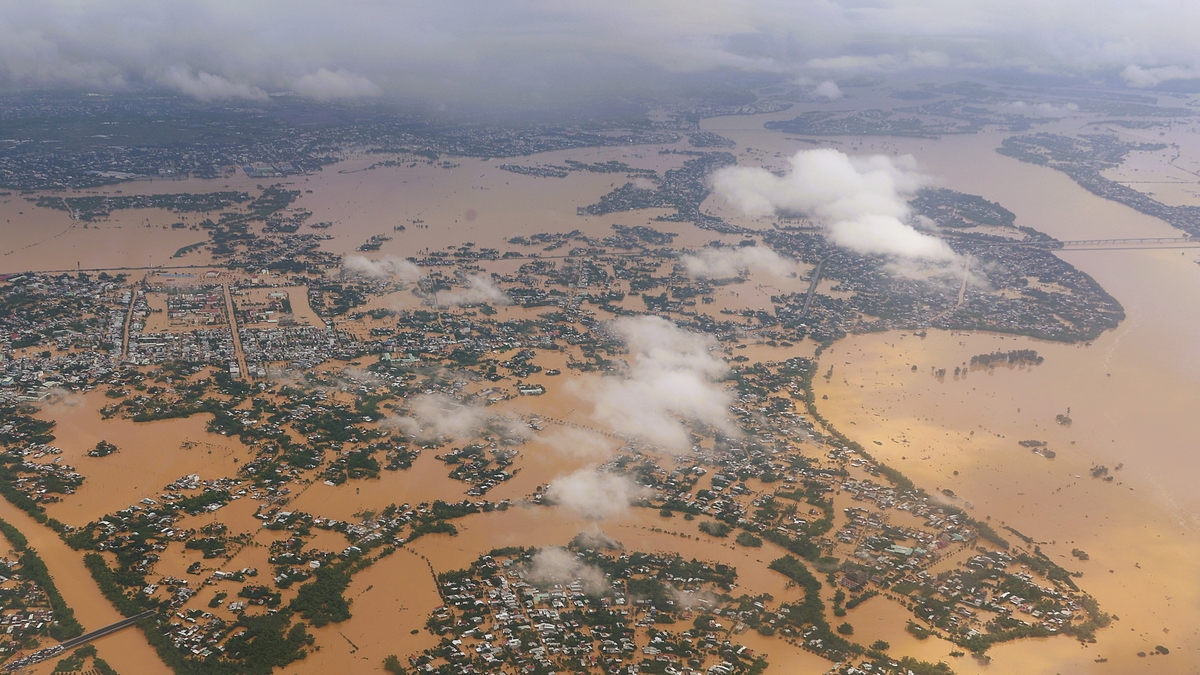
The giant house
The International Space Station (ISS) is not only a symbol of international cooperation in space research but also a giant "house" that has been continuously operating for the past two decades.
With more than 3.5 million photos of Earth taken from here by astronauts, the ISS has become an indispensable part in exploring the real potential for life beyond the planet.
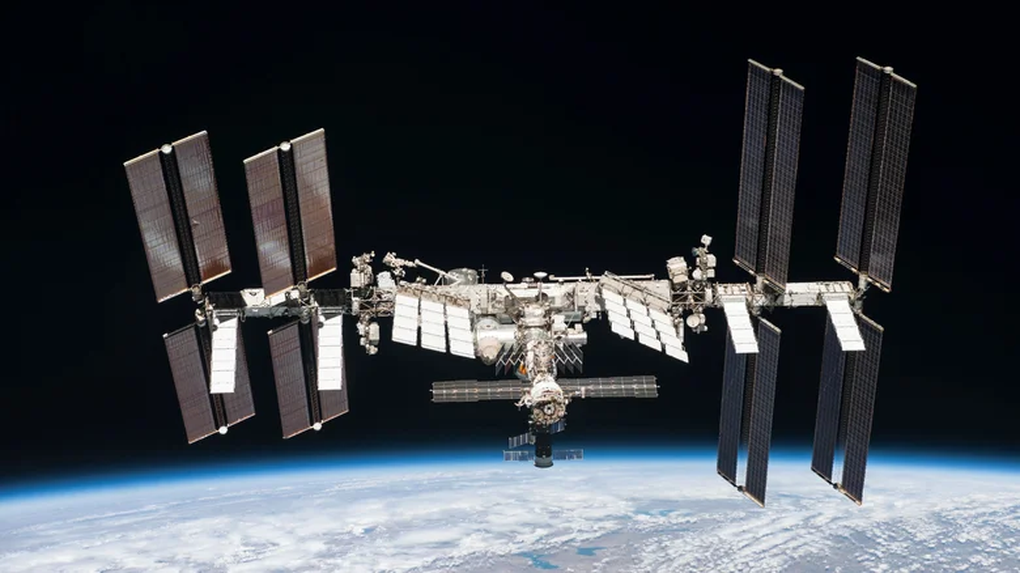

Since 2000, the ISS has become the largest and most ambitious manned space station in modern space history. It has witnessed countless amazing experiments and faced many near-disasters.
While only a handful of highly trained individuals can set foot on the ISS, it's not too difficult to imagine life on it when you know that the ISS is larger than a six-bedroom house and is arranged not unlike the inside of a jumbo jet.
Although the living space on the ISS is not as spacious as a typical suburban home, astronauts do not feel cramped at all.
Much of the ISS is made up of equipment like solar panels, but the actual living space is still large enough to accommodate a large crew. The station is arranged in a series of tubes and compartments, ensuring ISS residents have plenty of room to move around.
The length is about the same as a football field.

Seen through a telescope or in illustrations, the ISS may appear as simple as a small satellite.
The reality, however, is quite different. At nearly 118 meters from end to end, the ISS is the equivalent of a professional American football field, including the end zones.
The total mass of the station is up to 400,000 kg, equivalent to the weight of 2.3 Boeing 747 aircraft carrying no passengers.
According to NASA, the ISS was completed after 42 flights of transporting and assembling large modules and other components. Some of the largest modules are nearly the size of standalone satellites like the Hubble Telescope (about 13 meters long). For example, the Russian Multipurpose Laboratory module is about 12.7 meters in diameter.
Therefore, the ISS is not just a single satellite but a combination of many satellites linked together.
Comfortable living space, larger than a 6-bedroom apartment

Although the ISS is massive, much of its size is made up of uninhabitable equipment and modules, such as solar panels. However, about 66 meters of the station are pressurized, allowing humans to travel safely in microgravity.
This also explains why all forms of fire are prohibited on the ISS.
The station is made up of several interconnected modules, including converters for incoming and outgoing ships, air chambers, research modules, and living quarters.
The total living area between the work modules and the living modules gives ISS "residents" more room to move around than a six-bedroom house.
The living space includes six bedrooms, two bathrooms, a gym and a 360-degree dome for viewing Earth and the stars.
Some astronauts have likened the living space inside the ISS to the cabin of a Boeing 747. The obvious difference is that, unlike on a passenger plane, you don't need a floor, because everything is in zero gravity, so it's more like a series of tubes and tunnels than hallways.
If you have the chance, would you like to set foot in this special "house"?
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/khoa-hoc/tram-vu-tru-quoc-te-iss-ngoi-nha-khong-lo-giua-khong-giant-20251105031546063.htm


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives the delegation of the Semiconductor Manufacturing International (SEMI)](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/06/1762434628831_dsc-0219-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Closing of the 14th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/06/1762404919012_a1-bnd-5975-5183-jpg.webp)












































































































Comment (0)