Lighter, cheaper, more durable
The EV battery market is quite rich with many choices, including Lead-Acid (lead-acid batteries), Lithium-Ion, LFP (Lithium Ferrous Phosphate) and NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride). Currently, Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the most commonly used EV battery type, commonly used materials are lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) or nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) cathode…
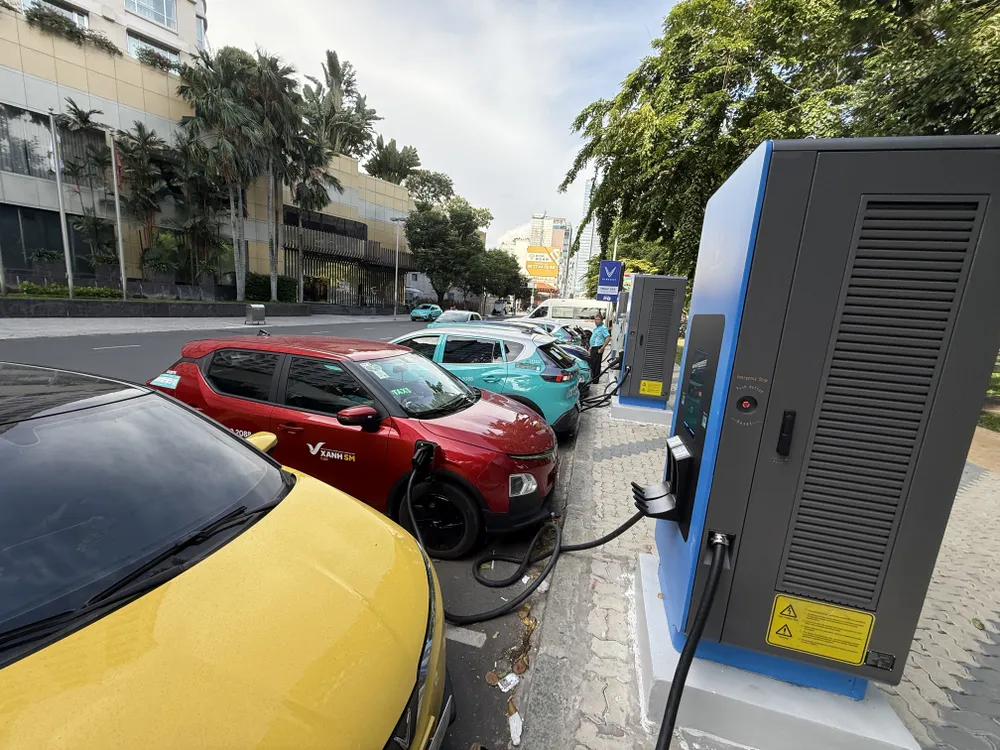

Among them, LFP is considered safer, lower cost and less dependent on rare metals, while providing a range of about 300-500km and can be quickly charged in 30-60 minutes. LFP batteries are recommended to be highly safe, minimizing the risk of explosion compared to conventional Lithium-Ion, especially suitable for hot and humid weather conditions in Vietnam. In contrast, NMC batteries are suitable for a longer range of about 500km, but the risk of explosion is higher if not well maintained.
For electric motorbikes, 48V-72V Lithium-Ion batteries are a popular choice, with a battery capacity of about 20-50Ah for a travel distance of 50-100km. In addition, solid-state battery technology is emerging as a leading trend when using solid electrolytes instead of liquid, helping to increase energy density up to 400Wh/kg, thereby extending the distance to 800-1,000km. This type of battery is lighter in weight, can last up to more than 10,000 charging cycles and has safety protection.
In addition, many new EV battery technologies are also being researched, such as Na-ion (Sodium ion - Sodium ion) batteries produced by CATL, a battery manufacturer in China, which are 30% cheaper than Li-ion; Li-S (Lithium Sulphur) batteries have good energy density, 2-3 times higher than normal but not very durable, Graphene-based batteries can be fully charged in just 5 minutes and have a travel time of up to 800km. Tesla has tested and deployed a line of low-cost, environmentally friendly EV batteries made from aluminum-ion or the LMR (Lithium Manganese-Rich) battery line that GM is expected to put into use in 2028, helping to reduce costs by up to 20%...
More profitable than petrol cars, but…
By 2025, the global EV market will see strong growth, dominated by Chinese companies. CATL, the world's largest battery manufacturer, currently leads the pack with a 37.9% market share. BYD continues to attract attention with its cobalt- and nickel-free LFP Blade battery, which offers a maximum range of 690km.
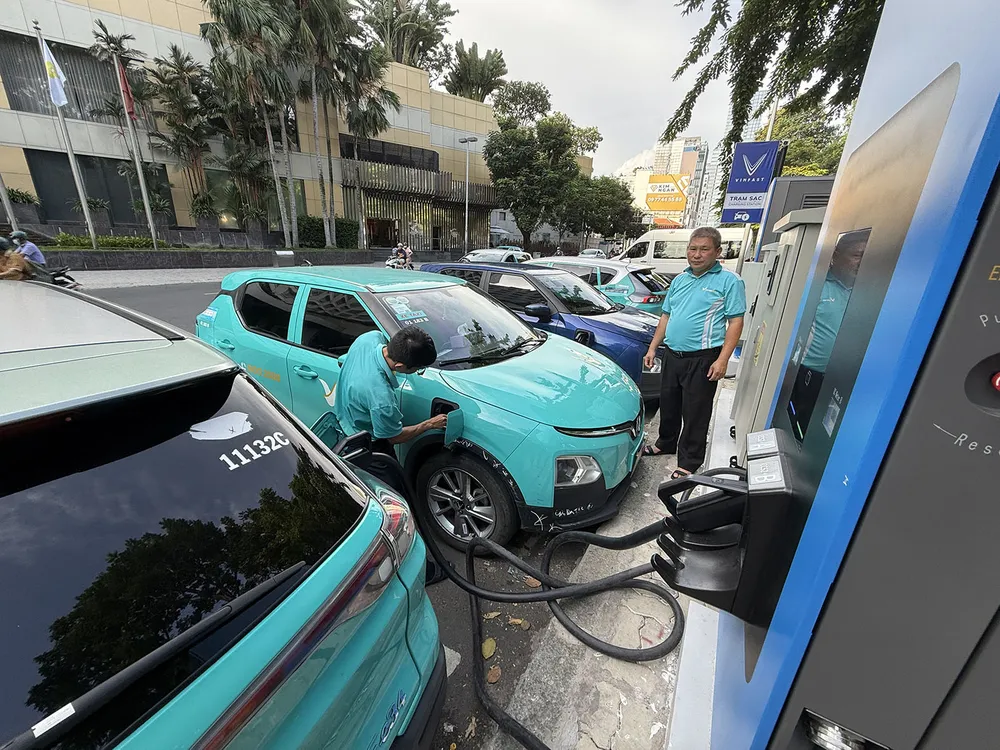

