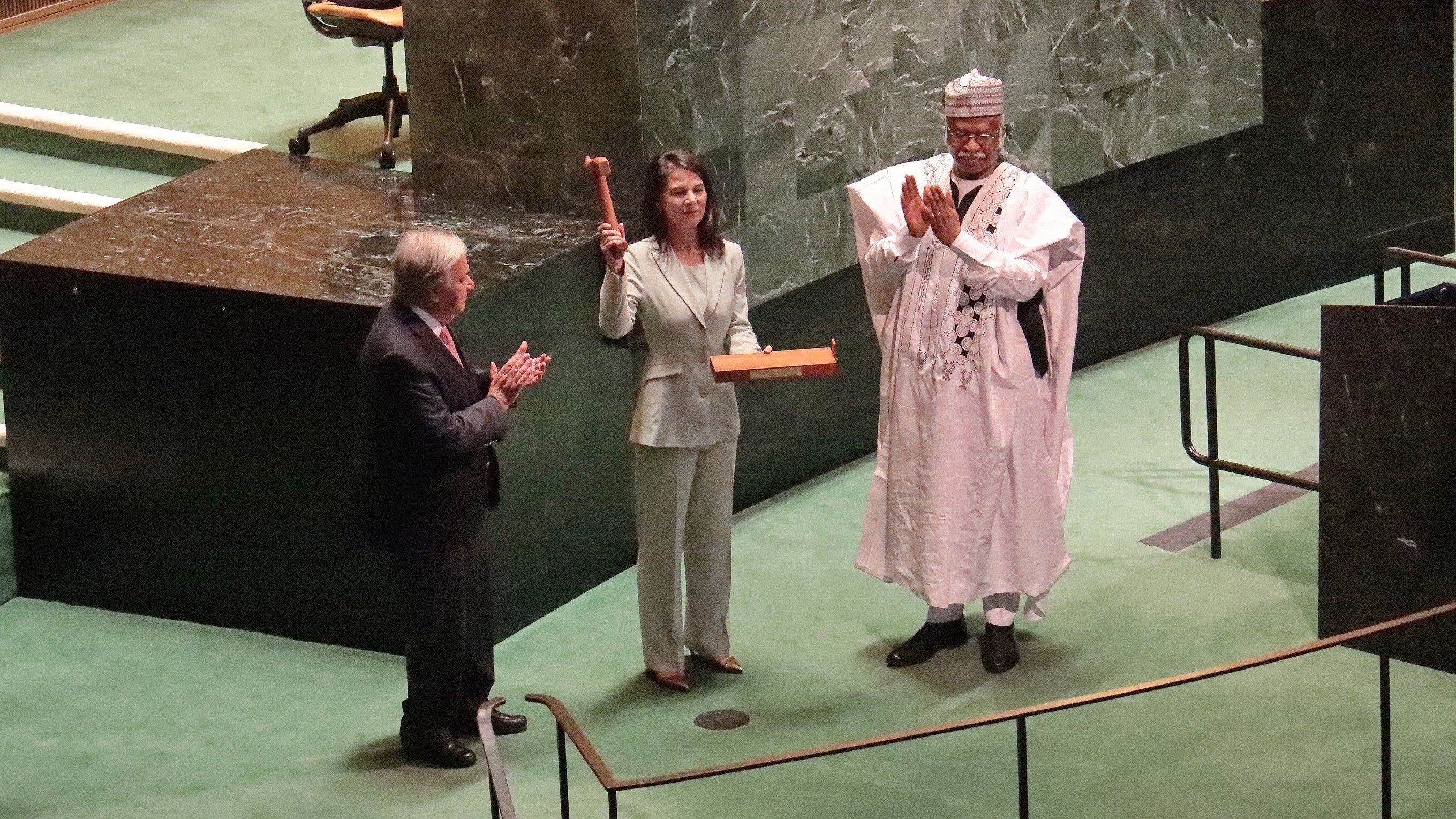

UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres witnessed the handover ceremony of the presidency of the 79th General Assembly from Mr. Philemon Yang to Ms. Annalena Baerbock_Photo: VNA
Position of President of the United Nations General Assembly
The birth of the United Nations in 1945 marked a major turning point in the history of international relations. After the devastating devastation of World War II, the United Nations was established to prevent the risk of war, maintain international peace and security, and promote global cooperation and development. Of the six main organs stipulated in the United Nations Charter, the United Nations General Assembly is the most comprehensive and democratic body, where all member states have equal voting rights, regardless of their size or overall national strength.
