
The brain is the organ that commands all of the body's activities, but it is also vulnerable to stress, aging, or a poor diet.
Several studies have shown that certain nutrients can help improve memory, concentration, and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
Here are nine supplements that are scientifically proven to benefit brain health.
1. Fish oil - an essential source of omega-3 for the brain
Fish oil contains omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA - components of brain cell membranes and essential for neurological activity. According to Harvard Health Publishing, DHA accounts for up to 40% of the total fatty acids in the human brain.
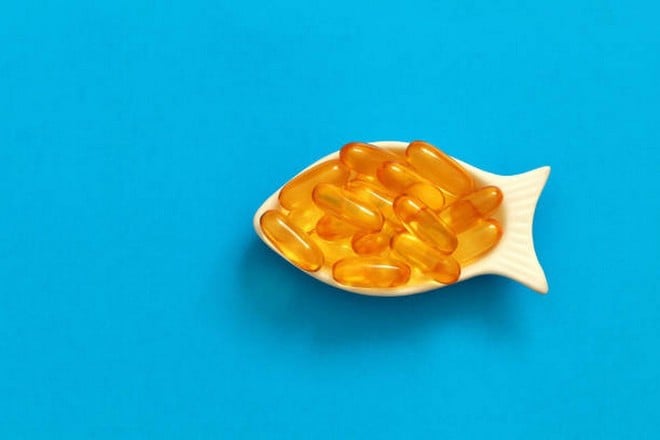
Fish oil supplements have been shown to improve memory, concentration, and reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. People who do not eat fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines) should consider taking a daily omega-3 supplement, with the recommended dose being 250-500 mg EPA+DHA.
2. Vitamin D - maintains cognitive function
Vitamin D not only helps keep bones strong, but also helps regulate nerve cell activity. Research from Johns Hopkins Medicine shows that vitamin D deficiency is associated with a higher risk of dementia and depression.

The body absorbs vitamin D best when exposed to early sunlight or through foods such as salmon, egg yolks, and vitamin D-fortified milk. If it is difficult to ensure the required amount, you can supplement 600-1,000 IU per day according to your doctor's advice.
3. Vitamin B12 - a nutrient that protects the nervous system
Vitamin B12 is needed for the formation of myelin, the sheath that helps transmit nerve signals quickly and accurately. A deficiency in B12 can lead to memory problems, poor concentration and fatigue.
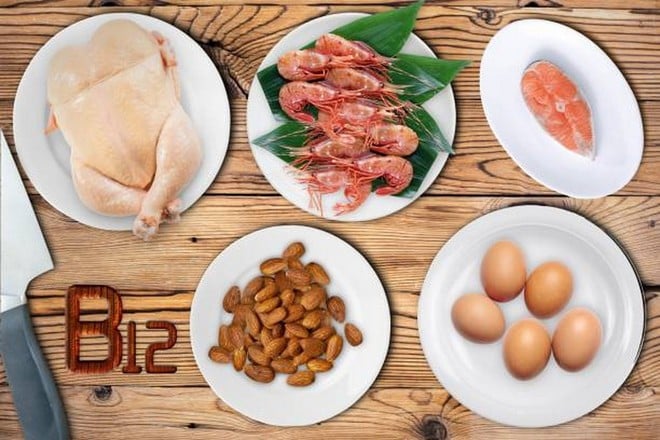

Vegetarians, the elderly, or people with stomach problems are more likely to be deficient in B12. According to the Cleveland Clinic, you should supplement 2.4 micrograms of vitamin B12 per day, through foods such as lean meat, fish, eggs, or multivitamins.
4. Zinc - a mineral that supports learning and memory
Zinc is involved in more than 100 enzyme reactions in the body, especially the activity of the hippocampus - the brain's memory storage center. Mayo Clinic notes that low zinc levels can reduce the ability to learn and concentrate.

Good sources of zinc include seafood (especially oysters), beef, lentils, and pumpkin seeds. If your diet is inadequate, you can supplement with 8-11mg of zinc per day.
5. Magnesium - helps the brain relax and reduce stress
Magnesium plays a role in regulating neurotransmitters, reducing stress and improving sleep. Magnesium deficiency can increase the risk of depression and anxiety.
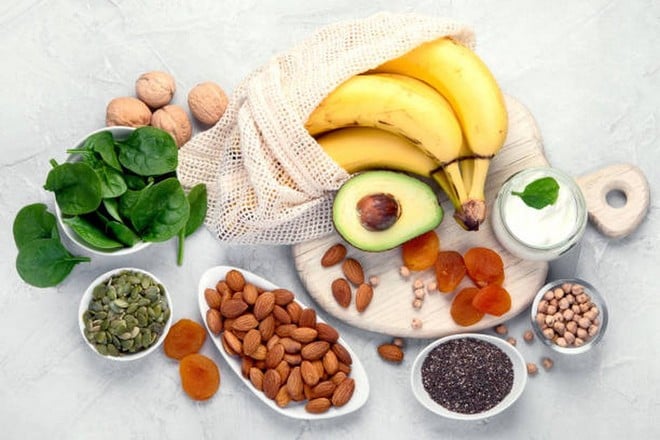

