1. What types of jute are there?
Malabar spinach is found in many places in the world , but in Vietnam there are two popular types of Malabar spinach: red Malabar spinach (purple Malabar spinach) and green Malabar spinach (also called white Malabar spinach). Red Malabar spinach was grown a long time ago in Vietnam with the characteristic of purple-red stems. White Malabar spinach is newly grown in Vietnam.
Red jute is scientifically named round jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) and long jute (Corchorus olitorius L.) is white jute. Some people often choose to buy young, soft red jute with small leaves and stems because they think that red jute does not have a slightly bitter taste like white jute.
When it comes to jute, the first characteristic is that the vegetable is very slimy. When washing, if you squeeze it hard or chop it, it will be even more slimy. But in fact, many people are fascinated by jute soup cooked with crab, clams or dried shrimp, the more slimy it is, the more delicious it is.
Although it is a popular vegetable, not everyone knows about the nutritional benefits of this special viscous vegetable.
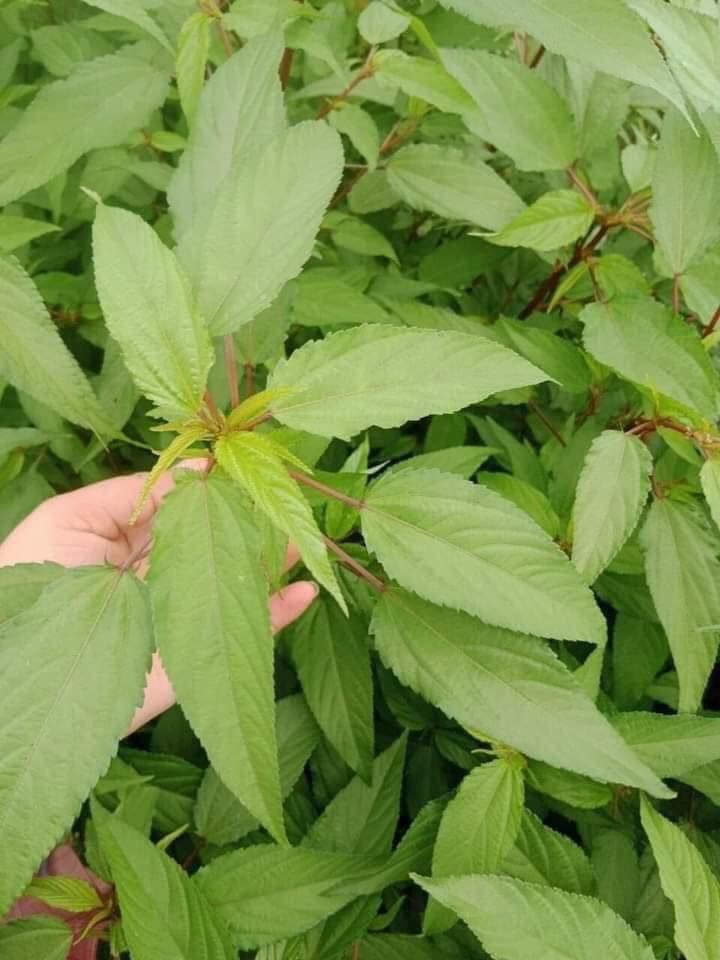