Unlike the United Nations Security Council - the body that concentrates decision-making power on the five permanent members and mainly deals with international security issues, the United Nations General Assembly operates on the principle of sovereign equality, comprehensively considering issues in all fields. The United Nations General Assembly is where 193 member states exchange, consult and orient solutions to global issues, from peace, security, disarmament to development, human rights, humanitarian, etc. Although the resolutions of the United Nations General Assembly are not legally binding, they have profound political and symbolic significance, reflecting the will and common voice of the international community.
As the head of the United Nations General Assembly, the President of the United Nations General Assembly holds one of the important leadership positions in the United Nations system. The two documents associated with this position are the United Nations Charter and the Rules of Procedure of the United Nations General Assembly. Article 21 of the United Nations Charter states that the United Nations General Assembly will elect the President of the United Nations General Assembly for each session, which lasts approximately one year, starting in September each year. The specific functions and duties of the President of the United Nations General Assembly are stipulated in the Rules of Procedure, notably Rule 30 (election), Rule 35 (conducting the session) and Rule 55 (recommending improvements to the efficiency of operations). Accordingly, the President of the United Nations General Assembly is responsible for running the session, directing discussions, determining priorities, promoting exchanges between member states and facilitating consensus. This position not only has the meaning of coordinating the work of the United Nations General Assembly, but also has profound political and symbolic value for the international community.
The evolution of the position of President of the United Nations General Assembly from 1946 to present
Over the past 80 years, the role and activities of the United Nations General Assembly have been continuously strengthened and expanded, especially the scope of the agenda has covered most of the urgent and high-priority issues of the international community. Along with that process, the position of President of the United Nations General Assembly has also undergone profound developments. From assuming a procedural function, the President of the United Nations General Assembly has now become an influential factor in the global governance system, contributing to promoting institutional reform, proposing initiatives and guiding discussions on strategic issues.
The development process of the role of President of the United Nations General Assembly can be summarized through the following stages:
1946 - 1950: In the early years of its establishment, the President of the United Nations General Assembly was mainly responsible for presiding over plenary sessions, coordinating discussions and ensuring compliance with processes and procedures. The President of the United Nations General Assembly had the power to control the proceedings of all sessions, including the right to propose speaking time, list of speakers, pause or postpone sessions. However, the scope of authority at that time was limited to procedural aspects, with almost no significant impact on the policy-making and decision-making process. During this period, the President of the United Nations General Assembly did not have its own Secretariat, had a limited operating budget, and depended on the support of the United Nations Secretariat and the coordination of member states, especially major countries. Therefore, the role of the President of the United Nations General Assembly was mainly ceremonial.
Despite its limited powers, the skillful coordination, balance and harmonious handling of procedural and membership issues have contributed to shaping the image of the President of the General Assembly as neutral, respecting the principle of consensus and promoting constructive dialogue. The President of the General Assembly is elected annually by rotation among member states, based on the principle of rotation among the five regional groups. This practice aims to ensure regional representation and balance in the leadership of the General Assembly.
Period 1950 - 1970: This was a period of great political upheaval in the world , notably the decolonization movement and the East-West confrontation during the Cold War, leading to a deadlock and stagnation in the operations of many United Nations agencies. In that context, the role of the President of the United Nations General Assembly was gradually expanded and made more substantial, especially the intermediary and coordination function to handle complex conflicts and crises.
A key milestone in this period was Resolution 377 (V) of 1950, commonly known as the “Unite for Peace” Resolution. Based on this resolution, in 1956, the United Nations General Assembly convened its first emergency special session to discuss the Suez Canal crisis. The session adopted a call for an immediate ceasefire and established the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF), the organization’s first peacekeeping force. This demonstrated that, in exceptional circumstances, the President of the United Nations General Assembly could play a coordinating role, contributing to promoting solutions to complex international problems.
