In 1900, there were only about 3,000 cars on the roads of France. To increase the demand for cars and therefore tires, tire manufacturers and brothers Édouard and André Michelin published a guide for French drivers called Guide Michelin .
The first Michelin Guide printed 35,000 copies, and included maps, instructions on how to repair and change tires. The book also included a list of restaurants, hotels, garages and gas stations along popular routes in France.
According to Escoffer.edu , since there were only a few thousand cars in all of France, the guidebook was given away for free in the hopes of creating demand for the cars.
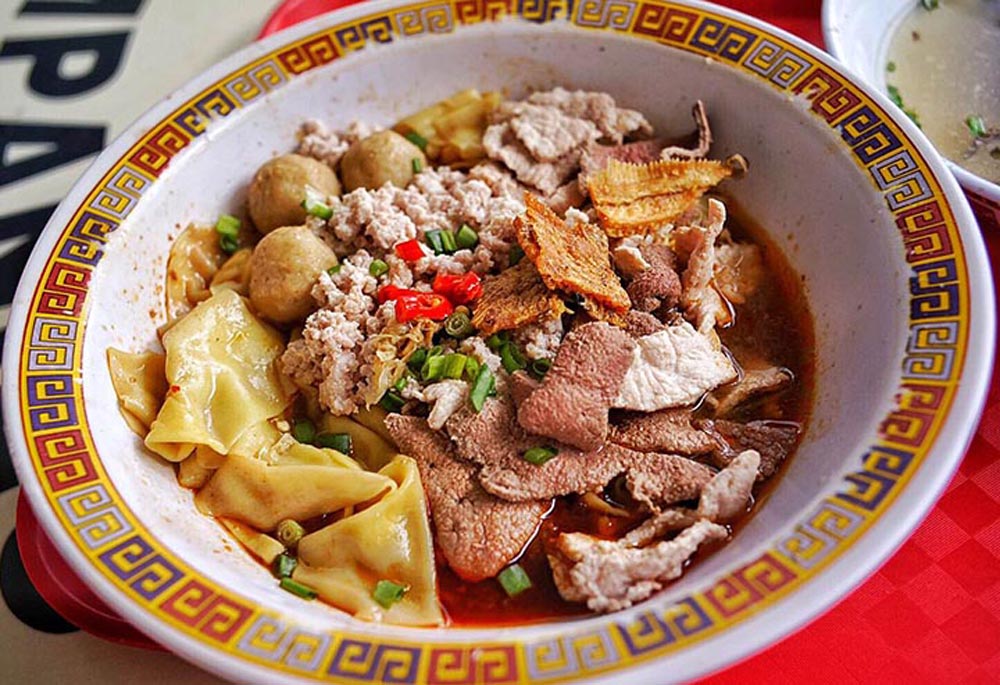

A bowl of pork noodles costs just S$5 at Tai Hwa Hill Street Pork Noodles in Singapore, one of only two street food stalls in the world to receive a Michelin star
During its first decade, the Michelin Guides grew rapidly and were available throughout Europe and North Africa. While the guides contained valuable information about restaurants, the Michelin brothers' ultimate goal was to generate sales and profits for their tire business.
The first Michelin star rating was introduced in 1926. Restaurants in France were awarded one star if they were considered “fine dining establishments”. In 1931, the rating system was expanded to a three-star Michelin rating, which it continues to this day. The editors of the Michelin Guide began awarding stars to fine dining establishments in 1926.
Initially, only one star was awarded. Then, in 1931, a 1, 2, and 3 star system was introduced. Finally, in 1936, the criteria for the star rating were published.
In 1955, the Michelin Guide introduced a rating system to recognize restaurants that served high-quality food at moderate prices, called Bib Gourmand. Because the ratings are customized by region and country based on the cost of living, Bib Gourmand gives diners the opportunity to eat well without breaking the bank.
In the early years after World War II, the lingering effects of wartime shortages led the Guide Michelin to impose a two-star limit. By 1950, the French edition of the Guide Michelin listed 38 restaurants that had been rated as qualified. The first Italian Guide Michelin was published in 1956, followed by the British in 1974.

