(NLDO) - The Palaeospondylus monster is classified into opposite groups by research groups, with completely different descriptions of its structure.
According to Sci-News , the ancient Palaeospondylus monster lineage was first discovered in the 1980s, with a general description of an animal that was part fish, part eel, with a variety of strange morphological features.
The most prominent of this monster family is Palaeospondylus gunni, 390 million years old, found in Scotland - England several times,
However, different research groups have interpreted their fossil structures quite differently, classifying them into most major groups of jawless and jawed vertebrates.
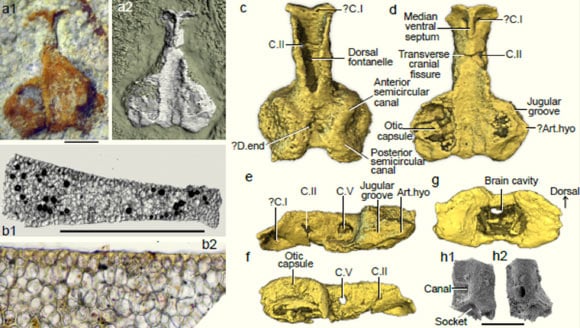
Palaeospondylus australis fossil unearthed in Australia - Photo: National Science Review
But now, another representative of this monster group has just appeared in Australia, promising to bring some light.
The mysterious creature, excavated from the Georgina Basin in western Queensland, central Australia, was superbly preserved in 3D in 400-million-year-old limestone, rather than crushed like the British specimens.
Named Palaeospondylus australis, it is a new species that appears to be a close relative of one found in Britain.
The new fossil's honeycomb-like structure and complex internal features hint at the early evolutionary significance of the creature, which scientists believe was an ancient fish.
Writing in the scientific journal National Science Review , the team of authors led by paleontologist Carole Burrow from the Queensland Museum (Australia) said the newly excavated creature showed that the adult still retained many characteristics of the juvenile.
Along with a number of other details, they found that it was most likely a relative of today's sharks.
The new fossil also reveals cranial neuroanatomy features of Palaeospondylus, adding important information about its relationships to other species.
However, these same data also provide some contradictory information, confusing scientists and hoping to be able to explain when other representatives of this species or genus of animals are found.
With two species found far apart in Europe and Australia, the Palaeospondylus lineage may have spread across the global oceans during the Devonian.
“This breakthrough not only enriches our understanding of Australia’s ancient ecosystems but also highlights the global interconnectedness of early vertebrate life across continents,” the authors said.
Source: https://nld.com.vn/hien-ra-sau-400-trieu-nam-quai-vat-nhieu-chan-dung-gay-boi-roi-196241215102410503.htm
































































































Comment (0)