The early 1960s marked an important turning point when the wave of decolonization spread, causing the number of member states to increase rapidly from 51 to 114 countries. In response to the new requirements of the situation, the United Nations General Assembly adjusted its organizational structure, increased the number of Vice Presidents of the United Nations General Assembly and established a number of specialized committees to meet the needs of discussing and handling global issues. Along with that, the President of the United Nations General Assembly was assigned a greater responsibility in coordinating an increasingly rich and complex agenda, reflecting the diverse interests of the member community, especially the newly joined countries.
Entering the 70s of the 20th century, the role of the President of the United Nations General Assembly was closely linked to the task of coordinating discussions and seeking consensus on important issues, such as establishing a new international economic order, disarmament, and eliminating apartheid. Since then, the President of the United Nations General Assembly has not only run the proceedings, but also held the position of a bridge to promote dialogue, reconcile the interests of developed and developing countries, and contribute to maintaining cooperation within the framework of the United Nations General Assembly.
Period 1986 - 1999: This is the period that marked an important shift in the role of the President of the United Nations General Assembly, from a mainly ceremonial and formal scope to taking on a substantive administrative function, directly participating in crisis handling and coordinating initiatives to reform the organizational apparatus.
In 1986, the United Nations faced a serious financial crisis, with budget cuts, many activities stagnating, and many units facing the risk of large-scale staff cuts. In that context, the President of the United Nations General Assembly played an important intermediary role between different interest groups, coordinating budget negotiations, contributing to protecting essential staffing levels and maintaining the organization's operations. This result laid the foundation for further reforms in budget mechanisms, enhancing financial transparency and improving the efficiency of United Nations resource management in the following decades.
After the end of the Cold War, the United Nations in general and the United Nations General Assembly in particular faced the need for strong reforms to improve operational efficiency, adapt to the emerging multipolar world order, and at the same time meet the reality of the continued increase in the number of member states. Resolution No. 45/45 (1990) and Resolution No. 48/264 (1994) laid the foundation for the process of "reforming the United Nations General Assembly", with the focus on streamlining the agenda, streamlining the working process, strengthening coordination with the United Nations Secretary-General and the United Nations Security Council, improving the quality of discussions and the effectiveness of decision-making. This reform marked a turning point in the role of the President of the United Nations General Assembly, becoming a real administrator, actively coordinating the agenda, leading discussions, building consensus and promoting internal improvements. The increased powers and responsibilities help the President of the United Nations General Assembly have a clearer voice on global issues, representing the common interests of the international community, while contributing to limiting the influence of individual interest groups.
In the context of the United Nations General Assembly increasingly asserting its central role in coordinating discussions and solving global problems, the President of the United Nations General Assembly continues to contribute to promoting innovation in global governance. This role is clearly demonstrated through the chairing and direct coordination of a series of major international conferences such as the World Conference on Women (1995), the Millennium Conference (2000)... A notable new point of these conferences is the expansion of the participation of non-governmental organizations in the global policy-making process, clearly demonstrated in the agenda and documents adopted at the conference.
Period from 2000 to present: In the context of increasingly deep globalization, the United Nations General Assembly continues to be strongly reformed, at the same time the position of President of the United Nations General Assembly is institutionalized in the direction of strengthening the role, authority and scope of activities. Two important resolutions of the United Nations General Assembly, Resolution No. 60/286 and Resolution No. 60/257 (2006), marked a new step forward, when for the first time the regular budget of the United Nations allocated 5 specialized positions for the Office of the President of the United Nations General Assembly, instead of relying only on seconded personnel or voluntary funding as before. This regulation helps the President of the United Nations General Assembly maintain a stable professional apparatus and the ability to respond to complex issues of the multilateral system. The President of the United Nations General Assembly is encouraged to proactively propose and organize thematic discussions on important international issues; publicly report periodically on finances and funding sources; at the same time, monitor the activities of the Procedures Committee and relevant agencies. In addition, the President of the United Nations General Assembly is assigned the important responsibility of presiding over negotiations on reform of the United Nations Security Council, promoting the comprehensive reform process and enhancing transparency in the activities of the United Nations.
The year 2016 marked a significant turning point in the history of the United Nations when, on the basis of the authority granted by Resolution 69/321, the President of the United Nations General Assembly, for the first time, held a public dialogue with candidates for the Secretary-General of the United Nations. This initiative set a new precedent in democratizing and making transparent the process of selecting a senior leadership position of the United Nations system. The dialogue sessions attracted approximately 1.4 million online views and received more than 2,000 questions from member states and non-governmental organizations. As a result, the Secretary-General was elected with a high level of consensus, reflecting the international community's expectations for a modern, more effective United Nations in leadership and governance.
