According to the global COVID-19 report that Nguoi Lao Dong Newspaper received from the World Health Organization (WHO) on the morning of May 19, in the most recent 28-day period, the world recorded 2.592 million new cases and 17,106 new deaths due to COVID-19.
While a decreasing trend was observed in most regions, two epidemiological regions, the Western Pacific and Southeast Asia, which correspond to most of Asia and Australia geographically, showed a strong increasing trend.
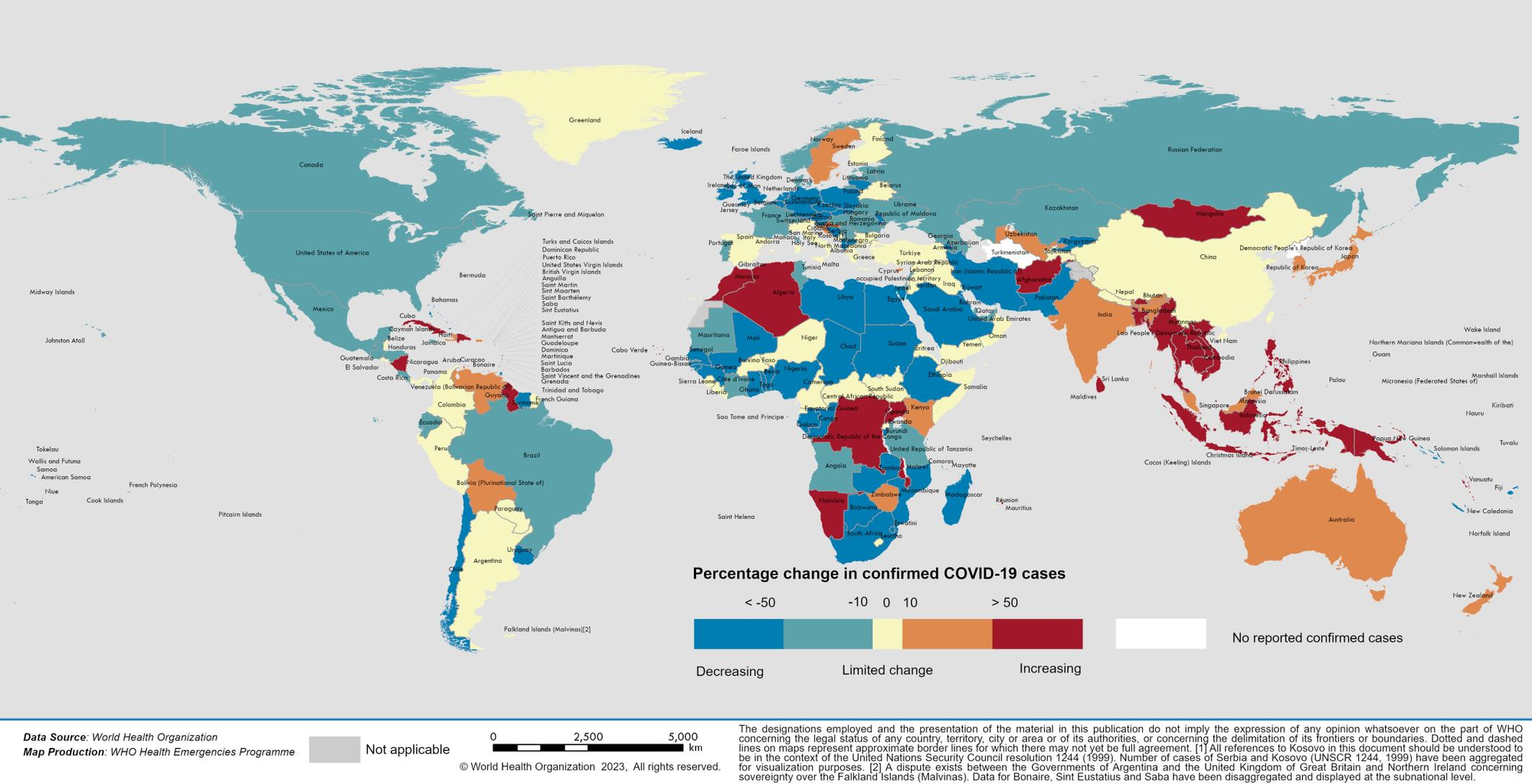
The map shows the increase in the rate of COVID-19 cases, in which orange and red represent increases and sharp increases, yellow represents rates that remain almost the same or increase slightly, green and blue represent decreases and sharp decreases - Photo: WHO
The Western Pacific - the region that WHO classifies Vietnam in - accounts for 40% of COVID-19 cases reported globally: more than 1.043 million cases, up 47% compared to the previous 28-day period, although the number of deaths decreased by 14%, equivalent to 1,402 cases.
Up to 40% of Western Pacific countries reported an increase of more than 20% in cases compared to the previous cycle, with the three countries with the highest increase rates being Vietnam (1,741%), Mongolia (906%) and the Philippines (321%). Although Vietnam's reported number of cases is not too high compared to the region (59,211 cases), the sharp increase is due to the fact that the previous 28-day cycle had only 3,271 cases.
The three countries with the highest number of cases in the Western Pacific are South Korea (418,960 cases, up 46%), Japan (229,877 cases, up 15%) and Australia (116,621 cases, up 46%). These are also the three countries with the highest number of deaths in the region, with Japan having 474 cases, Australia having 362 cases and South Korea having 231 cases.
Europe and the Americas have the second and third highest number of cases, with more than 687,000 and more than 606,000 cases respectively. However, these are the two regions where the number of reported deaths accounts for the majority of global deaths, with 5,814 and 8,143 respectively, despite a sharp decrease compared to the previous cycle.
The US is still one of the "hottest" countries with 355,829 cases and 5,333 deaths.
The Southeast Asia epidemiological region (excluding Indochina but including India and several neighboring countries) reported a 52% increase in cases and a further 153% increase in deaths. However, this is a much lower increase than reported in previous weeks, when the region-wide increase rate sometimes reached over 600%.
The countries with the highest growth rates in the region are Myanmar, Thailand, and Timor-Leste. While the countries with the highest number of cases are India, Indonesia, and Thailand.
The Eastern Mediterranean, an epicenter that includes much of geographical West Asia and where the new wave began at the same time as India, reported a sharp 42% drop in cases. Africa reported negligible cases.
Source

































































































Comment (0)