Hanoi 35-year-old female patient with atopic dermatitis went to the doctor due to ulcers, warts with red patches all over the body, itching, biopsy results diagnosed cancer.
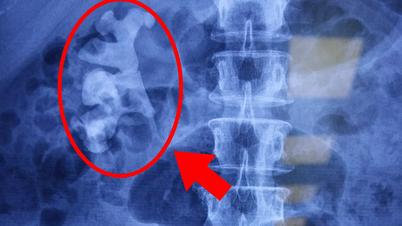
On January 11, Dr. Pham Cam Phuong, Director of the Nuclear Medicine and Oncology Center, Bach Mai Hospital, said that the patient had atopic dermatitis 10 years ago, and recently had skin ulcers all over his body, and was more itchy. The biopsy results diagnosed cutaneous T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (HC mycosis fungoides), stage IVA.
Patients must be hospitalized for 6-8 chemotherapy cycles, each cycle lasting 21 days to reduce skin warts.
Mycosis fungoides is the most common form of a type of blood cancer called cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma occurs when some white blood cells, called T cells, become cancerous. It causes different types of skin lesions and usually occurs in adults over the age of 50.
The earliest lesions seen in mycosis fungoides are erythematous or brown scaly plaques, which may show slight atrophy. In the plaque stage, lesions become larger, more infiltrated, and new lesions may appear, affecting the face and scalp. In the tumor stage, purplish papules or nodules become larger in diameter.
Depending on the stage, the doctor will prescribe different treatments. In cases where the tumor has spread further, the doctor will use a combination of direct treatments through the skin and systemic therapies, or allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.
Doctors recommend that when the skin appears small tumors, ulcers, dark spots, red spots, rough surface, moles with unclear edges, strange colors, itching, asymmetry... you should go to the doctor for appropriate treatment.
Thuy An
Source link






![[Photo] Award ceremony for works on studying and following President Ho Chi Minh](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/20/a08ce9374fa544c292cca22d4424e6c0)



























![[Photo] Vietnamese shipbuilding with the aspiration to reach out to the ocean](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/20/24ecf0ba837b4c2a8b73853b45e40aa7)


























































![[VIDEO] - Enhancing the value of Quang Nam OCOP products through trade connections](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/5be5b5fff1f14914986fad159097a677)
Comment (0)