The United Nations General Assembly also adopted Resolution 70/305 to further improve regulations on transparency and control mechanisms in internal operations. The Resolution stipulates that the President of the United Nations General Assembly shall take a public oath before taking office and comply with the Code of Ethics issued by the United Nations General Assembly; voluntary donations to the Office of the President of the United Nations General Assembly must be disclosed in detail and subject to the supervision of an independent audit agency. This adjustment is seen as a step forward in enhancing discipline, ensuring transparency and strengthening the international community's confidence in the governance of the United Nations.
Since 2020, the President of the United Nations General Assembly has continued to affirm his role in governance and coordination of global efforts to respond to multi-layered and emerging challenges. When the COVID-19 pandemic broke out, the President of the United Nations General Assembly proactively deployed online meetings or combined in-person and online meetings, ensuring that the activities of the United Nations General Assembly took place continuously and without interruption. In the following years, the President of the United Nations General Assembly continued to coordinate and lead many important international processes, including the Future Summit and the adoption of the Document for the Future in September 2024. In the context of increasingly fierce strategic competition between major countries, the mediating role of the President of the United Nations General Assembly has become increasingly important in maintaining and strengthening multilateral cooperation, while contributing to resolving the trend of fragmentation and division in international relations.
The history of the past eight decades shows that, from its initial position of being purely ceremonial and procedural in nature, the role of the President of the United Nations General Assembly has gradually developed into a center of coordination, governance, proactively proposing initiatives and promoting innovation. The core value of the title of President of the United Nations General Assembly lies in the ability to fairly represent the 193 member states, build consensus, promote dialogue and protect common principles in a volatile international environment.
The development of the role of President of the United Nations General Assembly reflects the process of movement and adaptation of the United Nations. In periods when the world faced security and political crises, East-West conflicts or socio-economic development challenges, the President of the United Nations General Assembly has assumed the role of a flexible intermediary, a bridge to reconcile interests between different groups of countries. His mark is clearly shown through the coordination of major topics, such as decolonization, establishing a new international economic order, promoting reconciliation or leading reform of the United Nations apparatus. The ability to exert influence from the position of President of the United Nations General Assembly does not only come from institutional authority, although there are some limitations, but also depends on diplomatic capacity, neutrality, the ability to build trust and the skill to reconcile interests between the group of developed and developing countries.
