A race for power once upon a time.
The turbocharger is a revolutionary invention that has made a significant contribution to the development of the automotive industry. The journey from its initial concept to its widespread application today has gone through many stages with important milestones.
First conceived in 1885 by Alfred Büchi, a Swiss engineer, it took Büchi 10 years to successfully build the first turbocharger for a diesel engine.
The world's first mass-produced cars with turbochargers were the Chevrolet Corvair Monza Spyder and the Oldsmobile Jetfire. And the Porsche 911 Turbo was the first commercially available car to use twin turbochargers (biturbochargers).
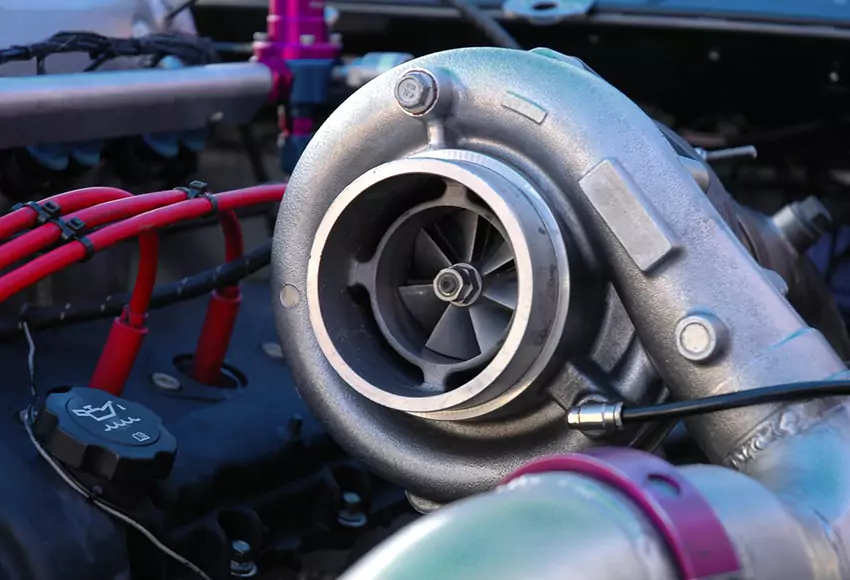
Turbochargers were once a technology widely adopted by many mainstream car manufacturers. (Illustrative image.)
However, the technology at the time made the production of turbocharged engines expensive. This explains why cars using turbocharged engines in the early 20th century were primarily sports cars, race cars, and high-end touring vehicles.
By the early 21st century, turbocharged engines were widely used in passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Automakers focused on developing compact, high-performance, fuel-efficient turbocharged engines with reduced emissions.
And turbocharged engines are one of the most advanced technologies in the automotive industry, demonstrating the relentless efforts of engineers and scientists to improve engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
Turbocharged engines are gradually losing ground in the era of green vehicles.
Throughout its development, turbocharged engines have brought about significant improvements, allowing cars to gain considerable power without needing large, bulky engine blocks.
However, nowadays, with stricter emission standards, many car manufacturers have gradually reduced engine displacement, as they no longer need as much power from internal combustion engines as before.
Instead, they use engines with just enough power and equip them with a hybrid system to reduce the car's emissions while still ensuring sufficient engine power.

Today, automakers prefer hybrid engines. (Illustrative image.)
This is easily observable in Vietnam. In the product range of mainstream car manufacturers, turbocharged engines are no longer common. Instead, hybrid products are considered the mainstay and are the trend that many car manufacturers are investing in developing.
The green vehicle revolution is rapidly gaining momentum, with new energy vehicles constantly being introduced. The gap between charging time and refueling with gasoline is also narrowing.
Automakers have also gradually outlined roadmaps for electrifying their products, and in the future, green vehicles will gradually replace them, with turbocharged engines in particular and internal combustion engines in general becoming a thing of the past.
Source: https://xe.baogiaothong.vn/dong-co-tang-ap-lep-ve-truc-ky-nguyen-xe-xanh-192240710141740408.htm



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives the Governor of Tochigi Province (Japan)](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765892133176_dsc-8082-6425-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

![[Live] 2025 Community Action Awards Gala](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765899631650_ndo_tr_z7334013144784-9f9fe10a6d63584c85aff40f2957c250-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Image] Leaked images ahead of the 2025 Community Action Awards gala.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765882828720_ndo_br_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-45-png.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Lao Minister of Education and Sports Thongsalith Mangnormek](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765876834721_dsc-7519-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)












































































![[Live] Closing Ceremony and Award Presentation for the "Impressive Vietnam Tourism" Video/Clip Creation Contest 2025](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/17/1765974650260_z7273498850699-00d2fd6b0972cb39494cfa2559bf85ac-1765959338756946072104-627-0-1338-1138-crop-1765959347256801551121.jpeg)

























Comment (0)