A team of scientists from the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry (IOCB) in Prague (Czech Republic) has successfully decoded the structure of a protein called methyltransferase from the virus that causes mpox, formerly known as monkeypox. It is thanks to this protein that the virus escapes human immunity and causes disease, according to the medical journal News Medical (UK).
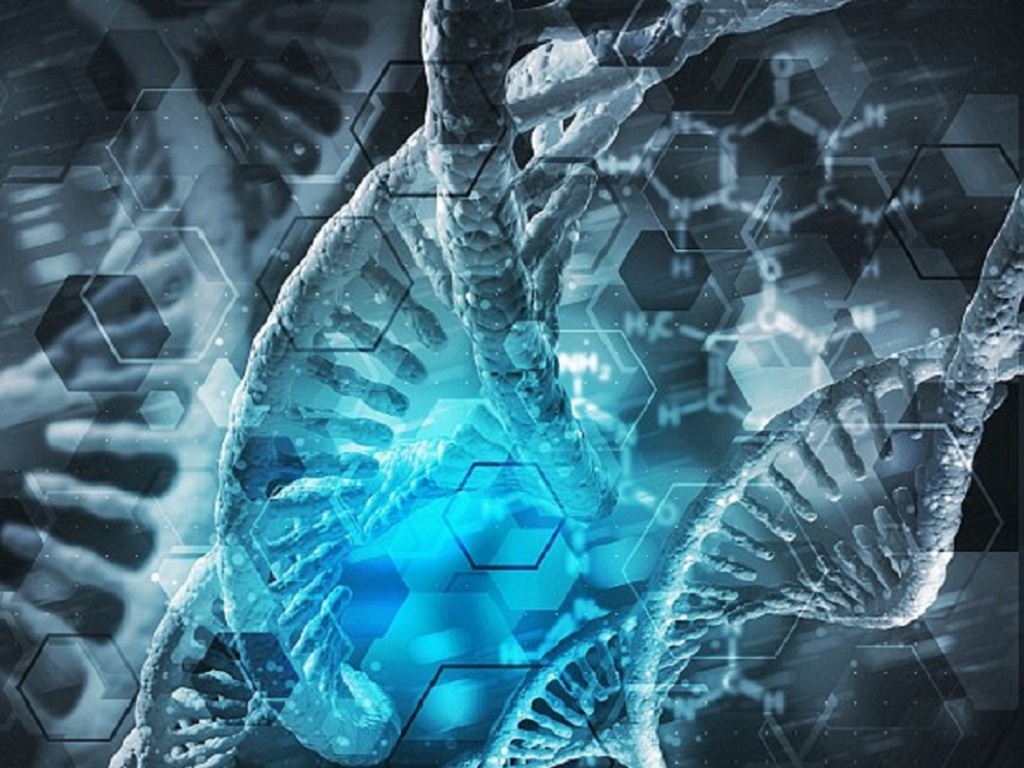

Decoding the methyltransferase protein in the mpox virus brings scientists closer to creating new antiviral drugs
Thanks to the discovery , scientists will experiment and find substances that can inhibit the activity of the methyltransferase protein. They may even soon develop a new antiviral drug capable of treating mpox.
Not only that, the research team said the new antiviral drug could also be effective against other viruses, such as the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes Covid-19. The research results were published in the journal Nature Communications .
Experts at the IOCB have spent years studying viruses that cause serious illness. They have previously focused on the Zika virus, which is a flavivirus, and SARS-CoV-2, which is a coronavirus.
Since May 2022, mpox has spread to more than 100 countries and infected more than 86,900 people. Symptoms of mpox are similar to smallpox, including fever, severe headache, back pain, muscle aches, weakness and swollen lymph nodes.
The mpox virus lives in rodents and primates. When it infects humans, the fatality rate is between 3 and 6%. Meanwhile, Covid-19 has infected more than 763 million people worldwide , according to News Medical .
Source link





























































































Comment (0)