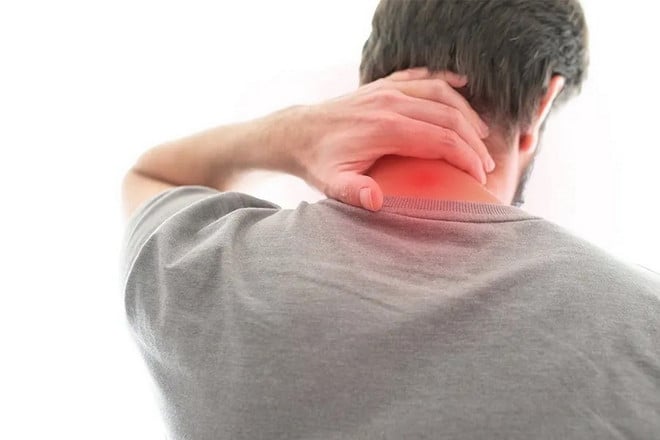
- When you bow your head, your neck may become stiff and uncomfortable.
- The initial characteristic skin symptom is erythematous papules, however, they will quickly transform into petechiae or bruises after 1-2 days from the onset of fever. These signs often spread quickly, can form in the form of maps or blisters, mainly concentrated in the two lower limbs.
(Photo: Getty images)
Why do diseases increase in the summer?
Meningococcal meningitis can occur year-round, but outbreaks often peak in the summer, when the climate becomes hot and humid.
Several factors contributed to the increase in cases during this period including:
Increased close contact
Activities such as summer camps, festivals, and travel often bring many people together in the same place and participate in group activities. This facilitates the spread of bacteria through respiratory droplets from the nose or throat of infected people when they cough, sneeze, or talk.
Dehydration and decreased resistance
Severe heat, lack of personal hygiene or inadequate nutrition can easily weaken the immune system, especially in young children and people with underlying medical conditions. A dehydrated body also becomes more susceptible to harmful agents.
(Photo: Getty images)
Changes in the mucosal immune system of the nose and throat
Summer weather with high temperatures, dust and air pollution (especially in urban areas) makes the respiratory tract drier and more vulnerable. This creates favorable conditions for Neisseria meningitidis bacteria to grow, infect and cause disease./.
(Vietnam+)
Source: https://www.vietnamplus.vn/vi-sao-benh-viem-nao-mo-cau-thuong-bung-phat-vao-mua-he-post1039139.vnp




![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam chairs a working session with the Central Internal Affairs Commission](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/3b7790f499da45b2803d8ae253207ef1)
![[Photo] Press delegation meeting to visit Truong Sa and DK1 Platform](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/6b8d232877ec421a9e8187d83b9f8006)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting on draft Resolution of National Assembly on International Financial Center in Vietnam](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/d398664ff1a140629169ea5a24e1b4d0)
![[Photo] T&T 1 and Ho Chi Minh City 1 People's Police Teams won the men's and women's team championships](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/39db06ae67cb4001b7a556e8d9a56d07)













































![[Infographic] Investment project to build Tu Lien bridge and roads at both ends of the bridge](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/23/3c167ece69cb4aecb3e55de5ebc38b88)


























![[Podcast] Week introducing more than 500 OCOP products in Hanoi](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/d144aac2416744718388dbae3260e7fd)





Comment (0)