Along with the process of "reforming the United Nations General Assembly" and reforming the United Nations from the end of the 20th century to the 21st century, the powers and responsibilities of the President of the United Nations General Assembly continue to be substantially expanded, from building a streamlined agenda, chairing plenary dialogue, enhancing transparency to participating in promoting reform of the United Nations Security Council, coordinating global negotiations, adapting to strategic competition and leading major initiatives, such as the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Global Compact on Migration, the Convention on Cybercrime, the Future Summit, etc.
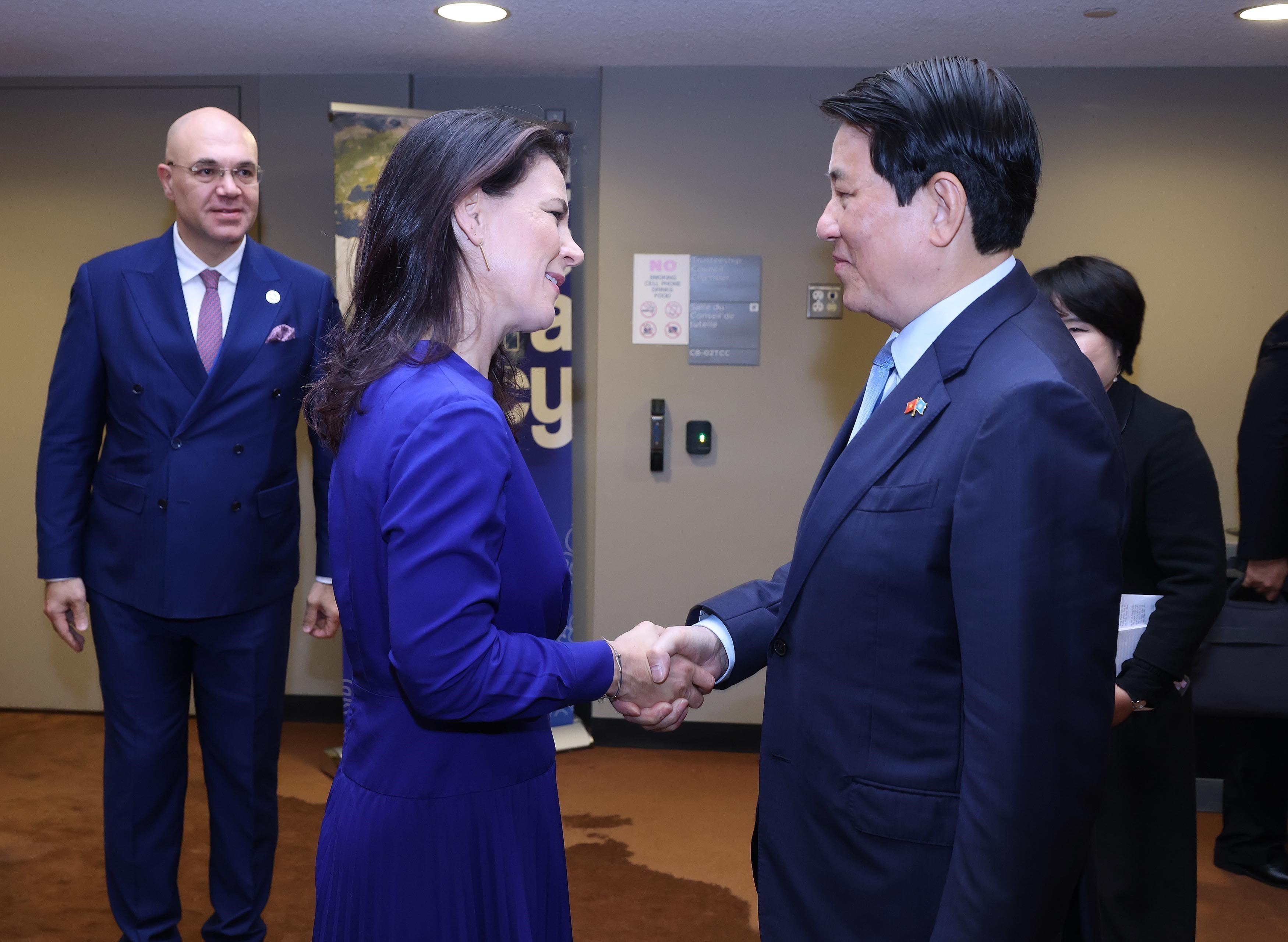

Politburo member and President Luong Cuong met with President of the United Nations General Assembly Annalena Baerbock during his visit to attend the High-level General Debate of the 80th session of the United Nations General Assembly_Photo: VNA
Assuming the Presidency of the United Nations General Assembly: Prospects and Requirements
In the context of a rapidly changing world, the position of President of the United Nations General Assembly is increasingly strategic, not only in its coordinating role, but also in its ability to promote dialogue, narrow differences and consolidate the fundamental principles of the United Nations Charter. Considering running for and assuming the position of President of the United Nations General Assembly is an opportunity to affirm the capacity, prestige and national identity in the international arena. To assume the position of President of the United Nations General Assembly, it is necessary to converge many foundations and favorable conditions.
Firstly, multilateral diplomacy is an important part of national diplomacy. The assumption of the position of President of the United Nations General Assembly needs to be placed in the context of a more proactive and profound development of multilateral foreign policy, shifting from the mindset of "participation" to "proactive participation, active contribution, enhancing the role of the country in building and shaping multilateral institutions and international political and economic order"; striving to play a core, leading or mediating role in multilateral organizations and forums of international significance.
strategy.
Second, making substantial and effective contributions in all areas of the United Nations' pillar activities, demonstrated through increasingly deep and proactive participation in the activities of the largest multilateral organization on the planet; upholding the principles of compliance with the United Nations Charter and international law, while actively promoting initiatives on peace, sustainable development, gender equality, response to climate change and promoting the role of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) at United Nations forums. Substantial and effective contributions in all areas of the United Nations' pillar activities are also demonstrated in many other activities, such as sending forces to participate in peacekeeping forces at missions in countries and regions around the world. This is a clear demonstration of the member state's commitment, responsibility and spirit of contribution to global peace and security; At the same time, demonstrate a proactive role in promoting dialogue and initiatives in line with the priorities of the international community in the new context, such as cooperation on artificial intelligence (AI), disease prevention and control, and other non-traditional security challenges.