In Vietnam, the electric vehicle market is growing strongly thanks to VinFast 's preferential policies. VinFast has delivered more than 11,000 vehicles per month, maintaining its leading position in the domestic EV market. VinFast is using 3 types of EV battery technology, including: Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries for VF e34, VF8 and VF9 models, LFP batteries for VF5 Plus, VF6 and VF7 models. In addition, Lead-Acid batteries are used for electric motorbike models such as Feliz and Klara A2.
Electric vehicles stand out in terms of energy efficiency when converting 87%-91% of electricity into kinetic energy, while gasoline vehicles only reach 20%-30%, which helps to significantly reduce operating costs. It can also be compared that currently, charging an EV battery for 100km only costs about 20,000 - 30,000 VND, 40% lower than using traditional fuel. EV also limits direct emissions into the environment, contributing to reducing environmental pollution compared to gasoline vehicles...
However, the disadvantages of EVs are still worth noting, such as the high initial purchase price because EV batteries account for up to 30% of the vehicle's value. Charging times range from 30 minutes to 8 hours, making EVs less flexible than conventional fuel-powered vehicles on long trips. Hot and humid weather also affects the durability of EV batteries, and importing batteries from abroad poses risks of supply chain dependence... Environmentally, EV battery production emits more CO2 than gasoline vehicles initially, due to the mining of lithium, cobalt, and nickel. In addition, battery recycling remains a challenge, with a reuse rate of only 50%-80% by 2025, leading to electronic waste. In Vietnam, importing batteries from China increases supply chain dependence, and hot climates can cause batteries to degrade 20% faster than in temperate regions...
Choose the right battery to avoid the risk of fire or explosion
For electric cars, users should prioritize LFP batteries for urban travel needs, thanks to their high safety (no explosion under high temperatures or collisions) and good durability. For electric motorbikes, 48V-72V Lithium-Ion batteries are a popular choice, with a capacity of 20-50Ah, providing a distance of 50-100km. For example, 48V-30Ah batteries can reach 70-95km, while 72V-50Ah batteries can reach up to 120-160km. LFP batteries are recommended to be safer, reducing the risk of explosion compared to conventional Lithium-Ion. Lead-acid batteries should be avoided, although cheap, but heavy (20-30kg) and short distance (25-40km), only suitable for short travel needs.
In Vietnam, with hot and humid weather, LFP batteries stand out because they do not contain cobalt and do not explode under strong impact. Lithium-Ion batteries have high energy density but are prone to fire if charged incorrectly (such as using an incompatible charger). To choose the right battery, consumers should check international certification (UL/CE) to ensure quality and safety.
Associate Professor, Dr. Do Van Dung
(Vice President of Ho Chi Minh City Automobile - Engine Association, former Principal of Ho Chi Minh City University of Technical Education)
Source: https://www.sggp.org.vn/giam-rui-ro-khi-su-dung-xe-dien-post807174.html


![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Vice President of Luxshare-ICT Group (China)](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/15/1763211137119_a1-bnd-7809-8939-jpg.webp)


![[Photo] Panorama of the 2025 Community Action Awards Final Round](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/15/1763206932975_chi-7868-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with representatives of outstanding teachers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/15/1763215934276_dsc-0578-jpg.webp)




































































































Comment (0)