Tongue discoloration, pain, swelling, ulcers and changes in taste when eating can warn of tongue diseases such as thrush, fissured tongue, leukoplakia.
Thrush
Thrush is a fungal infection of the mouth that commonly occurs in young children and adults with weakened immune systems, such as those infected with HIV.
The disease causes white lesions on the tongue, cheeks, gums, tonsils, or roof of the mouth. Symptoms include loss of taste; redness and soreness inside and at the corners of the mouth; and difficulty swallowing. Thrush is usually treated with antifungal medications.
Middle rhomboid glossitis
This is a special form of Candida infection, characterized by a red atrophic patch in the midline of the tongue, at the junction of the anterior two-thirds and posterior one-third of the tongue. The disease usually has smooth, red, flat or raised nodules 2-3 cm; usually occurs in men 30-50 years old, sometimes with little or no symptoms.
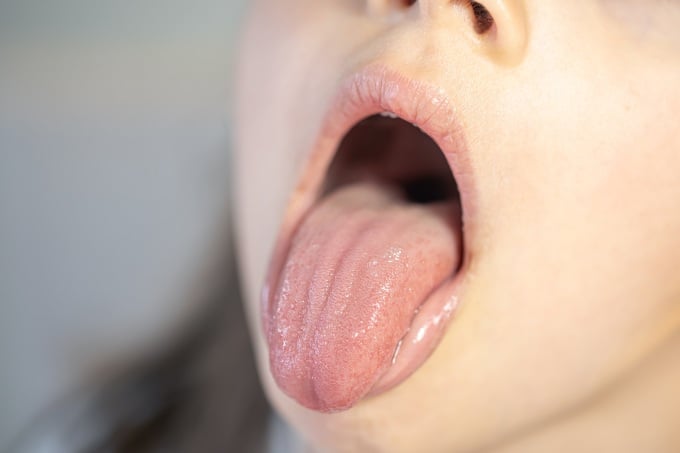
Taste changes warn of tongue disease. Photo: Freepik
Fissured tongue
Fissured tongue creates small grooves on the surface. The fissures can be deep or shallow, multiple or just one. The condition is more common in older people, and affects men more than women. Fissured tongue is not contagious and is not dangerous.
Atrophic glossitis
Atrophic glossitis can occur due to trauma, allergic reactions, diseases, anemia, malnutrition. Vitamin and mineral deficiencies such as iron, folic acid, zinc, vitamin B12 can also lead to this disease. Symptoms include swelling, burning or itching of the tongue, tongue discoloration, difficulty swallowing.
Map tongue
Geographic tongue is a benign oral inflammatory condition characterized by loss of epithelium, especially the papillae on the dorsum of the tongue. Geographic tongue is also called benign migratory glossitis because the lesions move around. Lesions sometimes appear on the cheeks, under the tongue, on the gums, or on the roof of the mouth.
Hairy tongue
The condition is characterized by an abnormal hairy coating on the surface of the tongue, with flaking of the tissue covering the tongue. This condition occurs due to lack of stimulation to the tip of the tongue.
The appearance of hairy tongue varies depending on the cause. The tongue can be green, white, brown, or pink. If yeast or bacteria are present, the tongue will appear black. Hairy tongue can cause an unusual taste, burning sensation, and difficulty swallowing.
Leukoplakia
This condition is characterized by white spots or patches appearing on and under the tongue and inside the cheeks. It is often caused by heavy smoking and alcohol use.
Leukoplakia can be a sign of developing tongue cancer. Determining cancer depends on the abnormal cells and the shape and size of the white patches, usually by biopsy.
Tongue burn
This is a condition in which the roof of the mouth and tongue feels hot and painful, often with sudden onset and then disappears. The main symptom of a burn tongue is a feeling of dry mouth.
People with diabetes, vitamin B12, B9, iron deficiency or oral yeast infection often have symptoms of burning tongue.
Enlarged tongue
Macroglossia, also known as macroglossia, is a condition in which the tongue becomes abnormally enlarged. Symptoms include slurred speech, difficulty eating and swallowing, snoring, mouth ulcers, and abnormal development of teeth and jaws.
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, congenital hypothyroidism, and Down syndrome can lead to macroglossia. Treatment with surgery and speech therapy can improve speech, chewing, and appearance.
Mai Cat (According to Very Well Health )
| Readers ask questions about ear, nose and throat diseases here for doctors to answer |
Source link


![[Photo] Comrade Nguyen Duy Ngoc holds the position of Secretary of the Hanoi Party Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762234472658_a1-bnd-5518-8538-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Panorama of the Patriotic Emulation Congress of Nhan Dan Newspaper for the period 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762252775462_ndo_br_dhthiduayeuncbaond-6125-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] The road connecting Dong Nai with Ho Chi Minh City is still unfinished after 5 years of construction.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762241675985_ndo_br_dji-20251104104418-0635-d-resize-1295-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Ca Mau "struggling" to cope with the highest tide of the year, forecast to exceed alert level 3](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762235371445_ndo_br_trieu-cuong-2-6486-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Ho Chi Minh City Youth Take Action for a Cleaner Environment](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762233574890_550816358-1108586934787014-6430522970717297480-n-1-jpg.webp)





























































































Comment (0)