Third, experience and prestige in undertaking multilateral responsibilities within the framework of the United Nations. This is demonstrated through experience and prestige in undertaking multilateral responsibilities within the framework of the United Nations, such as non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, member of the Human Rights Council, Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), holding other important positions in the General Assembly and other specialized agencies of the United Nations. Experience and prestige in undertaking multilateral responsibilities within the framework of the United Nations is also demonstrated through active participation in the process of forming cooperation mechanisms, building common rules and standards, such as building codes of conduct, organizing high-level international conferences, etc.
However, assuming the responsibility of President of the United Nations General Assembly also poses many difficulties, especially in the context of a world of profound and widespread changes, with many unpredictable factors, and multi-dimensional challenges that strongly impact international cooperation and the role of the United Nations.
First, conflicts and non-traditional security issues continue to pose major challenges to multilateral cooperation. Strategic competition among major powers increases the complexity of the United Nations' mediation role; small and medium-sized countries are under pressure to "choose sides", while the rise of small multilateral initiatives has somewhat impacted the United Nations' global influence, requiring further strengthening of coordination capacity and maintenance of multilateral cooperation to avoid the risk of global polarization.
The World Economic Forum's Global Risks 2025 report predicts that extreme weather will be the top risk in the next decade. The World Food Programme says that hunger and poverty are affecting about 720 million people worldwide. Cyber attacks are expected to increase by 30% between 2023 and 2025, while the rapid development of AI, digital transformation and green transformation pose urgent demands for cooperation in global governance. This is a factor that is expected to complicate the agenda of the UN General Assembly in particular and the UN in general.
Second , the “UN80” process initiated by the UN Secretary-General in March 2025, with the aim of improving operational efficiency, reviewing functions, tasks and restructuring the UN system, is expected to have a direct impact on the activities of the UN General Assembly. This adjustment is likely to have a profound impact on the operating methods, organizational structure and participation mechanisms of member states, thereby reshaping the role and operation of the UN General Assembly in the coming period.
Faced with intertwined opportunities and challenges, running for election and assuming the role of an active and responsible member in important international agencies and positions in the United Nations system, including the position of President of the United Nations General Assembly, is not only in line with national interests, but also contributes to promoting deep and comprehensive international integration on the basis of an independent, self-reliant, peaceful, cooperative and developmental foreign policy; at the same time, it demonstrates the country's position and prestige in the international arena.
Being elected as President of the United Nations General Assembly will help member states participate more deeply in the process of planning the agenda and organizing the implementation of decisions of the United Nations General Assembly, thereby contributing to solving important political, economic and social issues of the world and the region. This is also an opportunity to strengthen connections and consolidate relations between member states and the United Nations, while promoting bilateral relations with member states. To undertake this responsibility, member states need to prepare carefully in terms of content, capacity and coordination methods, especially in the context of unpredictable changes in the world and the United Nations./.
----------------------------
* Dr. Hoang Thi Thanh Nga, Pham Binh Anh, Vu Thuy Minh, Nguyen Hong Nhat, Pham Hong Anh, Mai Ngan Ha, Le Thi Minh Thoa
Source: https://tapchicongsan.org.vn/web/guest/the-gioi-van-de-su-kien/-/2018/1154702/chu-tich-dai-hoi-dong-lien-hop-quoc--y-nghia%2C-co-hoi%2C-vinh-du-doi-voi-quoc-gia-thanh-vien-dam-nhiem-trong-trach.aspx






































![[Video] The craft of making Dong Ho folk paintings has been inscribed by UNESCO on the List of Crafts in Need of Urgent Safeguarding.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/10/1765350246533_tranh-dong-ho-734-jpg.webp)







































































Comment (0)