Green leafy vegetables, sunflower seeds, soybeans, bananas, and dark chocolate are good natural sources of magnesium. Magnesium supplements (200-400 mg/day) may be helpful for people who have trouble sleeping, are stressed, or do mental work.
6. Curcumin - the "golden" active ingredient from turmeric
Curcumin, the main compound in turmeric, is known for its powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Several studies published in Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience have shown that curcumin can help improve memory and slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease by preventing the buildup of beta-amyloid plaques in the brain.

You can use turmeric in cooking or take 500-1,000mg curcumin supplements daily, combined with black pepper to increase absorption.
7. Ginkgo biloba - supports blood circulation to the brain
Ginkgo biloba leaf extract is widely used in Europe to improve memory and cerebral circulation. Some clinical trials have shown that ginkgo may help reduce symptoms of mild cognitive impairment, especially in older adults.
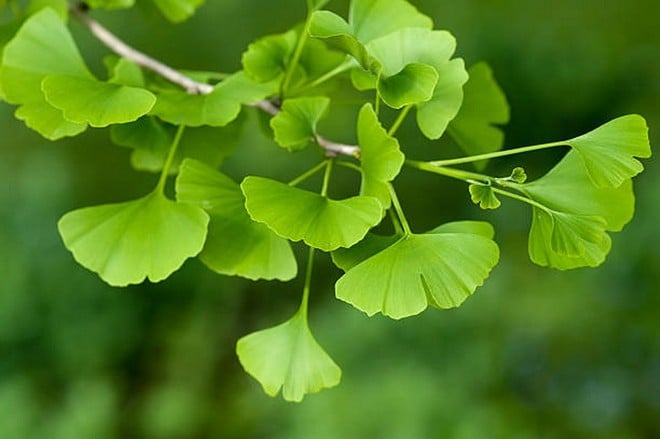

However, effects may vary from person to person. The recommended dose is usually 120-240 mg/day, divided into two doses after meals.
8. Caffeine and L-theanine - help focus
Caffeine helps increase alertness, while L-theanine, an amino acid found in green tea, provides a mild sedative and improves concentration. When combined, the two create a balanced effect: alert but not jittery.

A morning cup of coffee or green tea can be enough to jump-start your brain. If you take supplements, keep your caffeine intake below 400 mg/day to avoid insomnia or heart palpitations.
9. Coenzyme Q10 - increases energy for brain cells
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is an antioxidant that helps cells produce energy and protects the brain from free radical damage. Natural CoQ10 levels decrease with age, making the brain more susceptible to fatigue and memory loss.

CoQ10 supplementation (100-200 mg/day) may improve cognitive function, especially in the elderly or those taking statin drugs - drugs that reduce CoQ10 levels in the body.
The right nutrients, combined with a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and regular exercise, can significantly support brain health. However, before starting any supplement, consult your doctor to choose the right dosage and form. A smart diet is the foundation for a sharp and resilient brain over time./.
Notes when using brain supplements
Dietary supplements are not a substitute for medical treatment or a balanced diet.
Do not combine multiple medications at the same time, especially if you are taking medication for heart disease, diabetes, or depression.
Drink enough water and eat with main meals to increase absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Elderly people, pregnant women or people with underlying medical conditions should consult a doctor before use./.
Source: https://baolangson.vn/9-duong-chat-vang-giup-nao-bo-luon-khoe-manh-va-minh-man-5062592.html




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting on nuclear power plant construction](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/22/1761137852450_dsc-9299-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Da Nang: Shock forces protect people's lives and property from natural disasters](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/22/1761145662726_ndo_tr_z7144555003331-7912dd3d47479764c3df11043a705f22-3095-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Award Ceremony of the Political Contest on Protecting the Party's Ideological Foundation](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/22/1761151665557_giaia-jpg.webp)



















![[Photo] Comrade Nguyen Duy Ngoc visited and worked at SITRA Innovation Fund and ICEYE Space Technology Company](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/23/1761174470916_dcngoc1-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam and his wife begin their official visit to Bulgaria](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/23/1761174468226_tbtpn5-jpg.webp)














































































Comment (0)