Malabar spinach.
2. Nutritional composition of jute
According to Dr. Nguyen Van Tien, National Institute of Nutrition: Vegetables such as jute, amaranth, and Malabar spinach have high nutritional value, with consistent levels of carotene, vitamin C (179 - 64 - 52mg%), iron (2.8 - 2.5 - 2.1mg%), rich in minerals, trace minerals, and protein content 3 - 5 times higher than other vegetables (3 - 6g%).
In addition to the common benefits of jute that many people know such as supporting constipation treatment, helping with bowel movements, diuretic, lactation, cooling and detoxifying, jute also has "secrets". According to Dr. Yen Lam Phuc, Military Medical Academy, jute is in the top of vegetables containing a lot of calcium (ranked 4th among vegetables used for eating), iron (ranked 1st), beta carotene (ranked 4th), vitamin C (ranked 3rd).
Malabar spinach is low in calories and rich in important vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A and C, riboflavin, folate, and iron. Cooked Malabar spinach provides higher levels of vitamins and minerals.
In addition to culinary uses, jute leaves have also been used for medicinal purposes in Ayurvedic treatment for centuries.
3. Some benefits of jute
Malabar spinach contains a lot of vitamin K.
This vitamin is helpful in blood clotting. It also helps reduce the risk of jaundice and poor nutrient absorption.
Malabar spinach has high vitamin B6 content.
Nutritional deficiencies and poor diet often affect the eyes. Research shows that vitamin B6, folate, and other vitamins help prevent eye problems. Malabar spinach contains vitamin B6, and eating Malabar spinach is good for the eyes.
Malabar spinach contains iron
Malabar spinach is rich in iron, containing a whopping 2.73 mg of iron. This is about 34.13% of the daily recommended intake.
Malabar spinach leaves contain vitamin A.
Vitamin A is great for speeding up the healing and regeneration of skin. Malabar spinach is rich in vitamin A which is great for cell growth and skin health.
Eat jute to get vitamin C
Jute leaves are rich in vitamin C, which helps boost the immune system. In the process, it improves the body's ability to fight viruses and colds. When you take vitamin C supplements when you have a cold or flu, you can prevent the risk of complications.
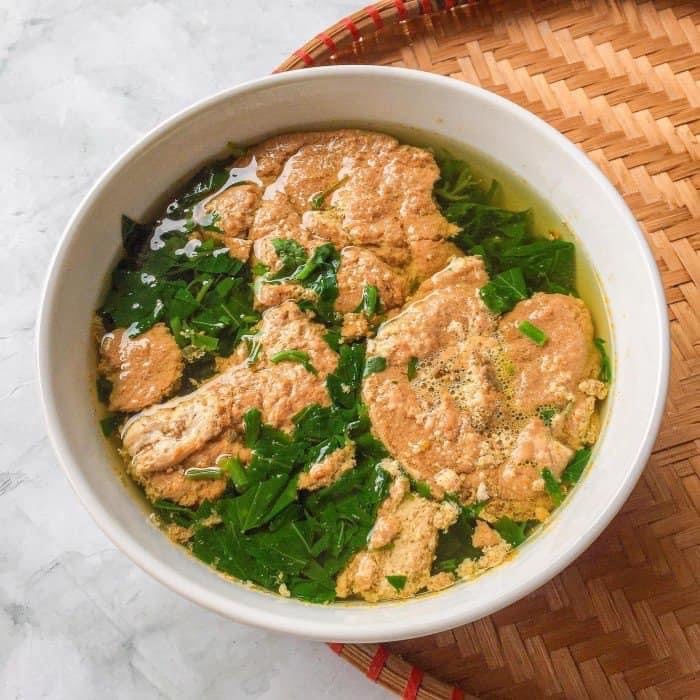

Crab and jute salad is a delicious dish to eat with rice on a summer day. Photo: Kim Oanh.
There is omega-3 content in jute
Omega-3 fats are important for brain development and can help reduce inflammation in the body. Omega-3 fats can also be found in jute leaves, with one study finding that jute leaves had the highest omega-3 fat content of any vegetable reported.
However, jute leaves only provide alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is converted to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) – the active forms the body needs – at a low conversion rate of 5-8%, so consider jute leaves a modest contributor to overall omega-3 intake rather than a potent source.
Malabar spinach also contains lycopene.
This is an antioxidant that helps protect cells against oxidative damage, which increases the risk of disease. Their lycopene content can vary depending on the preparation method. Cooked and mature jute leaves have higher levels.
Vitamin B9
Jute leaves contain vitamin B9, which is a vitamin that helps reduce the risk of developing certain types of cancer. Jute leaves contain 90 micrograms of vitamin B9. This is about 22.50% of the recommended daily intake.
Calcium in jute helps strengthen bones and teeth
Calcium helps protect teeth and keep jawbones strong throughout childhood and adulthood. Malabar spinach leaves are rich in calcium and magnesium, two minerals that are essential for daily bodily functions. The combination of these two minerals is especially important in maintaining bone health, as they work together to help form and maintain strong bones and teeth.
Magnesium content in jute is good for people with asthma
If you have asthma, you can normalize your breathing by meeting your daily magnesium intake. Additionally, you can eat jute leaves which are rich in magnesium. This will help reduce shortness of breath and wheezing.
Reduce bad cholesterol levels
Studies show that copper helps reduce bad cholesterol in the body, helping to increase good cholesterol in the body. Malabar spinach contains 0.222 mg of copper. This is about 24.67% of the recommended daily intake for a normal adult.
Improve skin and hair health
Vitamin B2 helps maintain healthy collagen levels, which in turn leads to healthy hair and skin. Collagen is essential for maintaining youthful skin and hair. It helps prevent the development of wrinkles and fine lines. A deficiency of vitamin B12 leads to an aged appearance.
Support hepatitis prevention
Jute leaves may have anti-hepatitis effects. One study examined mice that ate jute leaves daily for 30 days. At the end of the study period, the mice had improved antioxidant status in their livers.
However, mouse research results do not necessarily apply to human health, so more human research is needed.
It should be noted that although each type of food has health benefits, the diet needs to meet nutritional balance, adequate nutrient groups, and food diversity. Therefore, although jute is good, you should not eat too much. In addition, people with poor health or medical conditions should consult a doctor or nutritionist for advice on a suitable diet.
Source



![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man received a delegation of the Social Democratic Party of Germany](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761652150406_ndo_br_cover-3345-jpg.webp)


![[Photo] Draft documents of the 14th Party Congress reach people at the Commune Cultural Post Offices](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761642182616_du-thao-tai-tinh-hung-yen-4070-5235-jpg.webp)






















![[Photo] President Luong Cuong attends the 80th Anniversary of the Traditional Day of the Armed Forces of Military Region 3](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761635584312_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)











































































Comment (0)