Preventing obesity and overweight in children is related to diet, exercise, sleep and lifestyle.
According to Master, Doctor Nguyen Anh Duy Tung - Nutrihome Nutrition Clinic System, preventing obesity in children is very important, helping to minimize negative impacts on health and treatment costs. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that obese children and adolescents are at higher risk of asthma, type 2 diabetes, heart disease and some other diseases.
People who are obese as children are more likely to become obese as adults. Adults who are obese are at higher risk of stroke, certain cancers, and mental health conditions.
Treating childhood obesity with medications and bariatric surgery can be costly. Complications from these medical interventions can also pose some risks. To prevent childhood obesity, Dr. Tung suggests some ways below.
Diet
Establishing a balanced, nutritious eating plan can help prevent obesity in children. In particular, parents should pay more attention to green vegetables, fruits and foods of plant origin. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that a diet to prevent obesity in children should limit foods high in calories, fat and sugar, along with increasing fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains and nuts.
Eating with your family can help your child become accustomed to healthy eating and aware of the dangers of overeating.
Workout Mode
Exercise is another important factor in preventing childhood obesity. Exercise not only helps prevent obesity but also helps strengthen bones, lower blood pressure, and reduce stress and anxiety in children. Therefore, parents should encourage their children to exercise every day.
Physical activity recommendations for children depend on age. According to the CDC, children ages 3 to 5 should be active most of the day. Older children, tweens, and teens are encouraged to be active for at least 60 minutes a day.
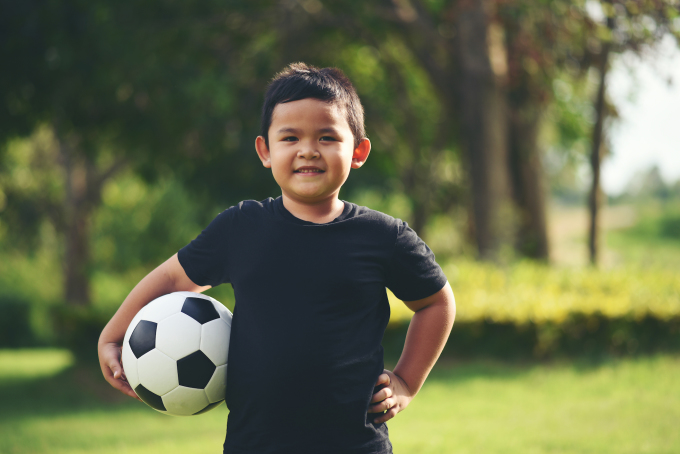

Regular, moderate exercise in children is the key to preventing obesity and overweight. Photo: Freepik
Exercise recommendations for children aged 6–17 years are moderate to vigorous intensity, including a combination of aerobic exercise and muscle- and bone-strengthening exercise.
Some recommended exercises for children include: jumping rope, jogging, aerobics, cycling, sports such as swimming, badminton, volleyball, basketball...
Sleep
There is growing evidence of the negative effects of sleep deprivation on weight gain in adults and children. Sleep deprivation affects several hormones that influence weight, activity levels, and calorie intake.
Dr. Tung warns that children who lack sleep are at high risk of gaining unwanted and unhealthy weight. Staying up too much can make children eat more and sleeping less can also make them lazy because they feel tired and exhausted.
Current obesity prevention strategies often involve improving sleep. The US CDC recommends that establishing a suitable bedtime can help prevent childhood obesity. Accordingly, the amount of sleep children and adolescents need to maintain each day is: toddlers (1-2 years old) 11-14 hours, preschoolers (3-5 years old) 10-13 hours, school-age (6-12 years old) 9-12 hours, adolescents (13-18 years old) 8-10 hours.
Some ways to help your child sleep better include: establishing a consistent sleep routine; keeping the bedroom dark, quiet, comfortable and relaxing; avoiding the use of electronic devices before bed; not eating or drinking a few hours before bed; exercising daily...
According to Dr. Tung, children who spend a lot of time playing games and watching electronic devices can lead to obesity. Parents should limit their children's playing time and replace it with other healthy activities such as walking together, exercising or helping with housework such as sweeping and mopping the floor...
Bao Bao
Source link








































































































Comment (0)