The first Michelin Guide was published in 1900.
In 2005, the Michelin Guide was first published in the United States, featuring 500 restaurants in the five boroughs of New York City and 50 hotels in Manhattan. In 2007, the Michelin Guide Tokyo was launched. As of 2013, the Michelin Guide is published in 14 editions in 23 countries. The top 5 countries with Michelin-starred restaurants are: France (758 restaurants), Japan (554), Italy (432), Germany (384) and the United States (276).
How does a restaurant get a Michelin star?
First, the Guide Michelin team selects a number of restaurants in specific locations for an anonymous reviewer to inspect. After the reviewer visits the selected restaurant, they write a comprehensive report on the overall dining experience, including the quality and presentation of the dishes, along with many other evaluation criteria. The Guide Michelin reviewers then meet to analyze the reports and discuss in depth which restaurants deserve Michelin stars.
Chef Curtis Duffy collaborated with Michael Muser to build Grace restaurant in Chicago (USA), which was honored with three Michelin stars for four consecutive years, from 2015 to 2018. In July 2020, Duffy opened a new restaurant called Ever, which won two Michelin stars.
The five criteria for evaluating Michelin-starred restaurants include: Product quality; Mastery of flavors and cooking techniques; The chef's personality expressed in the dining experience; Value of the dish in terms of money; Consistency and consensus among inspectors.
According to Guide.Michelin.com , restaurants are awarded stars based on the quality of the food served, not the individual. World-class dining is often a team effort, not a one-person effort.
The Michelin Guide is updated annually, and restaurants can lose their stars if they close during the year of review or fail to maintain their standards for inclusion in the next edition of the guide. Conversely, the star rating remains unaffected even if a restaurant's head chef decides to leave mid-year and a new chef comes in.
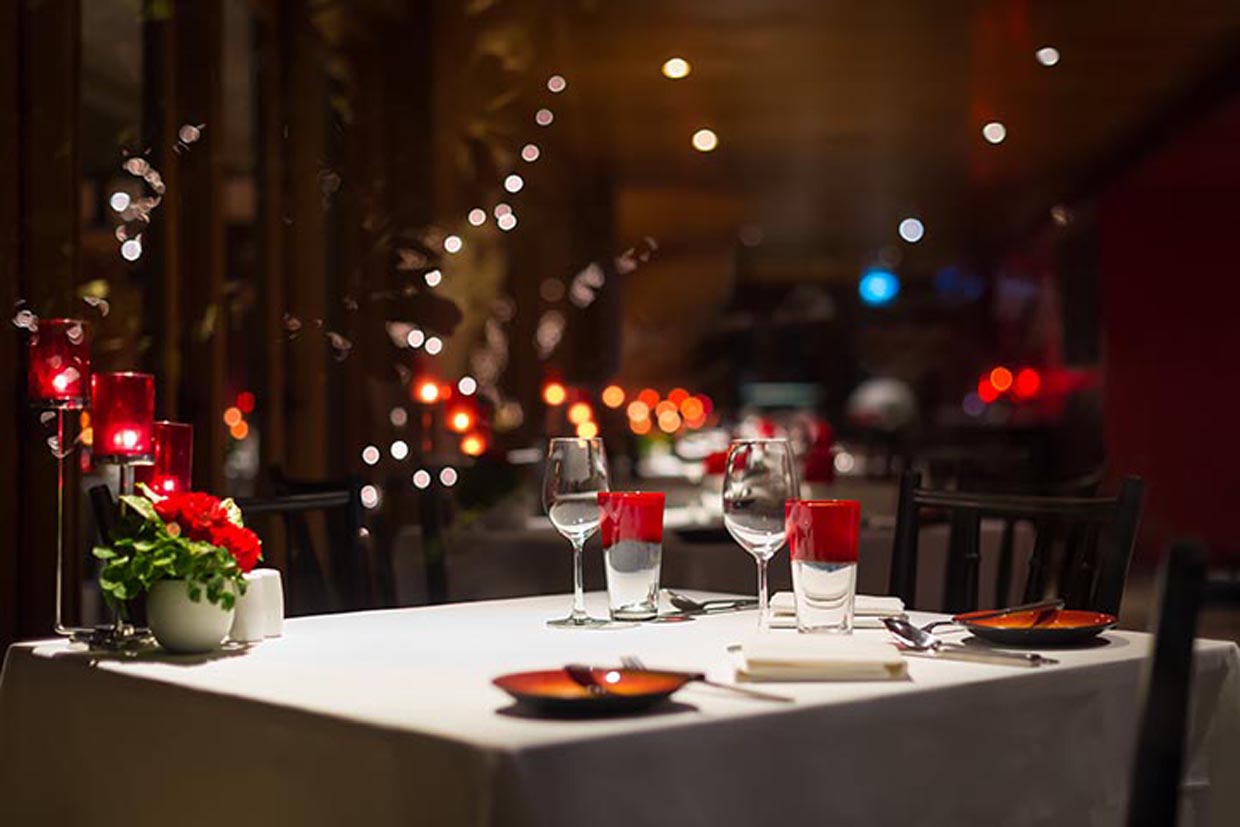

Food presentation is also one of the conditions for receiving a Michelin star.
The five criteria for evaluating Michelin-starred restaurants include: Product quality; Mastery of flavors and cooking techniques; The chef's personality expressed in the dining experience; Value of the dish in terms of money; Consistency and consensus among inspectors.
Although chefs do not receive Michelin stars, head chefs are often recognized for the success of their restaurants. Therefore, many young chefs dream of one day leading a Michelin-starred restaurant.
One way to start this journey is to attend culinary school. Culinary arts schools introduce students to a variety of topics including food safety, world cuisines, flavor development, and entrepreneurship. But students don’t just learn about these topics in the classroom; they practice in the kitchen and ultimately test their skills through a culinary internship.
Restaurants that receive Michelin stars are filled with pride, gain prestige, increase customer exposure, and grow their business. However, due to the extremely high expectations of the rating system, there is a growing trend of Michelin star rejections around the world. Some restaurant owners have even requested that their Michelin star ratings be removed, feeling that the star system’s expectations are unreasonable and restrict the creativity of chefs.
Source link
























![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man visits Vietnamese Heroic Mother Ta Thi Tran](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/20/765c0bd057dd44ad83ab89fe0255b783)




































































Comment (0)